
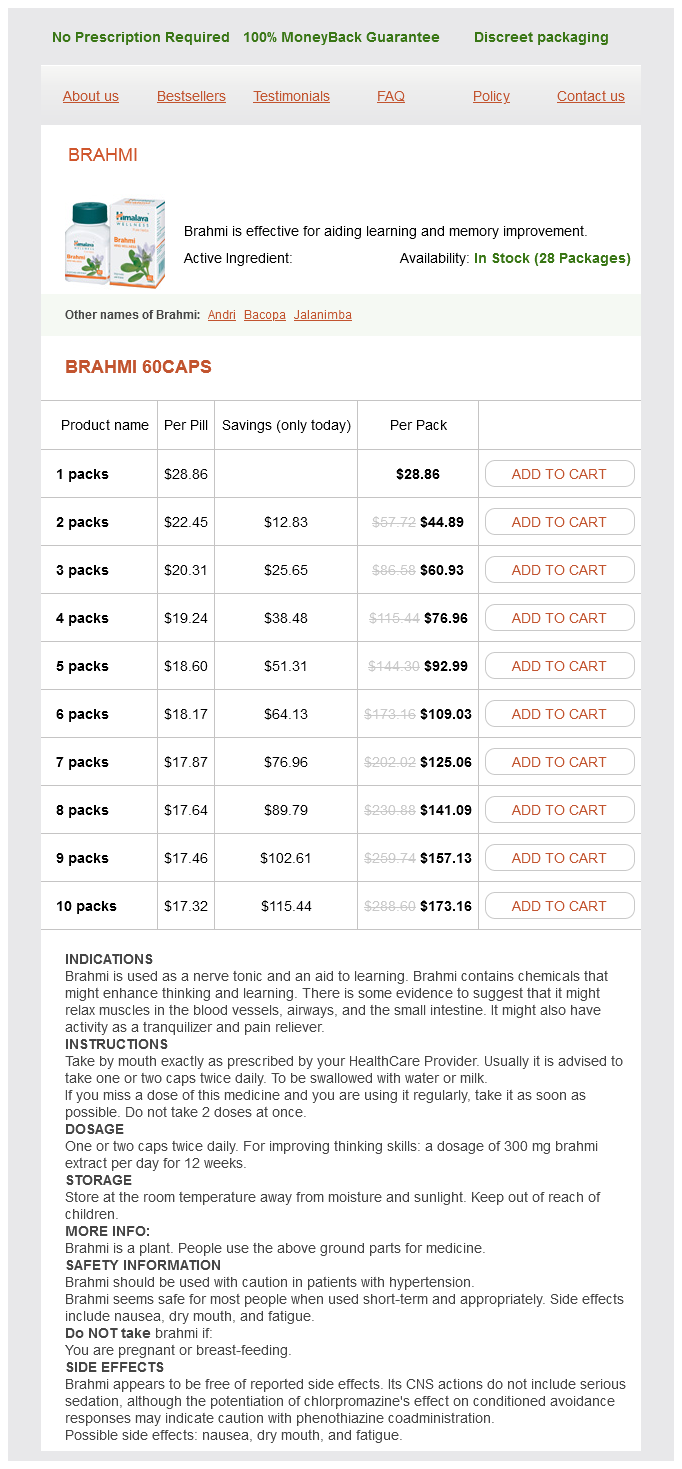
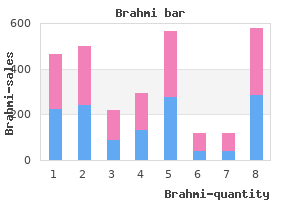
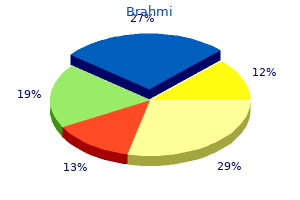
Brahmi
| Contato
Página Inicial
"Brahmi 60 caps amex, treatment walking pneumonia".
