
Cleocin
| Contato
Página Inicial

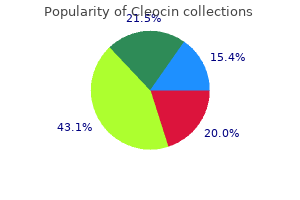
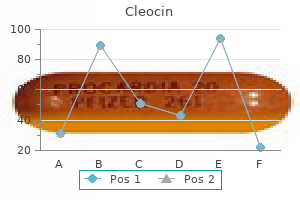
"Discount 150 mg cleocin with mastercard, acne inversa images".
V. Ines, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, Idaho College of Osteopathic Medicine
The chest radiograph shows multiple faint skin care qualifications cleocin 150 mg discount with visa, rounded opacities with or without cavitation acne 40 years old purchase cleocin 150 mg fast delivery. Septic pulmonary embolism refers to the hematogenous spread into the lungs of thrombi that comprise microorganisms (usually Staphylococcus aureus) acne at 40 buy 150 mg cleocin amex. Tuberculosis is an an infection with cardio gram-positive organisms of the genus Mycobacterium acne research cleocin 150 mg purchase visa. Multidrug-resistant strains not delicate to the standard antibiotics rifampicin and isoniazid have gotten more widespread in these regions. A main an infection denotes initial contact with tuberculosis before antibodies have been developed. Pulmonary tuberculosis is acquired by droplet inhalation, which regularly happens in childhood. This stage is asymptomatic in immunocompetent sufferers or could current with signs of a light cold. The mycobacteria are phagocytosed in the alveolar area to form a Ghon focus, a caseating granuloma that contains mycobacteria at its center. Transport to the regional (hilar) lymph nodes leads to hilar lymphadenopathy with enlargement of the hilar nodes. The Ghon focus and associated lymphadenitis are known as the primary advanced (also called the Ranke complex). In immunocompetent people, the primary complicated heals by fibrosis and will calcify. Viable micro organism stay walled-off within the 142 Downloaded by: Tulane University. This can result in bronchogenic unfold of the infectious organisms and the event of pneumonia. Postprimary tuberculosis with cavitation requires differentiation from adenocarcinoma and lung abscess. Miliary tuberculosis is a subtype of postprimary tuberculosis that happens in immunocompromised sufferers. Caution Primary pulmonary tuberculosis could be very rarely detected as a result of its gentle scientific presentation in immunocompetent individuals (absence of symptoms, or symptoms of a slight cold). Postprimary tuberculosis may comply with the primary an infection and relies on hematogenous dissemination of the causal organisms, which may spread to virtually all organs within the body including the lung. Fungi of the genus Aspergillus embody molds and happen ubiquitously in the surroundings. Species pathogenic to humans are Aspergillus fumigatus, which alone is answerable for 80% of all Aspergillus infections, as properly as A. Aspergilli are dimorphic and will occur as spores (conidia) or hyphae, which can sprout to form mycelia. Aspergillus fumigatus can usually be isolated from the nasopharynx of healthy people. The colonization price is 50% in cystic fibrosis sufferers and 20% in sufferers with pulmonary fibrosis. Three various kinds of aspergillosis are known: Aspergilloma: this refers to fungal involvement of a preexisting cavity in the lung, forming a fungus ball composed of mycelia and cellular particles. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: this type occurs as an allergic response to fungal spores in an asthma patient, resulting in the destruction of lung parenchyma and the event of bronchiectasis. The pathophysiology entails granuloma formation in the bronchial lumen, causing obstruction of the bronchus and retained secretions (endobronchial mucoid impaction). Angioinvasive aspergillosis: this type, with the subtype of bronchoinvasive (semi-invasive) aspergillosis, occurs in immunocompromised sufferers. Since phagocytosis is impaired in the immunocompromised host, inhaled fungal spores can develop into hyphae that infiltrate the lung tissue and vessels, causing occlusions. Imaging signs Aspergilloma: the conglomeration of fungal hyphae seems as a rounded opacity within a cavity. The fungus ball may initially comprise air inclusions, just like a sponge, however might later be very dense and include calcifications. Invasive aspergillosis: this type is characterised by rapidly progressive opacities in the chest radiographs. Peripheral wedge-shaped densities may develop because of vascular invasion and tissue infarction. Semi-invasive aspergillosis is marked by the development of slowly progressive opacities or nodules in the apical area. