
Amaryl
| Contato
Página Inicial

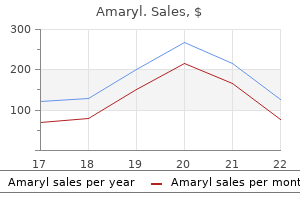
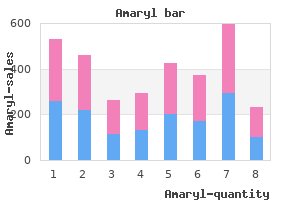
"1 mg amaryl best, diabetes mellitus type 2 case study scribd".
E. Nafalem, M.A.S., M.D.
Co-Director, University of Alaska at Fairbanks
Prevention Prevention outcomes from gentleness and avoiding repeated use of techniques diabetes type 2 causes buy cheap amaryl 2 mg on line, significantly blind ones xerosis and type 2 diabetes amaryl 1 mg purchase fast delivery, once they show to be ineffective diabetes testing supplies commercial generic 1 mg amaryl with amex. Treatment A excessive index of suspicion by the anesthesiologist and early signs of injury should be sought with vigilance diabetic episode amaryl 2 mg generic with mastercard. Management An instant dental consultation should be sought when dental trauma is suspected. Fluoroscopic footage should be obtained to guarantee no frag- 487 Complications in Anesthesia 28 28. They account for approximately 3% of cases reported within the closed claims database of the American Society of Anesthesiologists. Corneal Abrasion Corneal abrasion is the most typical ocular complication following basic anesthesia, accounting for approximately 35% of claims related to ocular accidents. In roughly 16% of the claims, corneal abrasions resulted in everlasting damage. Potential causes of harm are chemical harm (skin antiseptic solutions); direct trauma during the anesthesia; pressure from the surgeon, anesthetist, or instruments; injury from insertion of lubricant; and self-infliction (most related to eye rubbing). It manifests as a sudden onset of painless vision loss and can have an result on both eyes in two-third of cases. However, a fundoscopic exam is initially normal but optic nerve pallor and atrophy seem 4�6 weeks later. Examination exhibits poor pupillary response to light, full blindness, altitudinal subject defect, and central scotomas. A funduscopic examination reveals a swollen optic disc with or without peripapillary hemorrhage at the optic disc margin. Patients complain of imaginative and prescient loss after waking from anesthesia, and a funduscopy reveals retinal whitening and pathognomonic cherry pink spots within the macula. It has been reported that dehydration of the cornea is demonstrable after 10 min of publicity without blinking. General anesthesia is associated with a major discount in tear production, which exacerbates the problem. Clinical Presentation It sometimes presents with acute ocular pain accompanied by the feeling of a overseas body within the eye. Other manifestations embody photophobia, tearing, blurred imaginative and prescient, and blepharospasm. Prevention Unanimously accepted strategies to prevent corneal abrasions throughout anesthesia are missing: 1. The efficacy of eye ointment probably depends on the specifics of the ointment used. Petroleum-based ointments are associated with affected person complaints relating to blurred vision and decreased visible acuity, which can stimulate rubbing of the eyes, subsequently causing a self-inflicted corneal abrasion. The male sex, weight problems, use of a Wilson frame, a long anesthesia time, Treatment this includes quick consultation and affirmation of the diagnosis by ophthalmologic examination, which generally entails a slit lamp examination after instillation of fluorescein. Sumathi larger estimated blood loss, and decreased percent colloid administration are threat elements. Patients who endure spine surgery in place susceptible and individuals who have lengthy procedures and experience substantial blood losses are at high danger. An pressing ophthalmology consult ought to be obtained if any visual loss presents postoperatively. Patient hemodynamics and head position should be optimized until the patient is seen by an ophthalmologist. Respiratory compromise: Airway compression from a hematoma, tracheal and laryngeal damage, pneumothorax three. Subcutaneous/mediastinal emphysema 5 Thromboembolic: 5 Venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, arterial thrombosis and embolism (air, clot), catheter or guidewire embolism 5 Infectious: 5 Insertion website infection, catheter an infection, bloodstream an infection, endocarditis 5 Misinterpretation of data 5 Misuse of equipment Box 28. The most common complication associated to a central catheter during a closed declare study is a wire or catheter embolus adopted by cardiac tamponade, carotid artery puncture/cannulation, hemothorax, and pneumothorax. The different complications contain hydrothorax/pleural effusion, fluid extravasation in the neck, air embolism, pulmonary artery rupture, a miscellaneous vessel harm (arteriovenous fistula, aorta damage, and subclavian artery damage leading to arterial