
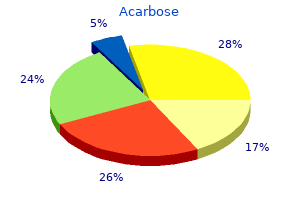
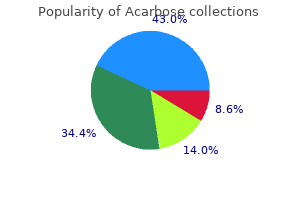
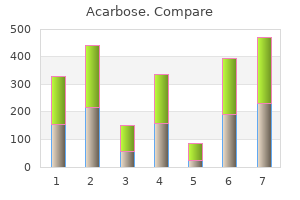
Acarbose
| Contato
Página Inicial

"50 mg acarbose cheap with visa, blood glucose goals for gestational diabetes".
J. Kalan, M.A., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, University of Hawaii at Manoa John A. Burns School of Medicine
Note each H&E (A) and immunostaining (B) for beta-catenin diabetes remix purchase 25 mg acarbose visa, during which nuclear staining is attribute for this illness control diabetes naturally generic 25 mg acarbose with amex. Tumors in an accessible website blood glucose quality control record acarbose 25 mg discount overnight delivery, not adjoining to vital structures diabetes test how long after eating acarbose 50 mg purchase without a prescription, are extra amenable to gross whole excision than those adjoining to major nerves or vessels. The downside of the extent of excision leads us to the first of several controversies in the administration of pediatric desmoid tumors. This excessive native management leads to margin-positive patients and the truth that salvage therapy of patients who failed regionally is usually successful warrant a coverage of putting such patients on statement. In distinction, margin-positive resection of recurrent desmoid tumors is an unequivocal indication for additional treatment. In contrast to this argument, one can flip to a latest evaluate by Nuyttens (203) of 22 articles concerning the treatment of desmoid tumors. Data of this type may be used to argue for the routine use of postoperative irradiation in patients with constructive margins. If one weighs the conflicting information on this point, a quantity of issues should be thought-about: � the long-term ill results of radiation therapy in kids with desmoid tumors can be appreciable. A vital variety of these sufferers might be locally managed with surgical procedure alone, even with constructive margins. For those who relapse, one could use surgery and radiation remedy to acquire native management. The likelihood of native control with surgical procedure alone is very debatable, and a extensive range of native management charges are reported (50,seventy two,199,200,205�207). A consensus view is that local control in sufferers with free margins is obtained in about 70% of cases. Several types of sufferers are at particularly excessive threat for native recurrence and development. These include these with unresectable lesions, those that have undergone resection and gross tumor has been left behind, those that have undergone resection with massive areas of clearly positive histologic tumor margins, and these that have already suffered a quantity of native recurrences after primary surgical therapy. Several retrospective collection, combining pediatric and grownup sufferers, have demonstrated that fractionated exterior beam irradiation or external beam plus brachytherapy can domestically management roughly 75% of desmoid tumors (Tables 12. The tumor slowly regressed, and local management has been maintained up to the time of this writing (2009). There is partial atrophy of the right buttock musculature, the bones of the best hemipelvis are smaller than those of the left hemipelvis, and the affected person walks with a marked limp. Judes Cancer Research Hospital (209), pediatric instances only) University of Washington (234) University of Florida (210,217,232) University of Heidelberg (235) Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea (236) Princess Margaret Hosp. Complete or partial resolution could take 2�3 years after completion of a course of therapy (200,208). For some patients, "native control" means cessation of progress rather than tumor regression. The long-term unwell results of radiation therapy for the treatment of desmoid tumors can embrace fibrosis in the treated area, paresthesias which are most frequently related to growth of tumor into a nerve, limb edema, fracture associated with surgical stripping of the ostium or curettage, skin ulcers, cellulitis, and the induction of second malignant neoplasms. This danger of late results raises the query of whether or not one ought to be particularly cautious in using radiation therapy in youngsters with desmoid tumors. This adverse biologic habits, at the side of the related ill effects of radiation, argues towards the usage of radiation remedy in desmoid tumors. The desmoid tumors arose from a particularly uncommon set of areas, such as the paraspinal area in five circumstances and the nasopharynx and pterygoid fossa in two cases. A wide variety of remedies have been used, including surgical procedure and chemotherapy, in addition to radiation therapy. Therefore, it appears reasonable