Z. Sobota, M.A., M.D.
Clinical Director, California Health Sciences University
National Institutes of Health consensus improvement convention assertion: management of hepatitis B medicine 968 order brahmi 60 caps with amex. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: what we knew in 1981 and what we all know in 2005 symptoms wisdom teeth buy discount brahmi 60 caps online. Acute exacerbations of chronic sort B hepatitis are accompanied by elevated T cell responses to hepatitis B core and e antigens medications or therapy purchase brahmi 60 caps with mastercard. Intrahepatic distribution of hepatitis B floor and core antigens in chronic hepatitis B virus an infection medications adhd discount brahmi 60 caps overnight delivery. Hepatocyte with cytoplasmic/membranous hepatitis B core antigen as a attainable goal for immune hepatocytolysis. The improvement of cirrhosis in sufferers with persistent kind B hepatitis: a prospective examine. Serologic and medical outcomes of 1536 Alaska Natives chronically contaminated with hepatitis B virus. Wild-type and e antigen-minus hepatitis B viruses and course of persistent hepatitis. Predicting cirrhosis danger based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2012 replace. A remedy algorithm for the management of continual hepatitis B virus an infection within the United States: 2008 update. Asian-Pacific consensus assertion on the management of continual hepatitis B: a 2008 replace. While a liver biopsy can help assess the severity of liver fibrosis and irritation andp to exclude competing causes of liver injury [12], biopsies are costly and topic to sampling error, and carry risks of morbidity and mortality. Liver elastography can present immediate data regarding liver stiffness at the point of care, however can only reliably distinguish cirrhosis from non-cirrhosis [13]. Since individuals with bridging fibrosis and cirrhosis are at increased threat of creating issues of superior liver illness, especially hepatocellular carcinoma, they require 6�12-monthly imaging surveillance for liver cancer and 1�3-yearly screening for varices [14, 15]. Potential obstacles to initiation embrace medical or psychiatric comorbidities, lack of acceptance of treatment. High priority ought to be given to treating patients on the highest risk for liverrelated issues. The evidence obtainable to inform decision-making and recommendations is evolving rapidly. Abbreviation 3D Drug Name Ombitasvir/Paritaprevir/Ritonavir plus Dasabuvir (Viekira) Daclatasvir Dosing 12. The suggestions that comply with address variations in treatment primarily based on these factors. Daily fixed-dose combination of grazoprevir (100 mg) and elbasvir (50 mg) in fixed dose combination for 12 weeks (dosing and period of grazoprevir based mostly on section three examine outcomes and given in anticipation of regulatory approval). Daily velpatasvir (100 mg)/sofosbuvir (400 mg) in mounted dose mixture for 12 weeks (dosing and length of velpatasvir based on part three research results and given in anticipation of regulatory approval). Most adverse occasions occur in ribavirin-containing arms, with discontinuation rates low even for sufferers with cirrhosis (approximately 2%). In addition, the post hoc nature of the analysis limits confidence in abbreviating period of therapy. Postmarketing knowledge with sofosbuvir when coadministered with amiodarone have been associated with symptomatic bradycardia and, in one case, fatal cardiac arrest. Amiodarone should be stopped for a minimum of 4 weeks prior to initiating sofosbuvir. The research enrolled two cohorts: cohort 1 included patients with a previous null response to peginterferon-based therapy (n = 80, Metavir F0 to F3 fibrosis), and cohort 2 included peginterferon-based therapy-responder and nullresponder patients with Metavir stage F3 or F4 fibrosis (n = 87). Each cohort had 12- and 24-week treatment arms, with and without ribavirin, to handle size of treatment and the role of weightbased ribavirin. The small dimension of the examine precluded willpower of a good factor about extended (24 vs. Nuances for Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir the every day fixed-dose mixture of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir has a important interaction with acid-suppressing medications. Acidsuppressing medicines should be held for a week before and through the remedy period. For sufferers who require acid suppression, famotidine forty mg/day or omeprazole 20 mg/day or equal can be supplied. Ledipasvir or velpatasvir ought to be dosed >8 hours after famotidine, with cranberry or orange juice. Based on its pharmacokinetics, important effects can be predicted for widespread immunosuppression agents, especially cyclosporine, of an analogous sort to these for simeprevir. In the absence of realworld data relating to drug�drug interactions between grazoprevir and immunosuppressive agents, we suggest avoiding this agent within the post-transplant setting. Daily fixed-dose mixture of grazoprevir (100 mg) and elbasvir (50 mg) for 12 weeks (dosing and duration of grazoprevir based on section three study outcomes and given in anticipation of regulatory approval). Daily fixed-dose combination of paritaprevir (150 mg)/ritonavir (100 mg)/ombitasvir (25 mg) plus twice-daily dosed dasabuvir (250 mg) and weight-based ribavirin (1000 mg (<75 kg) to 1200 mg (75 kg)) for 12 weeks. Daily sofosbuvir (400 mg) and weight-based ribavirin (1000 mg (<75 kg) to 1200 mg (75 kg)) for 24 weeks. Daclatasvir/sofosbuvir/ribavirin for 12 weeks is of equal efficacy to 24 weeks in sufferers with