thrombosis, arterial aneurysm, and neck hematoma) or a non-vessel injury (phrenic nerve palsy and atrial fibrillation). Preparation: One should use maximal sterile-barrier precautions, including a mask, a cap, a sterile gown, sterile gloves, and a large sterile drape to reduce an infection. Minimize the variety of insertion attempts, for the rationale that incidence of mechanical issues after three or extra insertion attempts is six times the rate after 1 attempt. Use of ultrasound guidance: the use of ultrasound guidance has been promoted as a method for decreasing the danger of problems throughout central venous catheterization. Hematomas and arterial punctures are frequent throughout femoral venous catheterizations. Selection of the subclavian site appears to cut back the chance of infectious issues. Subclavian venous catheterization carries the bottom risk of catheter-related thrombosis. Pressure transduction of introducer needle prior to the use of introducer to keep away from arterial damage. Maintenance of the insertion website and catheter: Changing the tip cap with every use is useful to reduce infection. A chest X-ray is obligatory to affirm the catheter position and to rule out peumothorax. Tension pneumothorax: an instantaneous needle thoracotomy, adopted by chest tube placement, must be accomplished to relieve strain. Pulmonary artery rupture: Management should give consideration to resuscitation and instant control of the hemorrhage. The first precedence is ensuring sufficient oxygenation and air flow, which can require endobronchial intubation with either a single- or double-lumen endotracheal tube to selectively ventilate and protect the unaffected lung. Any anticoagulation ought to be reversed, until the affected person should remain on cardiopulmonary bypass. Nerves: Mandibular branch of facial nerve resulting in transient facial nerve paralysis. Prevention and Treatment Appropriate use of masks during masks ventilation is the key to avoiding issues. Nerve Injuries from Tourniquet Use During the Surgery Tourniquets, including pneumatic Esmarch bandage tourniquets, are utilized by orthopedic surgeons to lower blood loss and to present favorable working conditions throughout extremity surgical procedure. Mechanic trauma as a end result of tourniquet use and ischemia have attributed to nerve injuries. The radial nerve is probably the most weak, followed by the ulnar and medial nerves within the upper limb, while nerve damage within the decrease extremities most frequently includes the sciatic nerve [11]. Pathophysiology Mechanical pressure underneath the cuff performs a extra important role than ischemia in a nerve harm [11]. Nerve compression causes intraneural microvascular abnormalities and edema formation, and these subsequently compromise native tissue vitamin, resulting in axonal degeneration. Tissue trauma is most marked at the proximal and distal edges of a compression tourniquet, where shear stress forces are maximal [11]. Arterial Cannulation Complications after arterial cannulations embody distal ischemia, pseudoaneurysm, arteriovenous fistula, hemorrhage, hematoma, arterial embolization, local an infection, sepsis, peripheral neuropathy, misinterpretation of data, and misuse of kit [10]. Prevention For prevention of nerve harm from tourniquet use: 5 the bottom inflation pressure that causes arterial occlusion must be used. Pressure 50�100 mm of Hg above systolic is used for the arm; double systolic blood pressure is for the thigh; alternatively, standard pressures for the arm 200�250 mm Hg, leg 250�350 mm Hg (large cuffs are really helpful for bigger limbs instead of increasing pressure). Prevention and Treatment Vigilance should be maintained throughout and publish cannulation for issues and early administration. Calibration ought to be checked biweekly in opposition to a mercury thermometer and 3-month maintenance is recommended. Cuffs should exceed the circumference of the extremity by 7�15 cm, and should be positioned on the level of maximum circumference of the limb. A complete preoperative historical past and physical evaluation will establish that patients can comfortably tolerate the anticipated operative position and establish preexisting illness 2. Patients positioned prone could comfortably tolerate arm abductions larger than 90�. In supine place with arm on the arm board: the arm ought to be positioned on a padded arm board. For a supine affected person with arms tucked at their side, the forearm ought to be in a neutral place and extended stress on the radial nerve in the spiral groove of the humerus should be averted. As the sciatic nerve or its branches cross each the hip and the knee joints, limited extension and flexion of these joints ought to be thought-about.