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: this entity is characterized by opacities that migrate over a interval of a number of days. Other fungal infections similar to Wegener granulomatosis must be thought of within the differential analysis. Pulmonary embolism with infarction can usually be positively distinguished from angioinvasive aspergillosis primarily based on the scientific presentation. Cough, fever, chills, and chest ache are the dominant scientific symptoms, making it troublesome to distinguish aspergillosis from bacterial pneumonia. Differentiation is aided by correlation with laboratory findings (neutropenia) and imaging signs. The clinical elements of various types of aspergillosis are reviewed under: Aspergilloma happens in immunocompetent patients; it requires a preexisting cavity. Invasive aspergillosis is a disease of severely immunocompromised patients, occurring in approximately 20% of sufferers with acute leukemia and 20% of patients after chemotherapy or transplantation. Neutropenia is the essential danger issue and may counsel angioinvasive aspergillosis when combined with fever and lung opacities. Even with acceptable remedy, invasive aspergillosis has a high mortality fee, at 40%. Approximately 40% of patients develop hemoptysis from the erosion of bronchial arteries at some time during the course of the disease. The central density consists largely of infarcted necrotic lung tissue permeated by fungi. Semi-invasive aspergillosis might develop in patients with slight immunodeficiency (due to corticosteroid remedy, diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, etc. Patients with cystic fibrosis or bronchial bronchial asthma are at excessive risk, with an incidence of 20%. Focal ground-glass opacities with both sharp or hazy margins are termed "ground-glass nodules. On the one hand, a fantastic many patients are discovered to have small nodules, and the proportion of sufferers with nodules detected by the way in reconstructed skinny slices is almost 50%. On the other hand, the extent of follow-up ought to be commensurate with the chance that the detected lesions are actually malignant. With these issues in mind, the Fleischner Society has published recommendations on the follow-up of pulmonary nodules. Its suggestions are primarily based on worldwide research published till 2005 dealing with screening for the early detection of lung cancer. Swyer�James�MacLeod syndrome is the end result of obliterative bronchiolitis in early childhood with the destruction of lung parenchyma. Adenoviruses, respiratory syncytial virus, and Mycoplasma micro organism have been recognized as causative brokers. Differentiation is required primarily from hypoplastic lung (aplasia or hypoplasia of the pulmonary artery) and congenital emphysema. With congenital emphysema, often just one lobe is affected and the affected lobe is overinflated and never diminished in volume as in Swyer�James�MacLeod syndrome. To keep away from unnecessary follow-ups with the disadvantages of radiation publicity, high cost, and psychosocial stress to the affected person, the Fleischner Society has devised a staged approach to followup that takes into consideration nodule size and affected person risk components (Table 4. Smoking is the greatest risk issue and will increase the danger for people who smoke by an element of 10 to 35 compared with nonsmokers. Other risk components are publicity to asbestos or uranium and the inhalation of radon. Intrapulmonary scarring is one other danger issue that often creates a beginning point for lung most cancers. In a screening study of 233 sufferers with positive findings on baseline scans, 7% of the by the way detected stable nodules have been malignant compared with 63% of subsolid nodules and 18% of ground-glass (nonsolid) nodules. The new classification of lung adenocarcinoma takes into account the prognostic differences among the subtypes.