decompensated cirrhosis. Daily velpatasvir (100mg)/ sofosbuvir (400mg) in fastened dose combination for 12 weeks (dosing and period of velpatasvir primarily based on part three research outcomes and given in anticipation of regulatory approval). Nonetheless, for those patients for whom immediate treatment is required, the previous recommendations have been drawn from obtainable information. Though treatment of chronic hepatitis C an infection has turn into highly efficient and safe, many nuances persist. Careful consideration of patient and viral elements continues to be needed to have the ability to achieve optimum outcomes and, importantly, to keep away from critical drug�drug interactions and therapy failures. The changing epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001 through 2010. Fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C correlates significantly with physique mass index and steatosis. Efficacy and safety of high-dose pravastatin in hypercholesterolemic sufferers with well-compensated chronic liver disease: results of a potential, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Blood checks to diagnose fibrosis or cirrhosis in patients with continual hepatitis C virus infection. The pure history of compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C virus: a 17-year cohort study of 214 patients. Factors that decide the development and progression of gastroesophageal varices in sufferers with persistent hepatitis C. A sustained virologic response is durable in patients with chronic hepatitis C handled with peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin. Long-term clearance of hepatitis C virus following interferon alpha-2b or peginterferon alpha-2b, alone or together with ribavirin. Sustained virologic response is associated with improved health-related quality of life in relapsed chronic hepatitis C patients. Impact of pegylated interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin on liver fibrosis in patients with persistent hepatitis C. Sustained virologic response and medical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis C and advanced fibrosis. Patterns and predictors of remedy initiation and completion in sufferers with continual hepatitis C virus an infection. These happen by unfold from contiguous organs or hematogenous seeding, or by toxic results from distant infections and their treatment. The scientific displays of these infections vary from no symptoms to hepatitis, abscess, granulomas, biliary obstruction, and liver failure. This chapter summarizes the varied infections of the liver and biliary tree and their prognosis and remedy. Pyogenic Liver Abscess Microbiology essentially the most frequently found organisms are Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae, streptococci, and anaerobes [1�3].
In a cohort of Ontario residents medications covered by medicare generic brahmi 60 caps without prescription, while the relative risk of colorectal most cancers after colonoscopy was 0 keratin treatment buy brahmi 60 caps with mastercard. In this similar cohort symptoms ptsd discount brahmi 60 caps without a prescription, colonoscopy carried out by a nongastroenterologist was more prone to treatment 3rd stage breast cancer brahmi 60 caps discount amex be associated with discovering colorectal most cancers after unfavorable colonoscopy [17]. In a cross-sectional German cohort, the prevalence of colorectal most cancers in patients who had undergone colonoscopy prior to now 10 years was decreased in comparability with that in those with out previous colonoscopy, with an adjusted prevalence ratio 0. Compared to the other available screening checks, colonoscopy carries a higher burden of problems. Bleeding is a risk after polypectomy, and the chance of perforation is 1/1000 within the Medicare population [20]. Additional opposed events, including cardiac arrhythmias, may outcome from the utilization of sedation for colonoscopy. Most pointers suggest a 10-year interval for follow-up after a traditional colonoscopy. This interval is predicated on stories that counsel a gradual growth rate of adenomatous polyps, a few of which will finally become cancers, but there are few data to support it. Only 19% of these randomized to colonoscopy really underwent a colonoscopy, but adenoma detection was greater in the colonoscopy arm. It has only lately been integrated into the Joint Guideline [2] as an appropriate type of colorectal cancer screening. Case Continued Cancer screening by colonoscopy should begin at age 40 or at 10 years youthful than the youngest member of the family with colorectal cancer. If suspicion is raised for a familial syndrome, then genetic counseling should be provided. Discussion of the Guidelines Several completely different organizations and skilled societies have created tips for colorectal screening and surveillance. The guidelines differ barely as to when to initiate colorectal most cancers screening, though for many asymptomatic individuals with a adverse family history, screening ought to begin at age 50. A thorough household history, together with age of analysis and type of cancer for every affected family member, should be thought-about an essential a part of most cancers screening for every particular person; those with important household histories could warrant extra aggressive screening. Once polyps or cancer has been identified, the affected person enters right into a program of surveillance by colonoscopy. Conclusion Colorectal cancer screening has assumed two targets: reduction of mortality as a result of colorectal most