to use radiation remedy to treat desmoid tumors in children, albeit with the cautions about positive margins raised earlier in this part. Marginal relapses account for a really large variety of the relapses after exterior beam radiation therapy (203,210,213,217,219). There could also be a better local recurrence price when dosages lower than 50 Gy are used. In 1984, Kiel and Suit (199) suggested that dosages greater than 60 Gy could also be related to a greater incidence of native control and have handled some patients with 70 Gy, typically utilizing photons and protons. They also found greater irradiation-associated morbidity in sufferers who received dosages lower than fifty six Gy. Evidence indicates that a complete dosage of 50�55 Gy is suitable and that greater dosages might improve the danger of complications without commensurate acquire in native tumor control (200,207,208). Brachytherapy has been reported as a treatment for desmoids, either alone or with exterior beam therapy, by one establishment (213). Because of considerations in regards to the evaluation of tumor margins and their coverage, we consider that the position of brachytherapy is proscribed in youngsters with desmoids. There have been some efforts to use cytotoxic chemotherapy, largely employed to treat recurrent tumor after surgical procedure and radiation. Of a total of 27 patients, 16 had recurrent desmoid tumor and eleven had untreated illness not amenable to both surgical procedure or irradiation. There have been different anecdotal stories of the utilization of gemcitabine, liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin, and temozolomide. Several reviews on the pathophysiology of desmoid tumors present expression of plateletderived development factor receptor (223,224), estrogen receptor (225,226), somatostatin receptors (227), and cyclooxygenase-2 (228). In flip, this has provided a rationale for the reported use of assorted "targeted therapies" either alone or in combos. This has included imatinib mesylate (223,224), tamoxifen or different estrogen antagonists (225,226,229), octreotide radiolabeled with Y-90 (227), and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicine (229�231). Finally, there have been anecdotal reports of responses to other brokers including colchicine and interferons. The worth of postoperative radiotherapy in childhood nonrhabdomyosarcoma delicate tissue sarcoma. Clinical options and end result of initially unresected nonmetastatic pediatric nonrhabdomyosarcoma soft tissue sarcoma. Long-term outcomes of a, potential randomized trial of adjuvant brachytherapy in the administration of fully resected delicate tissue sarcomas of the extremity and superficial trunk. A potential randomized trial of adjuvant brachytherapy in the management of low-grade gentle tissue sarcomas of the extremity and superficial trunk. Function and health status outcomes in a randomized trial comparing preoperative and postoperative radiotherapy in extremity gentle tissue sarcoma. A systematic meta-analysis, of randomized controlled trials of adjuvant chemotherapy for localized resectable soft-tissue sarcoma. The American Brachytherapy Society suggestions for brachytherapy of sentimental tissue sarcomas. Intraoperative high-dose-rate brachytherapy for the remedy of pediatric tumors: the Ohio State University experience. In 1879, renowned doctor William Osler (3) described two instances of "myosarcoma of the kidney," one of which had tumor extension into the proper heart and pulmonary artery. Max Wilms (1867�1918), who was educated in pathology, inner drugs, and surgical procedure, totally reviewed the pertinent literature and added seven new sufferers in his 1899 monograph Die Mischgeschwuelste. In addition to renal tumors, Wilms described the histologically "combined tumors" of the ovary, testicle, head and neck, bladder, and different organs (4). It was due to Wilms distinctive monograph that his name grew to become related with this childhood tumor. C: Wilms described the blastemal, epithelial (tubules), and stromal elements seen on microscopic examination of "mixed" renal tumor. X-ray remedy is used and consists of abdominal x-ray baths to cover the whole tumor and any possible intra-abdominal extension. An interval of 6 weeks to three months is then allowed during which the tumor mass completely disappears. The important point in the remedy of Wilms tumor is to do not forget that even monumental tumors could be made operable and that radiation adopted by nephrectomy can undoubtedly acquire cure in some cases. It is the commonest abdominal tumor in kids and represents 6% of childhood cancer. The incidence rate is roughly 3 times higher for blacks within the United States and Africa than for East Asians.