Gastric emptying in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis: the impression of autonomic neuropathy metabolic disorder uric acid 4 mg amaryl order with amex. Achalasia secondary to neoplasia: a disease with a altering differential diagnosis diabetes mellitus type 2 lifestyle changes 4 mg amaryl discount visa. Upper airway tract and higher gastrointestinal tract involvement in patients with pemphigus vulgaris diabetes onset amaryl 1 mg buy lowest price. Technical elements in endoscopic biopsy of lesions in esophageal pemphigus vulgaris diabetic quinoa salad recipes amaryl 4 mg cheap without a prescription. Gastrostomy tube feeding in youngsters with epidermolysis bullosa: consideration of key points. High prevalence of esophageal involvement in lichen planus: a examine using magnification chromoendoscopy. Lichenoid esophagitis: clinicopathologic overlap with established esophageal lichen planus. Defining the endoscopic appearances of tylosis utilizing typical and narrow-band imaging: a case collection. The etiology and pathogenesis of these disorders is poorly understood and likely multifactorial. Visceral hypersensitivity to acid or other stimuli is among the major theories in pathogenesis. Case A 49-year-old female pharmacist presents for analysis of frequent and chronic retrosternal heartburn and regurgitation for greater than 9 months. She was initially treated with omeprazole 20 mg day by day (40 minutes prior to breakfast) for eight weeks. After an extra 8 weeks of remedy, she seeks consultation for unabated symptoms. Globus is a standard symptom and has been reported by up to 46% of apparently healthy people, with a peak incidence in middle age and with three of 4 subjects looking for well being care being girls [4]. Other proposed causes embody: increased susceptibility of the esophageal mucosa to reflux from acid, disrupting the intercellular connections of the squamous esophageal mucosa and exposing nociceptive nerve fibers; and non-acid triggering components such as stress and longitudinal muscle contraction of the esophagus. Longitudinal muscle contraction of the esophagus, detected by intraluminal ultrasound, has been found to produce the sensation of heartburn [5]. Globus: A persistent or intermittent, non-painful sensation of a lump or overseas physique in the throat. Intraesophageal balloon-distension studies have shown an elevated threshold perception in maintaining with a defect in visceral sensitivity [7]. Other studies utilizing balloon-distension strategies have shown both reproduction of dysphagia and generation of irregular motility patterns, suggesting a defect within the neural circuit of the esophagus [8]. In addition, sufferers with non-obstructive dysphagia present a defect within the triggering of secondary peristalsis and useful clearance by impedance manometry [10,11]. Increased stress can also induce abnormal esophageal motility responses [12], but no direct link to useful dysphagia exists. Functional Chest Pain Patients sometimes present after in depth cardiac workup for further analysis. It is the final consensus of most experts that taking sufferers off reflux medications prior to such testing supplies the greatest diagnostic yield [13]. Functional Esophageal Disorders 171 increased heartburn, leisure training has been recommended. Hypnotherapy may cut back pain depth and provide enchancment in total well-being [17]. Anecdotal therapies include reassurance, careful food mastication, and avoidance of any precipitating components. Another therapeutic choice is empiric dilation, which has been proven to be useful in some, however not all studies [18, 19]. Globus Explanation, reassurance, empiric trials of antidepressants, and speech remedy could additionally be of help. Manometric responses to balloon distention in patients with nonobstructive dysphagia. Evaluation of esophageal motility problems triggered by ingestion of solids in the case of non-obstructive dysphagia. Identification of impaired oesophageal bolus transit and clearance by secondary peristalsis in sufferers with non-obstructive dysphagia. Utilization of wi-fi pH monitoring technologies: a summary of the proceedings from the Esophageal Diagnostic Working Group. Effects of antidepressants in patients with useful esophageal issues or gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. A meta-analysis of hypnosis for persistent pain issues: a comparability between hypnosis, commonplace care and other psychological interventions. The short- and long-term effiacy of empirical esophageal dilation in sufferers with nonobstructive dysphagia: a potential, randomized study. Sellin 28 Small-Intestinal Hormones and Neurotransmitters, 181 James Reynolds 29 Mucosal Immunology of the Intestine, 187 Maneesh Dave and William A. Mainly, the main target is centered on the pathogenesis, analysis, and management features of the clinical problem. Rarely, we delve in to the anatomy of the organ system responsible for the presentation. However, some embryological anomalies can current in later decades of life and current unexpected and tough challenges in each diagnosis and