cancers and prevention of colorectal cancer by way of the removing of polyps. Colonoscopy has long been considered the gold standard for polyp detection and elimination, though miss rates for even the detection of most cancers have been reported to be as excessive as 4% [14, 15]. In addition, emerging proof suggests that the effectiveness of colonoscopy as a colorectal cancer prevention device is lowered, significantly in the best colon [16�19]. Average-risk people age 50 and older should be encouraged to take part in colorectal cancer screening. Some are extra acceptable to patients and extra possible for health care systems [2]. Future research should concentrate on interventions aimed toward implementing applicable screening and should determine methods to reduce the need for more invasive and costly checks. Take Home Points r Colorectal most cancers screening has been shown to cut back mortality from colorectal most cancers. These checks need to be repeated at their instructed intervals to ensure that screening to be efficient. Furthermore, risk assessment is important to determining whether the person to be screened is at average or excessive threat for creating colorectal cancer primarily based on private or household history. The affected person should settle for screening and adjust to applicable directions for the screening take a look at. Positive tests must be followed up in a well timed method, to have the ability to diagnose colorectal most cancers in an early and treatable stage. Some colorectal most cancers screening tests are more acceptable to patients and extra possible for health care methods. In techniques or settings where assets are limited, any of the permitted modalities is preferable to the choice of no screening. A randomised study of screening for colorectal most cancers utilizing faecal occult blood testing: results after thirteen years and seven biennial screening rounds. Measures for ascertaining use of colorectal cancer screening in behavioral, health providers, and epidemiologic research. Feasibility of colonoscopy screening: discussion of issues and recommendations concerning implementation. Colonoscopic miss charges for right-sided colon cancer: a population-based analysis. Relative sensitivity of colonoscopy and barium enema for detection of colorectal most cancers in clinical follow. Risk of growing proximal versus distal colorectal most cancers after a unfavorable colonoscopy: a population-based study. Endoscopist specialty is related to incident colorectal cancer after a negative colonoscopy. Protection from right- and left-sided colorectal neoplasms after colonoscopy: population-based study. Risk of perforation after colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy: a population-based study. Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer � analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. Polyp guideline: diagnosis, remedy, and surveillance for sufferers with colorectal polyps. Endoscopic palliation of malignant biliary obstruction is mentioned in Chapter seventy four. Finally, endoscopic placement of gastrostomy tubes for supplemental diet and/or decompression can be used for palliation of obstruction. A probe that passes via the endoscope channel permits necrosis and ablation of tissue at excessive power settings. Endoscopic placement of brachytherapy catheters can deliever radiation therapy to the esophagus and supply palliation of malignant dysphagia [2]. The endoscope may be handed alongside the stent in order that the stent is deployed beneath direct endoscopic visualization. A laser-diffusion fiber is inserted through the endoscope and positioned throughout the stricture for a defined time period. Argon beam coagulation has replaced laser in most endoscopy items and is utilized by passing the probe into the esophagus. At high energy settings and in close proximity to the lesion, the tissue is coagulated to induce necrosis of the tumor [3]. Brachytherapy is carried out by endoscopically putting a guidewire into the abdomen and positioning the catheter fluoroscopically. The stents have a lattice configuration and are preloaded on to a delivery system in a constrained trend. This ends in release of cytotoxic oxygen radicals, which kill tumor cells in the areas the place light exposure occurs. Malignant Dysphagia In patients with superior illness, palliation of dysphagia is performed to improve quality of life and nutritional status and to prevent aspiration pneumonia (Table forty four. Simple dilation using Practical Gastroenterology and Hepatology Board Review Toolkit, Second Edition. Esophageal stents Airway obstruction Aspiration Tracheoesophageal fistula Chest pain Reflux with aspiration, esophagitis Food impaction Obstruction: tumor ingrowth, overgrowth, tissue hyperplasia Bleeding Migration Perforation Tenesmus, incontinence (rectal stent placement) All stents balloon or bougie can enable temporary reduction of dysphagia. Stents are useful for palliating malignant dysphagia from each intrinsic tumors of the esophagus and malignant extrinsic compression. Unlike feeding tubes, stents can produce palliation of dysphagia, permitting peroral diet. Covered metallic stents and an expandable plastic stent permit closure of tracheoesophageal fistulas. Early issues after esophageal stent placement could embrace perforation, aspiration, chest pain, malpositioning of the stent, and acute airway obstruction (Table forty four. Stent occlusion can result from an impacted food bolus or from tumor ingrowth or tissue hyperplasia (through the uncovered portions of metal stents).