Segmental defects of the thoracic spine: a number of sagittal clefts or a number of butterfly vertebrae; block vertebrae and hemivertebrae in some circumstances acne attack 150 mg cleocin buy free shipping. A "zipper-like look" of the spine in the neonatal period acne yahoo answers cleocin 150 mg trusted, attributable to absent ossification of the vertebral our bodies and incompletely ossified skin care natural remedies generic cleocin 150 mg, partially fused posterior neural arches skin care help cleocin 150 mg discount with amex. Lumbosacral hypoplasia could cause myelopathy and cauda equina syndrome, resulting in deformities of the ankle and foot. Campomelic dysplasia: Spinal malformations are predominant within the cervicothoracic spine somewhat than the thoracolumbosacral region and are less conspicuous. Hypoplastic scapulae and hypoplastic thoracic vertebral pedicles are discriminating features. Most of the illustrated instances appear to be examples of acampomelic campomelic dysplasia (see Offiah et al. Electronic letter: Surviving campomelic dysplasia has the radiological features of the previously reported ischio-pubic-patella syndrome. Some thoracic vertebral bodies, decrease lumbar vertebral bodies, and the sacrum are unossified. The thoracolumbar vertebral bodies are hypoplastic, and a variety of other lumbar vertebral our bodies are unossified. There is progressive caudal narrowing of interpedicular distances in the lumbar backbone. The lumbar vertebral bodies have become ossified, whereas the sacrum stays unossified. Uncommon findings: choanal atresia; atresia of the exterior auditory canal; absence of the olfactory bulb; elbow dysplasia. Narrow, bell-shaped thorax, typically with unossified (fibrocartilaginous) gaps between ossified posterior and anterior ribs; most severely with small remnants of the posterior ribs and full absence of ossification of the anterior ribs. Survivors generally current with psychological deficiency and microcephaly as sequelae of perinatal asphyxia quite than syndromic parts. This series show variable manifestations of rib hypoplasia and/or rib gaps in decreasing severity. In addition, this patient showed several uncommon findings, together with hypoplasia of the clavicles, scapulae, and ilia. Facial abnormalities: broad brow, deep-set eyes, downslanting palpebral fissures, short nostril, malar hypoplasia, micrognathia with small mouth and higharched palate, simple and/or dysplastic pinnae with preauricular pits or tags. Urogenital hypoplasia: cryptorchidism, hypoplastic exterior genitalia, vaginal insertion of the urethra. Delayed ossification of the pubes and ischial bodies; defective ossification of the acetabulum; central dislocation of the femoral head. Goosecoid was recognized to be a determinant at the Xenopus gastrula organizer region and a segment-polarity determinant in drosophila. However, the differential prognosis is simple as a end result of craniosynostosis and syndactyly in Apert syndrome. The medial acetabular partitions are defective along with central dislocation of the proximal femora. Mild hypertelorism, distinguished, extensive open eyes ("gloomy") with periocular fullness, anteverted nares, full lips. The sufferers have severe quick stature but in any other case the prognosis is sweet with comparatively few complications reported. Russell-Silver syndrome: the characteristic asymmetry of Russell-Silver syndrome is absent in 3M sufferers and the facial features are totally different. Many newborns with 3M syndrome are initially recognized with achondroplasia previous to radiographic research, thus supporting the view that the prognosis of achondroplasia needs to be radiographically or molecularly confirmed even in so-called typical instances. Le Merrer M, Brauner R, Maroteaux P (1991) Dwarfism with gloomy face: a new syndrome with features of 3-M syndrome. This photograph shows the prominent heels that are typical of 3M syndrome and which will supply a diagnostic clue even in the prenatal interval. Despite a marked discount in length, the radiographs present only minor changes with all bones, together with the ribs, being considerably gracile. These radiographs also indicate that vital neonatal constipation is a recurrent (unrecognized) feature of 3M. The long bones are slender with undermodeling, and thus the metaphyses seem relatively giant. Both patients have slender long bones as properly as thin, brief tubular bones with diaphyseal constriction. Microphthalmia, extreme hypermetropia, often glaucoma, corneal clouding, retinal calcification, tortuous retinal vessels, pseudopapilledema. Narrowing of the medullary cavities of the tubular bones (medullary stenosis) with regular or elevated cortical thickness. Reduced diameter of the shafts of the tubular bones with relative flaring of the metaphyses. Arg569His) is recurrent and probably