Diseases
- Envenomization by bothrops lanceolatus
- Paruresis
- Chromophobe renal carcinoma
- Bifid nose dominant
- Spinocerebellar degeneration corneal dystrophy
- Primary hyperoxaluria
Duplex Doppler renal ultrasound is an acceptable initial study to provide a noninvasive and correct analysis diabetic diet carbohydrates buy acarbose 25 mg low cost. A and B managing diabetes bob greene order acarbose 25 mg with mastercard, Longitudinal and transverse ultrasound photographs of the adrenal and the proper kidney present a stable adrenal mass with numerous small cysts diabetic diet on a budget cheap acarbose 25 mg visa. Although its actual etiology is unclear diabete tipo 1 acarbose 50 mg with amex, danger components embody delivery trauma, septicemia, and hemorrhagic disorders. Acute scrotal swelling or hematoma or both have also been reported as presenting signs in several case reviews. The differential diagnosis consists of adrenal cysts, adrenal hemorrhage, neuroblastoma, renal malignancies, and renal duplication. A urine collection for homovanillic acid, vanillylmandelic acid, and catecholamines aids within the exclusion of neuroblastoma. If the mass fails to present indicators of regression by 6 weeks, or in the case of uncontrollable bleeding, surgical resection is appropriate. Renal ultrasound scan reveals various degrees of bladder dilation with bladder wall thickening and a dilated posterior urethra-the "keyhole" sign. A 5F or 8F feeding tube is right for bladder drainage and should be secured with a clear nonconstricting dressing. One must ensure the feeding tube is within the bladder and not coiled within the dilated prostatic urethra. Prophylactic antibiotics are started, and a metabolic panel is obtained to assess renal function. Depending on the condition of the toddler, bladder drainage is usually continued for 5 to 7 days, after which endoscopic resection of the valve leaflets may be carried out in secure patients. Prognosis depends largely on the degree of obstruction, which often correlates with the presence, severity, and timing of oligohydramnios. The degree of renal impairment might not correlate with the grade of hydronephrosis. Failure of the serum creatinine level to decrease to less than 1 mg/dL within the first 12 months is considered a poor prognostic indicator for future renal operate. Serum creatinine levels through the first 24 to 48 hours are reflective of maternal function and not that of the infant. Respiratory distress secondary to pulmonary hypoplasia, somewhat than renal insufficiency, is the principal reason for mortality during the early neonatal period. Prune-Belly Syndrome Prune-belly syndrome (Eagle-Barrett syndrome, triad syndrome) is quickly identified on physical examination by the thin, lax, "prune" appearance of the abdomen. The diagnostic criteria of stomach wall musculature hypoplasia, massive hypotonic bladder with dilated tortuous ureters, and bilateral cryptorchidism are specific for prune-belly syndrome. A, Longitudinal ultrasound of the bladder (bl) in a neonate confirmed dilated posterior urethra (p-u) with slightly thickened base of the bladder (arrow). C, Frontal view in another newborn with posterior urethral valve with the catheter still within the bladder exhibits a triangular-shaped trabeculated bladder wall almost conforming to the shape of a Christmas tree. Associated anomalies include severe urethral stenosis or atresia, megalourethra, and imperforate anus. Initial management includes prophylactic antibiotics, serial serum electrolytes, and a renal ultrasound scan to assess renal parenchyma and extent of dilation. Infection rather than obstruction represents the greatest menace to renal parenchyma. The immediate issues are often pulmonary (pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum are common). Any instrumentation of the urethra exposes the kid to infections that can be difficult to eradicate; a conservative approach is one of the best initial selection. Although roughly 50% void spontaneously, the true bladder perform requires an ongoing analysis. In the setting of deteriorating bladder perform or persistent an infection, a cutaneous vesicostomy must be considered with plans for future undiversion tailored for the person affected person. Urethral Atresia Congenital urethral atresia in a boy results in full urethral obstruction caused by a constricting membrane normally situated within the distal prostatic urethra with accompanying