Ketamine causes cerebral vasodilation and must be averted in patients with intracranial hypertension symptoms to pregnancy brahmi 60 caps buy fast delivery. Heart price and blood pressure are usually increased through sympathomimetic actions secondary to central stimulation and lowered postganglionic catecholamine uptake medicine cabinets with mirrors brahmi 60 caps order without a prescription. However administering medications 7th edition ebook brahmi 60 caps buy cheap on-line, you will want to administering medications 7th edition ebook generic brahmi 60 caps with amex keep in thoughts that this drug does have direct myocardial depressant effects and should be used with caution in sufferers with restricted myocardial reserve, for instance neonates with critical aortic stenosis. Dose-related respiratory melancholy may occur; however, most patients continue to breathe spontaneously after an induction dose of 2�3 mg/kg. Airway secretions are increased, and despite the actual fact that airway reflexes seem intact, aspiration could happen. It is essential that patients be fasted prior to administration of ketamine, and full airway administration gear have to be obtainable. An improve in airway secretions might cause laryngospasm throughout airway manipulation, and an antisialagogue such as atropine or glycopyrrolate should be administered concurrently. Side effects of emergence delirium and hallucinations may be ameliorated with the concurrent use of benzodiazepines. There are conflicting reviews about the effect of ketamine on pulmonary vascular resistance. One small research in children present process cardiac catheterization concluded that pulmonary vascular resistance was increased following ketamine in sufferers predisposed to pulmonary hypertension. Besides being used to facilitate intubation and managed mechanical air flow, patients with restricted cardiorespiratory reserve additionally benefit from paralysis due to reduced myocardial work and oxygen demand. However, prolonged paralysis carries the concomitant risks of extended ventilatory support and delayed institution of enteral nutrition, and will end in tolerance and Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care 63 prolonged muscle weak spot after discontinuing the muscle relaxant. There may be adverse interactions between the nondepolarizing muscle relaxants, steroids, and aminoglycosides resulting in prolonged weakness, particularly in older youngsters. Succinylcholine is a depolarizing muscle relaxant with a rapid onset and short length of motion. Its use could finest serve sufferers requiring speedy sequence induction due to the risk for aspiration of gastric contents. The usual intravenous dose of 1 mg/kg should be increased in newborns and infants to 2 mg/kg because of the larger surface area to weight ratio in these sufferers. The danger for bradycardia is exaggerated in kids, especially after multiple doses, and a 20 �g/kg dose of atropine should be administered concurrently. Rocuronium is an aminosteroid, nondepolarizing muscle relaxant with a quick onset and intermediate length of motion; the time to complete neuromuscular blockade for an intubating dose of 0. It is subsequently a suitable different to succinylcholine during rapid sequence induction. The period of motion averages 25 minutes, although recovery is slower in infants. Vecuronium and cisatracurium are nondepolarizing muscle relaxants with intermediate durations of actions. Both these brokers have minimal impact on the circulation and can be administered safely to patients with limited hemodynamic reserve. Cisatracurium is metabolized by plasma esterases and should be thought of for use in patients with severe hepatic and/or renal dysfunction. Pancuronium is a commonly used, longer duration, nondepolarizing relaxant that may be administered intermittently at a dose of 0. It could cause a gentle tachycardia and improve in blood pressure and can be protected to administer to sufferers with restricted hemodynamic reserve. In a examine of over 300 children with advanced cardiac illness present process surgical repair, both preoperative and postoperative elements impacted the chance of prolonged mechanical ventilation and the potential for early postoperative extubation. When contemplating early extubation, components corresponding to noncardiac anomalies, prematurity, single-ventricle physiology and healthcare-acquired circumstances ought to be considered. Although these will range from affected person to affected person, rigorously constructed postoperative