the most frequent mutation responsible for the Kenny-Caffey syndrome. Other mutations in the identical gene end in Osteocraniostenosis, a situation that has related but more extreme skeletal findings and is normally prenatally or perinatally lethal. Postnatal top development is inadequate, and the adult top varies between 122 and 152 cm. Hypocalcemia is often noticed in infancy and manifests with tetany and hypocalcemic seizures. Children could additionally be mildly affected and radiographic anomalies could also be detected incidentally within the work-up of quick stature. Pubertal delay, hypogonadism, and infertility appear to be frequent in affected males; the exact incidence stays to be decided. The phenotype is comparable however extra sever and normally not appropriate with prolonged survival. Sanjad-Sakati syndrome: Tubular stenosis is variably current in Sanjad-Sakati syndrome, but total the radiographic look and mineral disturbance are much like Kenny-Caffey dysplasia. Sanjad-Sakati syndrome is characterized by microcephaly and developmental delay, and its inheritance is recessive. The authentic statement of Kenny, Linarelli, and Caffey described an affected mom and son; certainly, the few circumstances of dominant transmission have only concerned affected moms, not fathers, probably due to infertility in affected males. The syndrome described by Sanjad and Sakati as "Kenny-Caffey" 798 Intrauterine hypomobilization: Narrow shafts of the tubular bones are nonspecific sequelae of extended immobilization, trigger by both neutromuscular disease or restricted interuterine house. Marfan syndrome, homocystinuria, additionally present with skinny tubular bones but sufferers are tall. Majewski F, Rosendahl W, Ranke M, Nolte K (1981) the Kenny syndrome-a rare sort of growth deficiency with tubular stenosis, transient hypoparathyroidism and anomalies of refraction. Craniofacial abnormalities embrace prominent brow, spherical face, deep-set eyes, and micrognathia. The diaphyses of the tubular bones have narrow medullary canals encased in comparatively thick cortical partitions. The overall look of the tubular bones is that of slender bones with medullary stenosis and regular or increased cortical thickness. As with the lengthy bones of the arms, there are narrow medullary canals in femurs which are also slender. Craniofacial abnormalities with temporal bulge, blepharophimosis; small nose, short philtrum, small mouth, micrognathia. Prenatal sonographic manifestations include brief limbs, bowed radius, and deformed skull. Cloverleaf or acrocephalic configuration of the skull; deficient calvarial mineralization. Intrauterine hypomobility ends in thin tubular bones which, nevertheless, lack the abrupt metaphyseal flare. Osteogenesis imperfecta: the tubular bones are osteopenic with a number of fractures and bowing deformities. Hallermann-Streiff syndrome: this disorder resembles osteocraniostenosis, and the 2 disorders have been thought to be causally associated. Kozlowski k, Kan a (1988) Intrauterine dwarfism peculiar facies and thin bones with a number of fractures-a new syndrome. The facial options are disfigured by extreme hydrops, but a small nose, small mouth, and micrognathia can be discerned. The shafts of the long bones are very thin (gracile) and dense, with out cortical demarcation.
The smaller pair skin care yoga cleocin 150 mg buy low price, termed the l ss r wings acne 7 day detox generic cleocin 150 mg online, are triangular and are practically horizontal acne treatment for sensitive skin order cleocin 150 mg on line, ending medially in the two ant ri r clin i pr c ss s skin care zinc cheap cleocin 150 mg amex. They project laterally rom the superoanterior portion o the body and extend to concerning the middle o every orbit. The gr at r wings extend laterally rom the edges o the physique and orm a portion o the oor o the skull and a portion o the perimeters o the skull. The shape o the sphenoid has been in contrast with a bat with its wings and legs extended as in ight. Arising rom the posterior facet o the l ss r wings are two bony projections termed ant ri r clin i pr c ss s. Between the anterior physique and the lesser wings on all sides are groovelike canals by way of which the optic nerve and certain arteries cross into the orbital cavity. These canals begin in the center as the chiasm atic (ki-az-mat-ik) or ptic gr v, which leads on each side to an ptic canal, which ends on the ptic f ram n, or the opening into the orbit. The optic oramina could be demonstrated radiographically with the parieto-orbital indirect projection (Rhese method) described later in this chapter. Slightly lateral and posterior to the optic oramina on each side are irregularly shaped openings, that are seen greatest on this indirect view, known as sup ri r rbital ssur s. These openings provide additional communication