hypoplastic urethra distally. A, Left anterior oblique view of the bladder in a affected person with prune-belly syndrome shows the dilated bladder and posterior urethra mimicking a posterior urethral valve. Note the bladder is elongated and on the dome (not shown) offers a misunderstanding of urachal cyst or remnant often giving an hourglass look. Dilation of the posterior urethra is also seen, and this is because of hypoplasia of the prostate and the lack of thickening of the base of the bladder. This distinctly differs from the looks of the posterior urethra in a affected person with posterior urethral valve (B). B, Left anterior indirect view of bladder in a affected person with posterior urethral valve shows the thickened bladder neck and dilated posterior urethra; the posterior urethral valve also is seen. Survival has been reported after vesicoamniotic shunting, however renal impairment is often extreme. Serial urethral dilations have been successful, however most circumstances require future urethral reconstruction. Myelomeningoceles A baby born with a myelomeningocele defect needs prompt urologic analysis. Appropriate urologic administration is crucial for long-term renal and bladder function. Initial evaluation is required to determine the bladder capability, voiding potential, and detrusor sphincter synergy. A baseline renal and bladder ultrasound should be obtained immediately along with cautious monitoring of voiding sample. The discovering of hydronephrosis and or excessive postvoid volumes suggests high-pressure techniques, which may be a result of bladder sphincter dyssynergia. The quick urologic concern is to decide whether or not high voiding stress exists, during which case the child needs intermittent catheterization. Parents must be endorsed about the dynamic nature and unpredictable sample of voiding function and the significance of continued monitoring. Casale Trauma is the leading reason for morbidity and mortality in youngsters at present and ends in extra childhood deaths than all other causes mixed. Over the previous half century, the advent of antibiotics improved remedy of infectious disease, and on the similar time society became dependent on the automobile resulting in extra motorcar accidents involving youngsters. Trauma to the urinary tract is second solely to trauma of the nervous system in childhood accidents. Modern management of trauma has advanced right into a group activity involving pediatricians, emergency physicians, surgeons, urologists, and other appropriate physicians. Because genitourinary accidents are seldom life-threatening, urologists are usually called as consultants after the preliminary evaluation has been completed. Although genitourinary injuries could not dominate the initial management interval, they often linger on, and the urologist could care for the kid for many of the hospitalization. The urologist should query any witnesses of the occasion about the utilization of seat belts in automobiles, loss of consciousness, the peak from which falls occur, how and where the affected person landed, and the immediate complaints of the injured youngster. Of particular importance are questions about bleeding from the urinary meatus, and if the kid voided before being examined. It is essential to communicate properly with the other staff members concerning the extent of the injuries to different organ techniques and planned treatment corresponding to laparotomy. The bodily examination can provide a considerable amount of useful information about the organs injured and the mechanism of the accidents. Abrasions or contusions of the genitalia, abdomen, again, and perineum could document the site of contact that produced the damage. Ecchymosis of the perineum within the shape of a butterfly signifies blood within the limits of Colles fascia which will end result from genital or pelvic 720 bleeding. A mass or ecchymosis of the flank may characterize a perinephric hematoma or urinoma. Labial or scrotal edema or hematoma might result from genital trauma or from pelvic accidents to the bladder or urethra. Blood from the urinary meatus or vagina can point out the presence of urethral or vaginal accidents. Abdominal or pelvic plenty might represent urinoma or hematoma from accidents to any portion of the urinary tract. A rectal examination might produce necessary information about the place of the urethra and bladder and possible plenty from pelvic hematoma.