order units are helpful to direct initial management and planning. This has been possible without important compromise of patient care, and a low sixty four Comprehensive Surgical Management of Congenital Heart Disease, Second Edition incidence for reintubation or hemodynamic instability has been reported. The surgical strategy and strategies for many cardiac procedures have additionally considerably changed over current years, particularly with the event of minimally invasive methods in both adults and children. While it may be thought that a minimally invasive incision could presumably be related to a more fast postoperative recovery because of less pain or decrease analgesic necessities, this has not been demonstrated. For other postoperative sufferers, the plan for weaning from mechanical ventilation ought to be individualized based on age, clinical status, surgical procedure performed, and anticipated postoperative administration. Neonates and Small Infants Two Ventricle Repairs the response to surgical procedure and bypass can range significantly between neonates and is commonly unpredictable. Nevertheless, an intensive understanding of the anticipated postoperative course is important. Neonates and infants present process two ventricle repairs are sometimes managed with sedation and/or paralysis in the instant postoperative interval until hemodynamic and respiratory stability has been attained, although there are clear variations depending on diagnosis and procedure. Right ventricular compliance often improves in the course of the first 2�3 postoperative days, evident by a fall in right-sided filling pressures, elevated arterial oxygen saturation, and improved cardiac output with heat extremities and an effective diuresis; sedation and/or paralysis can then be discontinued and the patient allowed to wean slowly from mechanical ventilation. Intensive monitoring is essential because the clinical status might change abruptly, leading to a fast deterioration. Deep sedation and, when clinically acceptable, paralysis should proceed initially following surgical procedure to decrease the stress response and any imbalance between oxygen supply and demand till the patient demonstrates a secure circulation and gasoline exchange. However, sure nonbypass procedures ought to nonetheless be thought of with a very cautious strategy. Despite short operative times, these procedures often trigger a significant hemodynamic alteration and inflammatory response, and will require mechanical air flow and deep sedation for at least the primary postoperative evening until cardiorespiratory stability is attained. Infants with a big volume load on the ventricle previous to surgical procedure or a labile pulmonary vascular resistance secondary to increased pulmonary blood move can be suitable for weaning and extubation within the early postoperative interval; however, administration ought to be guided by hemodynamic and respiratory perform as patients start to emerge from sedation. Cavopulmonary Connection Following creation of a cavopulmonary connection � a bidirectional Glenn shunt or a modified Fontan process � sufferers usually benefit from early weaning and tracheal extubation. Effective pulmonary blood flow is enhanced throughout spontaneous ventilation because of the lower imply intrathoracic stress. Following cavopulmonary connection, pulmonary blood flow is passive and pulmonary blood move is considerably larger throughout unfavorable stress spontaneous respiration than with positive stress air flow. Therefore, prolonged durations of constructive strain air flow can have a major impact on pulmonary blood move, systemic oxygen supply, and cardiac output. Despite this goal, these sufferers ought to only be weaned after hemodynamic stability has been achieved. The subsequent fall in cardiac output might be manifest early as an evolving acidosis, cool extremities, hepatomegaly, ascites, oliguria, and sometimes vital chest tube drainage. Hypertension and tachycardia are frequently a administration concern in these sufferers within the quick postoperative period. Preoperative Management Patients are initially managed with an infusion of prostaglandin El at zero. If the affected person presents in a steady situation with an SaO2 of more than 65�70%, a PaO2 greater than 25 mmHg, and a normal pH, the septostomy could be performed semi-electively. Occasionally, an pressing septostomy is indicated for sufferers who present with severe hypoxemia (PaO2 less than 20�25 mmHg) and a metabolic acidosis (pH less than 7. However, to