with the orbits or quite a few cranial nerves and blood vessels. Projecting downward rom the in erior sur ace o the physique are our processes that correspond to the legs o the imaginary bat. The extra lateral, at extensions are called the lat ral pt ryg i (ter-i-goyd) pr c ss s, which typically are called plates. Directly medial to these are two m ial pt ryg i pr c ss s or plates, which end in eriorly in small hooklike processes, known as the pt ryg i ham uli. The pterygoid processes or plates orm half o the lateral walls o the nasal cavities. De ormity o the sella turcica is o ten the only clue that a lesion exists intracranially as seen radiographically. The s lla turcica and the rsum s lla are additionally demonstrated finest on a lateral projection o the skull. The small higher horizontal portion o the bone, termed the cribrif rm plat, accommodates many small openings or oramina through which segmental branches o the ol actory nerves (or the nerves o smell) cross. Projecting downward in the midline is the p rp nicular plat, which helps to orm the bony nasal septum. The two lat ral labyrinths (masses) are suspended rom the undersur ace o the cribri orm plate on each side o the perpendicular plate. The lateral masses comprise the ethmoid air cells or sinuses and assist to orm the medial partitions o the orbits and the lateral partitions o the nasal cavity. Extending medially and downward rom the medial wall o every labyrinth are skinny, scroll-shaped projections o bone. The smaller crista galli and cribrif rm plat project superiorly, and the larger p rp n icular plat extends in eriorly. Shown once more is one o the 2 lengthy, slender pt ryg i pr c ss s or plates extending down and orward and ending with the small pointed course of called the pt ryg i ham ulus. The squam sal (skwa-mo-sal) sutur s are ormed by the in erior junctions o the two parietal bones with their respective temporal bones. Each finish o the sagittal suture is identif ed as some extent or area with a specif c name as labeled. The anterior finish o the sagittal suture is termed the br gm a (breg-mah), and the posterior finish is called the lam b a (lam-dah). The right and le t pt ri ns (ter-reons) are points at the junction o the rontal, parietals, temporals, and the higher wings o the sphenoid. These six recognizable bony points are used in surgery or other instances during which specif c re erence factors or cranial measurements are needed. Ossif cation o the person cranial bones is incomplete at birth, and the sutures are membrane-covered spaces that f ll in quickly a ter start. However, certain areas the place sutures be a part of are slower in their ossif cation, and these are referred to as f ntan ls (fon-tah-nels). Two smaller lateral ontanels that close quickly a ter start are the sph n i (pterion in an adult) and m ast i (asterion in an adult) f ntan ls, which are located on the sphenoid and mastoid angles o the parietal bones on all sides o the top. These isolated bones most o ten are ound within the lambdoidal suture however occasionally also are ound in the area o the ontanels, especially the posterior ontanel. In the adult skull, these are utterly ossif ed and are seen only by the sutural strains around their borders. A beneficial technique o evaluation and rein orcement is to cowl the solutions and f rst try to identi y every o the labeled parts rom reminiscence. Specif c anatomic elements may be more di f cult to recognize on radiographs compared with drawings, however understanding places and relationships to surrounding structures and bones ought to aid in identi ying these components. The organs o hearing and equilibrium are the primary buildings ound throughout the petrous portion o the temporal bones. The eardrum is located at an indirect angle, orming a despair, or nicely, at the decrease medial finish o the meatus. The tympanic membrane is taken into account half o the center ear even though it serves as a partition between the external and middle ears. The tympanic cavity communicates anteriorly with the nasopharynx by means o the ustachian tub, or au it ry tub. Eu sta ch ia n be Tu the ustachian tub is the passageway between the middle ear and the nasopharynx. A drawback related to this direct communication between the middle ear and the nasopharynx is that illness organisms have a direct passageway rom the throat to the middle ear. There ore, ear in ections o ten accompany sore throats, particularly in children whose immune system continues to be developing. This leads to a special transorbital view, which may be taken to demonstrate the int rnal ac ustic m atus. The lateral parts o the petrous ridges are at roughly the extent o the TeA (top o ear attachment). The a itus is the opening between the epitympanic recess and the mastoid portion o the temporal bone. The aditus connects directly to a big