Although the physician was less than cooperative blood glucose monitoring chart xls buy discount acarbose 25 mg online, he did reveal that the affected person has undergone a cardiac process and that the initial consensus was that the thrombocytopenia was induced by medication blood sugar jokes buy discount acarbose 50 mg line. The affected person was admitted and transfused with platelet concentrates diabetes symptoms young children generic acarbose 25 mg with amex, and the platelet rely elevated to fifty six � 109/L blood sugar blurred vision acarbose 25 mg purchase line. Which of the next is probably considered one of the key roles of thrombin with respect to fibrinogen Which of the next laboratory assays is normal in a patient with dysfibrinogenemia The means of fibrin degradation known as and is controlled by the enzyme. Earlier within the day, he was mountaineering and had been bitten on his leg by what he thought was probably a black snake. The affected person was given antivenin and supported by blood merchandise till his situation stabilized. The man denied any bleeding problems throughout his life and was taking no medications. A thrombin time was carried out in the unlikely event that the patient was somehow receiving heparin (most likely, low-molecular-weight heparin, which may be administered on an outpatient basis). Additionally, the incubated mixing examine confirmed that no slow-acting inhibitor is present. Thrombin time Using thrombin as a substrate, this assay measures the time it takes for fibrinogen to be transformed to fibrin 7. Influence of lipoprotein A ranges and isoforms on fibrinolytic exercise: Study in households with high lipoprotein A levels. Thrombomodulin in human plasma contributes to inhibit fibrinolysis via acceleration of thrombin dependent activation of plasma carboxypeptidase. Rapid D-dimer assay to exclude deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: Current standing and new developments. A evaluation of disseminated intravascular coagulation: Presentation, laboratory prognosis and treatment. Chapter 19 Introduction to Thrombosis and Anticoagulant Therapy Mitra Taghizadeh Physiologic and Pathologic Thrombosis Pathogenesis of Thrombosis Vascular Injury Platelet Abnormalities Coagulation Abnormalities Fibrinolytic Abnormalities Antithrombotic Factors (Coagulation Inhibitors) Objectives After completing this chapter, the coed will have the power to: 1. Describe antithrombin, protein C, and protein S with regard to properties, mode of motion, components affected, and problems associated with their deficiencies. Describe activated protein C resistance with regard to pathophysiology, mode of action, and related complications. Discuss the laboratory tests and outcomes used for the diagnosis of issue V Leiden and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. List the forms of anticoagulant medicine used for the remedy of thrombotic disorders. Describe the mechanism of motion of every anticoagulant drug generally used for the treatment of thrombotic problems. Discuss the laboratory check used for monitoring of heparin and Coumadin (warfarin) remedy. Arterial thrombi are primarily composed of platelets and small quantities of purple blood cells and white blood cells, whereas venous thrombi are composed of fibrin and purple blood cells. Thrombosis could result from vascular harm, platelet activation, coagulation activation, defects in the fibrinolytic system, or defects in physiologic inhibitors. Along with problems from thromboembolisms, arterial and venous thrombosis are an important causes of death in developed nations. Venous thrombosis is composed of huge amounts of fibrin and pink blood cells resembling the blood clot fashioned in the take a look at tube. This occlusion is related to slow blood flow, activation of coagulation, impairment of the fibrinolytic system, and deficiency of physiologic inhibitors. The most critical complication associated with venous thrombosis is demobilization of the clot, which occurs because the clot dislodges from its website of origin and filters out into the pulmonary circulation. Normal clot formation and clot dissolution are completed by interplay amongst five major hemostatic elements: vascular system, platelets, coagulation system, fibrinolytic