management. Hence, a sensible working knowledge on this subject is critical for the scientific gastroenterologist. These two watershed areas are most weak to ischemia during systemic hypotension. Aberrations in midgut improvement could lead to a big selection of anatomic anomalies (Table 27. Atresias have a reported incidence fee of 1 in 300 to 1 in 1500 live births, and are more widespread than stenoses. Clinically, the presentation is that of a proximal intestinal obstruction with bilious vomiting on the first day of life. Abdominal Wall Congenital Anomalies the congenital anomalies of the stomach wall are: r Gastrochisis: caused by an intact umbilical wire with evisceration of the bowel, however no overlaying membranes, through a defect within the belly wall [1]. Small and Large Intestine Anatomy and Embryogenesis At 4 weeks of gestation, the alimentary tract is split into three parts: foregut, midgut, and hindgut. The duodenum originates from the terminal portion of the foregut and cephalic a part of the midgut. With rotation of the abdomen, the duodenum turns into Cshaped and rotates to the best. The midgut provides rise to the duodenum distal to the ampulla, to the entire small bowel, and to the cecum, appendix, ascending colon, and the proximal two-thirds of the transverse colon. The distal third of the transverse colon, the descending colon and sigmoid, the rectum, and the upper part of the anal canal originate from the hindgut. The colon has a wealthy blood provide, with a specific vascular arcade formed by union of branches of superior mesenteric, inferior Diagnosis An stomach wall defect may be identified during routine prenatal ultrasonography. Both gastroschisis and omphalocele are associated with elevation of maternal serum -fetoprotein. The measurement of the omphalocele determines whether or not a major repair or delayed major closure is selected as the surgical strategy. Vitelline Duct Congenital Anomalies Persistence of the duct communication between the gut and the yolk sac beyond the embryonic stage might result in a quantity of anomalies of the omphalomesenteric or vitelline duct. Bleeding is the most common complication of Meckel diverticulum, related to acid-induced ulceration of adjoining small intestine from the presence of ectopic gastric mucosa. Obstruction, intussusception, diverticulitis, and perforation may also happen, especially in adults, because of the energetic ectopic pancreatic tissue or gastric mucosa. Twelve % of children with Hirschsprung disease have chromosomal abnormalities, 2 to 8% of that are trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) [4]. Some sufferers are identified later in infancy or in maturity with severe constipation, persistent stomach distension, vomiting, and failure to thrive. Diagnosis essentially the most helpful technique of detection of a Meckel diverticulum is technetium-99m pertechnetate scanning. The sensitivity of the scan can be increased minimally with use of cimetidine [3].
Satavari (Asparagus Racemosus). Amaryl.
- How does Asparagus Racemosus work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Asparagus Racemosus?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Pain, anxiety, stomach and uterine spasms, breast milk stimulation, uterine bleeding, premenstrual syndrome, alcohol withdrawal, indigestion, gastric ulcers, diarrhea, bronchitis, diabetes, dementia, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Asparagus Racemosus.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97111
However diabetes diet pregnant amaryl 1 mg order otc, it is also metabolic derangement or neurological causes diabetic diet how many calories cheap 1 mg amaryl with amex, both of which might result in diabetes prevention programs for native americans buy discount amaryl 4 mg on line serious outcomes diabetes in dogs diarrhea amaryl 2 mg buy low cost. The pharmacological reasons for "delayed awakening" might be actual or relative overdose or synergic impact of anesthetic agents, opioids, and benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines are efficient anxiolytics and can trigger prolonged unconsciousness within the extremes of age. Residual neuromuscular block may result from incomplete reversal or recurarization and it could result in hypoventilation. Residual effects of opioids and benzodiazepine may be reversed with naloxone and flumezanil, respectively. The effect of a bolus induction dose of propofol is unlikely to linger to trigger delayed awakening. Elimination of unstable anesthetic depends on alveolar air flow, partition coefficients (blood-gas and blood-fat) of the agent, and the period of use. Desflurane is linked to speedy recovery, particularly in an overweight patient because of its low blood-fat solubility. Non-pharmacological causes for delayed awakening could probably be hypoglycemia (40 mg/dL-1), hypothermia (< 33 �C), hyponatremia (< 110 mmol/L-1) or raised intracranial strain. However, intravenous acetaminophen, regional and local anesthetic methods, and physical remedy corresponding to ice packs or putting a pillow beneath the knees, to ease the belly muscle stretch could