maintain mixing on the atrial level, volume replacement with colloid or blood merchandise is usually necessary. If the patient is mechanically ventilated, a low imply airway pressure is crucial, and sometimes inotrope assist with dopamine is necessary to deal with hypotension until enough mixing is achieved. While the prostaglandin El infusion can normally be discontinued after an enough septostomy, it may must be continued if mixing is insufficient and the PaO2 remains under 25 mmHg. Surgical correction is usually performed within the first week of life after the septostomy, as quickly as the affected person is hemodynamically steady with out signs of finish organ dysfunction. The sudden onset of heart block or ventricular tachyarrhythmia may herald myocardial ischemia. Myocardial ischemia is most commonly secondary to mechanical obstruction of the coronary arteries, such as thrombosis, kinking, or extrinsic strain. Further investigation is important, beginning with echocardiography and sometimes continuing to catheterization and attainable reoperation if coronary compression, kinking, or obstruction is confirmed. The sudden onset of ischemia may indicate imminent circulatory collapse and have to be handled urgently. In this circumstance, it may be preferable to open the sternum and decompress the mediastinum.
Syndromes
- Paper coating
- Nausea
- Chest x-ray
- History of gallstones, chronic pancreatitis, or pancreatic cancer
- If the medication was prescribed for the patient
- Chest CT scan (in certain cases)
Continue through perioperative period (consider withholding amlodipine on the morning of surgery) symptoms wisdom teeth brahmi 60 caps buy without a prescription. Diuretics calcium channel blockers Oral hypoglycemics Hypoglycemia preoperatively and intraoperatively treatment hepatitis b order 60 caps brahmi with mastercard. Cerebral function evaluation: A temporary shunt may be positioned if evaluation shows the event of cerebral ischemia; shunts carry a threat of thromboembolic issues medicine 029 buy brahmi 60 caps free shipping. General anesthesia: � Induction: Goal of induction is to preserve hemodynamic stability while maximizing cerebral protection symptoms ibs buy 60 caps brahmi visa. Hypotension: Treat with a titratable direct-acting a: agonist corresponding to phenylephrine. Pblockers: Use with warning, as profound bradycardia could additionally be encountered with manipulation of carotid baroreceptors. Maintain nonnocapnia: Hypercapnia may cause cerebral steal syndrome, and hypocapnia can. Respiratory insufficiency: � Causes: Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, hypoglossal nerve harm, impaired carotid body response to hypoxemia, neck hematoma. Neurologic deficits: � Causes: Thromboembolism (leading to cerebral hypoperfusion), regional cerebral hyperperfusion. Preoperative Considerations � Anesthetic management of the patient for aortic surgical procedure may be difficult, particularly within the emergent, nonoptimized case, � Potential for large blood loss requiring aortic cross-clamp. Complications: � Paraplegia and spinal wire ischemia attributable to surgical injury to artery of Adamkiewicz, which is the main artery supplying decrease thoracic and lumbar spinal cord. Stanford type A includes any involvement of ascending aorta, whereas type B is proscribed to the descending aorta. DeBalcey varieties I and D can also be thought-about Stanford sort A DeBaley type Ill ia the rarne as a Stanford kind B. Risk of rupture t with increasing aneurysm measurement:> 6 em correlates to 50% rupture inside 1 12 months. Arterial catheterization (preferably on the right) could be obtained preinduction if vital comorbidities or broad adjustments in hemodynamics are expected during induction; in any other case, postinduction arterial line placement is appropriate. May want left radial artery, femoral or dorsalis pedis for arterial blood strain monitoring, because the innominate artery may be clamped. Intraoperative course may be difficult by giant volume shifts, blood loss, lengthy cross-clamp occasions, and new or worsening aortic regurgitation, often requiring valve substitute. Pblockers must be used with warning, as bradycardia can worsen aortic regurgitation. Cooling to 15-l8�C, steroids, mannitol, and thiopental can be utilized to obtain cerebral protection. One-lung anesthesia utilizing double-lumen tube or bronchial blocker can facilitate surgical exposure. Shunts and left atrial-femoral artery and femoral vein-femoral artery bypasses can cut back issues attributable to