chamber inside the mastoid portion termed the antrum. This communication permits in ection in the middle ear, which can have originated in the throat, to move into the mastoid area. In ection throughout the mastoid space is separated rom brain tissue solely by thin bone. Be ore e ective antibiotics had been generally used, this was o ten a pathway or nc phalitis, a severe in ection o the mind. The skinny plate o bone that orms the roo o the antrum, aditus, and attic area o the tympanic cavity known as the t gm n tym pani. The three auditory ossicles are located partly within the attic, or epitympanic recess, and partly within the tympanic cavity correct. These delicate bones bridge the middle ear cavity to transmit sound vibrations rom the tympanic membrane to the oval window o the interior ear. Vibrations are f rst picked up by the m all us, that means "hammer," which is hooked up directly to the inside sur ace o the tympanic membrane. The incus receives its name rom a supposed resemblance to an anvil, nevertheless it really seems extra like a premolar tooth with a physique and two roots. The incus connects to the stirrupshaped stap s, which is the smallest o the three auditory ossicles. The ootplate o the stapes is attached to one other membrane called the val win w, which leads into the inner ear. As could be seen rom the ront, probably the most lateral o the three bones is the m all us, whereas the most medial o the three bones is the stap s. The malleus, with its attachment to the eardrum, is situated barely anterior to the other two bones. The resemblance o the incus to a premolar tooth with a physique and two roots is properly visualized within the lateral drawing. The longer root o the incus connects to the stapes, which connects to the oval window o the cochlea, resulting within the sense o listening to.
A traumatic fracture of the tunica albuginea is related to a snapping sound and pain of sudden onset skin care in 30s cleocin 150 mg quality. The penile carcinoma (stars) is slightly hypointense to the corporal bodies in the T2 W pictures (a acne cream 150 mg cleocin discount overnight delivery, b) acne extractions cleocin 150 mg purchase with mastercard. The carcinoma reveals less enhancement than the corporal our bodies after administration of contrast medium (c skin care jerawat buy cleocin 150 mg mastercard, d). The inguinal lymph nodes exhibit regular measurement and form on each side (open arrow), indicating that inguinal lymph node metastasis has not occurred. Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis often presents initially as a painless, focal epithelial thickening on the glans penis; there could additionally be an associated ulcer. The prognosis is good within the absence of corporal invasion or lymph node metastasis. The scientific differential prognosis includes soft or hard chancre and condylomata acuminata. Penile carcinoma is a really rare tumor, accounting for lower than 1% of all male cancers. Both penile and urethral carcinoma are hypointense to the corporal our bodies on T1 W and T2 W pictures. Most penile carcinomas are squamous cell carcinomas and are manifested on the glans penis. Squamous cell carcinoma of the penis is hypointense to the corporal bodies on T1 W and T2 W images. Cephalad to the bottom of the prostate and lateral to the vas deferens are the paired, elongated seminal vesicles, which resemble clusters of grapes. The excretory duct of every seminal vesicle joins with the ipsilateral vas deferens to type the ejaculatory duct, which opens into the urethra on the seminal colliculus. The nerves and vessels that penetrate the prostate are sites of predilection for the extracapsular extension of prostate cancer. The peripheral zone accounts for approximately 70% of the prostate quantity in young males, the central zone 25%, and the transitional zone 5%. With getting older, the prostate not only enlarges but additionally reveals a change in relative zonal volumes because the transitional zone and, to a lesser degree, the periurethral zone turn out to be predominant as a end result of benign prostatic hyperplasia (p. Each zone consists of stromal and epithelial parts, the latter being greater within the peripheral zone than within the central gland. Approximately 70% of prostatic adenocarcinomas come up in the peripheral zone, 25% within the transitional zone, and 10% within the central zone. The peripheral zone usually shows high signal intensities because of its large glandular part while the central gland show decrease, heterogeneous signal intensities as a outcome of a larger stromal element. The grapelike seminal vesicles are situated cephalad to the base of the prostate and seem hyperintense on T2 W photographs. The urethra seems as a triangular midline structure within the posterior third of the central gland. The seminal colliculus with the opening of the ejaculatory duct is best displayed on coronal pictures. The neurovascular bundles are situated along the posterolateral aspect of the left and right sides of the gland and appear hyperintense with tubular structures on T2 W pictures. Posterior to the prostate is the rectum, which is distended when an endorectal coil is used. Lateral to the prostate are the muscular constructions of levator ani and obturator internus. Prostatitis syndrome is subdivided into a number of clinical forms: Acute bacterial prostatitis. Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis by which inflammatory cells can be detected by prostatic biopsy or in fluid expressed from the gland. Less frequent are acute and continual bacterial prostatitis, which are normally attributable to gram-negative organisms. Complications of acute bacterial prostatitis include prostatic abscess, cystitis, ascending pyelonephritis, and epididymitis. Both images show the hyperintense peripheral zone (stars), the enlarged, heterogeneous transitional zone (circles), and the hyperintense seminal vesicles with their grapelike configuration (diamonds). The vas deferens (plus signs) and urethra (arrow) are displayed in the coronal image (a), and the anterior fibromuscular tissue (open arrow) and bladder (triangle) are seen in the sagittal image (b). An space of chronic prostatitis (arrows) is seen in the peripheral zone on the right aspect. The surrounding inflammatory wall exhibits increased enhancement after administration of contrast medium. Acute bacterial prostatitis and prostatic abscess are usually related to fever, painful urination, and perineal and again pain. Be conscious that imaging research are restricted in their capacity to differentiate prostatitis from different situations. Low-grade cancers in particular might have imaging options which are indistinguishable from persistent prostatitis. High-grade prostate cancers tend to show more homogeneous hypointensity on T2 W pictures than chronic prostatitis. Both situations are hypointense on T2 W photographs, however chronic prostatitis is more more likely to appear wedge-shaped with a streaky signal pattern. Acute prostatitis has a typical scientific presentation that includes fever, painful urination, and perineal and back pain; typically, subsequently, imaging is unnecessary within the diagnosis of prostatitis. Nevertheless, the nonspecific options of chronic prostatitis should all the time be thought-about within the differential diagnosis of prostate most cancers. It is caused by a progressive hyperplasia of the stromal and epithelial components of the transitional zone. It consists of a quantity of nodules with a heterogeneous look due to the combined presence of stroma-rich (hypointense) and gland-rich (hyperintense) areas. The enlarged transitional zone is hypointense on T1 W pictures, just like the peripheral zone. Increasing enlargement of the prostate results in obstructive signs corresponding to incomplete bladder emptying and storage signs similar to pollakiuria and nocturia. The urinary obstruction leads to rising trabeculation and diverticulum formation within the bladder. A critical complication is acute urinary retention, which may be drug-induced or could end result from native or common anesthesia. Inexperienced practitioners in particular could misinterpret the enlarged transitional zone as prostate most cancers. Stroma-rich hypointense areas in the enlarged transitional zone are difficult to distinguish from prostate cancer. A prostatic utricle cyst (a, c, open arrows) is famous by the way at a typical website. It is attributable to progressive hyperplasia of the stromal and epithelial components of the transitional zone with increasing age, which finally ends up in voiding and storage symptoms. It consists of multiple nodules, which generally appear heterogeneous with a hypointense rim. Prostate most cancers is the most common malignant tumor in males and the second main cause of cancer deaths. Approximately 70% of prostatic adenocarcinomas come up in the peripheral zone and approximately 30% within the central gland. The malignancy of adenocarcinoma is usually graded with the Gleason rating, which describes the deviation from regular glandular architecture. Since the tumors are often heterogeneous, a two-part Gleason score is used, the first quantity denoting the tumor grade that contains most of the tumor: Low-grade prostate most cancers: Gleason score 3 + 3. Initial lymphogenous metastasis happens to the lymph nodes of the obturator fossa and along the iliac vessels. Cholinecontaining molecules and citrate are essential within the diagnosis of prostatic illness. Choline ranges are sometimes elevated in prostate cancer, while citrate ranges are decreased. This contrasts with the low choline and excessive citrate levels present in regular prostatic tissue.