presumably be useful. Temporally, it might be instantly after emergence from anesthesia, lasting about 30 min (emergence delirium), or prolonged over a couple of hours (postoperative delirium). There may also be long-term subtle lack of cognition, attention, and memory (postoperative cognitive decline). Emergence delirium (incidence of 5�21% among adults) is extra common among youthful males with history of preoperative nervousness and these who have been given a benzodiazepine premedication. Postoperative delirium is extra frequent within the elderly following major orthopedic and vascular surgeries, with a reported incidence of 3�53%. Deranged neurotransmission and neuro-inflammation with microglial activation are some of the theories suggested for the etiology of postoperative delirium. The diagnosis of delirium requires the presence of an acute onset of alteration in the psychological status in comparison with the preoperative period and symptoms of inattention together with both disorganized speech or altered degree of consciousness. Dexmedetomidine, an (alpha)2-agonist, has been shown to be related to much less postoperative delirium compared to midazolam or lorazepam. Judicious use of opioids is indicated as each over-dosage of opioids and under-treatment of pain can contribute to delirium. Managing sufferers with delirium entails nursing care in a secure environment by acquainted caregivers and fixed reassurance; remedy of aggravating elements corresponding to pain, hypoxia, electrolyte imbalance, or infection; and avoiding deliriogenic medicine. This can occur with improper affected person positioning, inflicting exterior compression of the attention, elevating the intraocular stress, and impairing circulate in the retinal artery. Prolonged surgical procedure, excessive hemorrhage, and related hypotension through the backbone surgical procedure could be contributing components; although hypotension by itself appears to be a rare trigger for retinal ischemia. Retinal artery occlusion can occur due to micro-embolus during an open heart surgery. Transient visible loss after transurethral resection of prostate can result as a outcome of extreme absorption of 1. Corneal abrasion may lead to irritation and redness of the eyes and trigger impaired vision. The usual presentation is a spectrum starting from mild symptoms corresponding to shivering and drowsiness to tremor, altered sensorium, muscle rigidity and hyperreflexia. In an excessive situation they might develop hyperthermia, rhabdomyolysis, metabolic acidosis, renal failure, and disseminated intravascular coagulopathy. In a postoperative affected person, mild signs such as shivering, restlessness, or drowsiness are easily ignored or handled with the medication that can worsen the scenario. The differential analysis consists of anti-cholinergic overdose, malignant hyperthermia, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome. The administration of serotonin syndrome is mainly supportive with removing of the precipitating agent and administration of benzodiazepine for sedation. In patients who develop hyperthermia (> forty one �C), along with the aforementioned remedy, sedation, neuromuscular paralysis, and endotracheal intubation with mechanical ventilation ought to be initiated. Although, the most typical cause is depletion of intravascular fluid quantity, it could be multifactorial. The causes might be "prerenal" (hypovolemia, intra-abdominal hypertension, low cardiac output), "renal" (ischemia, contrast dye nephropathy, rhabdomyolysis), or "post-renal" (surgical injury to the ureters, blockade of urinary catheter). A judicial "fluid problem" can be effective in restoring the urine output in most conditions. Aggressive hydration and loop diuretics to flush the renal tubules are the mainstay of management. The "Modified Aldrete Scoring System" is certainly one of the commonly used goal discharge standards (. Prophylactic antibiotics Pulmonary useless area decreases with which of the next A. All these imply adequacy of muscle energy and never recovery of airway protective reflexes. The frequent causes for delayed awakening after an anesthetic are residual anesthetic and residual curarization, hypothermia, and hypoglycemia. Pseudo-choline-esterase deficiency can lead to extended action of succinylcholine. This increases cardiac output and minute air flow resulting in myocardial ischemia and ventilator failure. Significant aspiration can result in hypoxemia, elevated airway resistance, and pulmonary edema. Anatomical lifeless space can be decreased by 75% by endotracheal intubation and almost eliminated by tracheostomy. Serotonin syndrome is a potentially deadly situation that happens because of extra serotonin within the central nervous system, secondary to an antagonistic drug response or a drug interaction. The ordinary presentation is a spectrum ranging from mild signs similar to shivering and drowsiness to tremor, altered sensorium, muscle rigidity, and hyper-reflexia. The terminal events are hyperthermia, rhabdomyolysis, metabolic acidosis, renal failure, and disseminated intravascular coagulopathy. Morbid