cross-clamping. Elective circumstances can profit from a thoracic epidural for postoperative pain administration but may be sophisticated with use of anticoagulation. Right radial arterial line, as clamping of left subclavian artery could also be necessary. Correction of coagulopathy and dosing of calcium chloride may profit those receiving large transfusions. More distal cross-clamping produces much less impact on left ventricular afterload and hemodynamics. Postoperative Management � � � Most sufferers undergoing surgical procedure to the proximal aorta should stay intubated and ventilated for the quick postoperative period. Immediate postoperative objective is to maintain stable hemodynamic parameters and proper coagulopathies. Anesthetic Mana1ement � � � � � � >~ ~ zero c:::1: t- c z Can be carried out under regional or basic anesthesia alone or as a combined regional-general method. Neuraxial anesthesia: these sufferers could already be on antiplatelet treatment or will require anticoagulation throughout surgical procedure; timing of epidural placement and removal must be made accordingly. Arterial catheterization may be required for patients with co-morbidities and severe vascular illness. Postoperative Management � � � Patients are intently observed for graft occlusion and might have revision. Reverse steal or Robin Hood effect: � Occurs in hyperventilated sufferers with focal ischemia. Major elements that occupy house within the skull: � Brain parenchyma: Neurons and glia. Volume � � � t in quantity are initially properly compensated until the restrict of spatial compensation is reached. Water intoxication: Intracellular motion of water from acute drop in serum osmolality. Detrimental drculatory lteal phenomenon is possible with unstable anesthetics in settings of focal ischemia. Normeperidine (metabolite ofmeperidine) mn induce seizures in sufferers with renal failure. Interpretation: � Activation (high frequency, low voltage): Light anesthesia or surgical stimulation. Opioids are an exception to this rule; they exhibit a monophasic pattern with dose-dependent melancholy (see Table 14-3). Sleep and anesthesia in adults, hyperventilation in awake children and young adults. Corticosteroids: Promote restore of blood-brain barrier if intracranial hemorrhage results from vasogenic edema secondary to tumors. Types of primary tumors: � Glial cell tumors (astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, glioblastoma). Small doses of opioids for preinduction insertion of invasive monitoring gadgets in awake, conversant sufferers to alleviate discomfort. Foley catheter: Guides fluid management in the face of blood loss and osmotic diuresis. Possible central venous catheterization for patients with extreme comorbid conditions. Combination of etomidate (6-8 mg) can be utilized in hemodynamically unstable sufferers. Crystalloids to substitute maintenance fluids and colloids to restore intravascular volume deficits from blood loss. Antihypertensive agents (labetalol, esmolol, nicardipine): Control H1N during emergence. Extubate solely after affected person is totally reversed from muscle paralysis, awake, and following commands (see Table 14-5 for causes of delayed awakening). Vital respiratory, circulatory centers, cranial nerves and nuclei may be affected. Facial nerve monitoring is sometimes carried out but requires absence of muscle relaxant. Aspirate entrained air with central venous catheter-many contemplate central venous catheter as necessity for sitting craniotomy. Bifrontal craniotomy: � Advantages: Direct visualization, access to larger tumors. Postoperative adrenal insufficiency: Treat with corticosteroids (avoid giving dexamethasone intraoperatively in order that pituitary perform may be monitored postoperatively). Circumstances of the harm: Time, length of unconsciousness, related alcohol or drug use. Assume all head trauma patients have cervical backbone injury till confirmed otherwise. Neurogenic pulmonary edema is secondary to intense sympathetic nervous system exercise, which causes systemic and pulmonary hypertension. Treatment contains intubation, mechanical ventilation, 100 percent oxygen, suctioning, diuresis. Assume all sufferers have full stomachs requiring a speedy sequence induction with muscle rest. Awake fiber-optic intubation or tracheostomy may be necessary if tough intubation is anticipated. Spinal cord accidents ~ sympathectomies (especially lesions to Tl-4) ~ spinal shock (vasodilatation and hypotension).
Purchase 60 caps brahmi. Umeed : Anxiety Leads to Depression..