system, and inhibitors. Imbalance in any of the above elements tilts the hemostatic scale in favor of either bleeding or thrombosis. Primary hemostasis refers to the method by which the platelet plug is shaped on the website of damage, whereas secondary hemostasis refers to the interaction of coagulation components to generate a cross-linked fibrin clot to stabilize the platelet plug to form physiologic thrombosis. Physiologic thrombosis results from the pure response of the body to vascular injury. Arterial thrombosis is primarily composed of platelets with small amounts of fibrin, red blood cells, and white blood cells. This clot could additionally be Vascular Injury Vascular accidents play an necessary function in arterial thrombosis. In addition, blood coagulation is initiated by tissue issue released from the damaged endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial harm might happen by endothelial cell injury, atherosclerosis, hyperhomocysteinemia, or other problems which will intrude with arterial blood flow. In cancer sufferers, vascular endothelial cell injury may happen secondary to the toxic effect of chemotherapeutic medication. As platelets interact with the injured vessels, platelet adhesion and aggregation occur. In normal hemostasis, excess platelet activation is prevented by the antiplatelet activities of endothelial cells corresponding to era of prostacyclin. In the disease state, extra platelet activation can mirror thromboembolic illness or acceleration of thrombotic episodes. Acquired threat factors are related to conditions that hinder regular hemostasis similar to cancer, nephrotic syndrome, vasculitis, antiphospholipid antibodies, myeloproliferative illness, hyperviscosity syndrome, and others (Table 19. These conditions disturb the hemostatic regulation in favor of increased risk of thrombosis. Plasmin, an activated type of plasminogen, has a main role in fibrin breakdown. It is a heparin-dependent issue whose inhibitory impact is primarily in opposition to thrombin. Protein C is activated by the action of the thrombin-thrombomodulin complicated with protein S as a cofactor. Type I deficiency is the commonest kind and is associated with reduction of immunologic and useful exercise of protein C to 50% of regular. Other reported complications embrace arterial thrombosis, neonatal purpura fulminans in homozygous newborns, and warfarin-induced skin necrosis. Protein S circulates in plasma in two forms: free (40%) and bound to C4bbinding protein (60%). Type I is a quantitative disorder by which complete protein S (free and bound), free protein S, and protein S activity levels are lowered to about 50% of regular. Similar to protein C deficiency, many sufferers with thrombosis have extra inherited or acquired risk components. However, arterial thrombosis has been reported in 25% of sufferers with protein S deficiency. Most circumstances (92%) are inherited and attributable to mutation of issue V, Arg506Gln, referred to as factor V Leiden. The thrombotic dangers increase additional if different inherited or acquired danger elements coexist. Smoking will increase the risk of thrombosis 30-fold in people with factor V Leiden. Prothrombin Mutations Prothrombin mutation (G20210A) is the second most prevalent explanation for an inherited form of hypercoagulability. Caused by a single point mutation, G20210A is an autosomal dominant disorder that causes increased focus of plasma prothrombin. Bleeding has been reported in 20% of circumstances, and 60% of sufferers may be asymptomatic. Homocysteine is an amino acid shaped through the conversion of methionine to cysteine in vitamin B12 synthesis. Hyperhomocysteinemia outcomes from deficiencies of both the enzymes needed for production of homocysteine (inherited form) or vitamin cofactors (vitamin B6, vitamin B12, and folate) in an acquired type. Drugs similar to oral contraceptives or hormone replacement remedy might predispose to thrombosis. The commonest causes of acquired thrombotic issues are antiphospholipid syndrome and heparininduced thrombocytopenia. Bleeding is rare, except the patient has thrombocytopenia or decreased prothrombin as properly. In a mixing study, the affected person plasma is blended with regular plasma, and the test is repeated.