obesity and postoperative pulmonary atelectasis: an underestimated problem. Practice advisory for perioperative visual loss associated with spine surgical procedure: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on perioperative visual loss. Transduction, transmission, and perception are necessary steps in pain physiology. Peripheral and central sensitization are key elements of acute and chronic pain formation. The concept of multimodal analgesia involves the blockade of peripheral and central nociceptors concerned in transduction, transmission, and perception of pain. A comprehensive preoperative analysis and ongoing postoperative evaluation of sufferers, comorbidities, and ache intensity is essential to present sufficient postoperative pain management. A careful choice of the approach, native anesthetic focus, and adjuvant analgesic is important to maximize the efficacy of every technique while minimizing antagonistic occasions. Iontophoretis supply of opioids have lately been described and shown some efficacy in postoperative ache administration. Surgical pain has the options of nociceptive, inflammatory, and neuropathic pain [2]. Therefore, it has been really helpful that more than one analgesic modality (multimodal analgesia) will be necessary to obtain adequate perioperative ache control, thus avoiding the unwanted effects of enormous doses of single analgesics, in particular opioids [3]. A multimodal analgesic approach entails the preoperative initiation, intraoperative continuation, and postoperative upkeep of a combination of regional anesthesia/analgesia strategies (whenever possible) with two or extra systemic analgesics. In the postoperative period, the addition of systemic analgesics is essential; particularly when regional anesthesia strategies are discontinued, as throughout this time sufferers could experience severe distress and discomfort ("analgesic hole interval"). Transduction is the primary essential step to convert a noxious stimulus (mechanical, chemical, and thermal) into electrical neural activity. Although nociceptors are located in the terminals of sensory afferent fibers with totally different diameters and velocities of conduction (A[delta] and C fibers); they may additionally be found in non-neuronal cells such as keratinocytes. Nociceptors are either ionotropic (ion channel) or metabotropic (second messenger-signaling cascade).
A lower blood:fuel coefficient transiently corresponds with a faster induction rate; for instance diabetes medications nclex proven amaryl 2 mg, nitrous diabet-x callus treatment best 1 mg amaryl, desflurane diabetes insipidus jcem amaryl 2 mg buy with mastercard, and sevoflurane have quicker induction charges than isoflurane and halothane (see managing diabetes low carb diet buy amaryl 2 mg online. For instance, a excessive uptake of nitrous oxide will accelerate the uptake of a second gas, corresponding to a unstable anesthetic [119, 120]. The cardiac output, in the absence of pulmonary shunting, immediately affects the uptake of the inhaled agent into the. Insoluble anesthetics show much less effect from the cardiac output since little is taken up in the alveolar blood flow. The ultimate consider determining the alveolar blood anesthetic uptake is the alveolar to venous partial stress distinction. These factors are determined by the tissue uptake of the anesthetic, primarily in vessel-rich teams that receive 75% of the cardiac output. The vessel wealthy groups-including the brain, heart, and kidneys-equilibrate rapidly with the Pa. It is affected by the blood:mind partition coefficient, the cerebral blood low and the arterial to venous partial pressure distinction (. Recovery from anesthesia is represented because the decreasing of the anesthetic concentration in the brain tissue. A majority of contemporary anesthetic elimination is through exhalation; however, a small proportion is elimination in biotransformation or transcutaneous loss. As such, lots of the similar components that determine induction pace account for the velocity of recovery: elimination of rebreathing, high contemporary gas flows, low circuit absorption, decreased agent solubility, high cerebral blood move, and elevated ventilation [72, 73]. The major distinction in restoration from anesthetics is that, in recovery, different tissues within the body have completely different partial pressures of the inhaled anesthetic. Because nitrous oxide is eliminated so shortly, it can dilute alveolar oxygen and carbon dioxide, inflicting diffusion hypoxia. Clinically, this hypoxia is avoided by administering one hundred pc oxygen for 5�10 min after discontinuing nitrous oxide [122]. Correlates with the vapor stress of the inhalational agent A pediatric affected person presents for an inhalational induction. All of the above While administering only an inhalational agent, you discover that the cardiac output of your affected person has decreased. Sevoflurane the beneficial contemporary fuel flows when utilizing sevoflurane is 2 L/min because: A. Sevoflurane biodegrades into peak concentrations of 50 (mu)mol/L of fluoride, which may cause nephrotoxicity. Postoperatively, she develops fever, eosinophilia, jaundice, and elevated serum transaminase levels. Kurra 10 A affected person undergoes a 25-h anesthetic for hand reconstruction after a crush harm with sevoflurane, nitrous oxide, fentanyl, and rocuronium. The anesthetic agent that the majority can produce regional myocardial ischemia during tachycardia as a end result of a preferential dilation of the traditional coronary arteries is: A. Metabolism plays an necessary function within the emergence from anesthesia with which of the next brokers: A. Inhalational brokers with excessive solubility within the blood are taken up very rapidly from the alveoli. This fast uptake lowers their partial stress in the lung and increases the latency for induction of anesthesia. A low blood solubility of an agent is fascinating as induction and restoration instances are quicker. Desflurane is a pungent fuel that may trigger airway irritability throughout induction, manifested as breath-holding, salivation, coughing, and possibly laryngospasm. At clinical anesthetic focus, halothane decreases the mean arterial pressure by decreasing myocardial contractility and cardiac output; whereas, isoflurane, sevoflurane, and desflurane lower systemic vascular resistance. Nitrous oxide will increase cardiac output due to a mild improve in sympathetic tone. Alkali, corresponding to soda lime, can degrade sevoflurane into one other proven nephritic product in animal fashions, compound A. Larger amounts of compound A are produced with lower fuel flows, increased respiratory temperatures, excessive sevoflurane concentrations, anesthetics of lengthy duration, and dessicated soda lime. It is clinically recommended to preserve recent fuel flows larger than 2 L/min to limit potential compound A manufacturing. Despite proven nephrotoxicity in rats, it has by no means shown postoperative renal impairment to indicate harm or toxicity in people. This immune-mediated response is believed to outcome from the trifluoroacetylated protein adducts within the liver. Severe circumstances are related to centrilobular necrosis which will lead to fulminant liver failure with a mortality rate of 50%. Megaloblastic modifications are seen in patients who obtain nitrous oxide for period of over 24 h. When the perfusion pressure of a coronary artery is decreased, solely the vessels which are capable of dilation can effectively compensate. As the most lipophilic inhaled anesthetic, methoxyflurane undergoes essentially the most biotransformation at an estimated 70% of the drug administered. Methoxyflurane is metabolized in each the kidneys and the liver and inorganic fluoride (F-) is produced throughout its metabolism in clinically significant quantities. Association between nitrous oxide and the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults: a scientific evaluation and metaanalysis. Vapor-liquid equilibria for the binary methods diethyl ether-halothane (1, 1, 1-trifluoro-2-bromo2-chloroethane), halothane-methanol, and diethyl ether-methanol. Characteristics of anesthetic brokers used for induction and upkeep of basic anesthesia. Inhaled anesthetics and immobility: mechanisms, mysteries, and minimum alveolar anesthetic focus. Halothane and isoflurane effects on Ca2+ fluxes of isolated myocardial sarcoplasmic reticulum. Effects of risky anesthetics on the kinetics of inhibitory postsynaptic currents in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Potentiation of gammaaminobutyric acidA receptor Cl- current correlates with in vivo anesthetic efficiency. Effects of gaseous anesthetics nitrous oxide and xenon on ligand-gated ion channels. Nonhalogenated anesthetic alkanes and perhalogenated nonimmobilizing alkanes inhibit alpha(4)beta(2) neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. The electroencephalographic sample during anesthesia with ethrane: results of depth of anesthesia, PaCo2, and nitrous oxide. Humans anesthetized with sevoflurane or isoflurane have comparable arrhythmic response to epinephrine. Inhalation anesthesiology and unstable liquid anesthetics: concentrate on isoflurane, desflurane, and sevoflurane. Absence of bronchodilation throughout desflurane anesthesia: a comparison to sevoflurane and thiopental. Clinical impressions and cardiorespiratory effects of a brand new fluorinated inhalation anaesthetic, desflurane (I�653), in volunteers. Intravenous opioids scale back airway irritation throughout induction of anaesthesia with desflurane in adults. The impact of humidification and smoking habit on the incidence of adverse airway events throughout deepening of anaesthesia with desflurane. Comparison in vitro of isoflurane and halothane potentiation of d- tubocurarine and succinylcholine assembly abstractss. A comparative research of halothane and halopropane anesthesia including technique for figuring out equipotency. Delayed onset of malignant hyperthermia disaster during a living donor liver transplantation attributable to sevoflurane. The effect of halothane on drug disposition: contribution of adjustments in intrinsic drug metabolizing capacity and hepatic blood flow.