
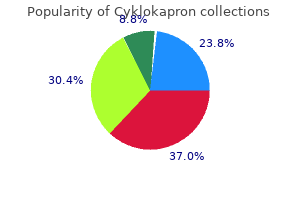
Cyklokapron
| Contato
Página Inicial

"500 mg cyklokapron discount fast delivery, medicine quizlet".
U. Chenor, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine
The carbohydrate moieties connected to the outer surface of the cell have a quantity of essential capabilities: 1 acute treatment order cyklokapron 500 mg without prescription. Many of them have a adverse electrical cost symptoms jock itch generic 500 mg cyklokapron with mastercard, which supplies most cells an total adverse surface cost that repels other negatively charged objects treatment sciatica order 500 mg cyklokapron. The glycocalyx of some cells attaches to the glycocalyx of different cells medicine for high blood pressure 500 mg cyklokapron generic with mastercard, thus attaching cells to one another. Many of the carbohydrates act as receptor sub stances for binding hormones, similar to insulin; when 14 certain, this mixture activates attached internal proteins that, in flip, activate a cascade of intracellular enzymes. Some carbohydrate moieties enter into immune reactions, as discussed in Chapter 35. The jelly-like fluid portion of the cytoplasm by which the particles are dispersed is identified as cytosol and contains mainly dissolved proteins, electrolytes, and glucose. Dispersed within the cytoplasm are impartial fat globules, glycogen granules, ribosomes, secretory vesicles, and 5 particularly necessary organelles: the endoplasmic reticu lum, the Golgi equipment, mitochondria, lysosomes, and peroxisomes. Also, their partitions are constructed of lipid bilayer membranes that include giant amounts of proteins, much like the cell membrane. The total floor area of this structure in some cells-the liver cells, for instance-can be as much as 30 to 40 occasions the cell membrane space. Electron micrographs show that the space inside the endoplasmic reticulum is linked with the house between the 2 membrane surfaces of the nuclear membrane. Substances shaped in some elements of the cell enter the house of the endoplasmic reticulum and are then directed to different elements of the cell. Also, the huge floor space of this reticulum and the a quantity of enzyme methods attached to its membranes present machinery for a major share of the metabolic features of the cell. The agranular reticulum functions for the synthesis of lipid substances and for different processes of the cells promoted by intrareticular enzymes. The Golgi equipment is usually composed of 4 or extra stacked layers of thin, flat, enclosed vesicles lying close to one facet of the nucleus. The transported substances are then processed in the Golgi equipment to type lysosomes, secretory vesicles, and different cytoplasmic parts that are mentioned later on this chapter. Attached to the outer surfaces of many components of the endoplasmic reticulum are large numbers of minute granular particles called ribosomes. Where these particles are current, the reticulum is called the granular endoplasmic reticulum. The lysosomes present an intracellular digestive system that enables the cell to digest (1) broken mobile structures, (2) food particles that have been ingested by the cell, and (3) undesirable matter corresponding to micro organism. It is surrounded by a typical lipid 15 plasmic reticulum has no attached ribosomes. This part Unit I Introduction to Physiology: the Cell and General Physiology bilayer membrane and is filled with giant numbers of small granules 5 to 8 nanometers in diameter, that are protein aggregates of as many as forty different hydrolase (digestive) enzymes. A hydrolytic enzyme is capable of splitting an natural compound into two or extra components by combining hydrogen from a water molecule with one a half of the compound and combining the hydroxyl portion of the water molecule with the opposite a part of the compound. For occasion, protein is hydrolyzed to form amino acids, glycogen is hydrolyzed to kind glucose, and lipids are hydrolyzed to form fatty acids and glycerol. Ordinarily, the membrane surrounding the lysosome prevents the enclosed hydrolytic enzymes from coming in touch with other substances within the cell and therefore prevents their digestive actions. However, some circumstances of the cell break the membranes of a few of the lysosomes, allowing launch of the digestive enzymes. These enzymes then cut up the natural substances with which they come in touch into small, highly diffusible substances corresponding to amino acids and glucose. Several of the oxidases are capable of combining oxygen with hydrogen ions derived from completely different intracellular chemical compounds to kind hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Hydrogen peroxide is a extremely oxidizing substance and is utilized in association with catalase, another oxidase enzyme current in giant quantities in peroxisomes, to oxidize many substances that may otherwise be poisonous to the cell. For instance, about half the alcohol a person drinks is detoxified into acetaldehyde by the peroxisomes of the liver cells on this manner. Without them, cells could be unable to extract sufficient vitality from the nutrients, and basically all cellular features would stop. The cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes), for example, use massive quantities of power and have way more mitochondria than do fat cells (adipocytes), that are a lot less active and use less vitality. Further, the mitochondria are concentrated in those portions of the cell that are liable for the main share of its power metabolism. Some mitochondria are only some hundred nanometers in diameter and are globular in form, whereas others are elongated and are as giant as 1 micrometer in diameter and 7 micrometers lengthy; still others are branching and filamentous. Many infoldings of the inside membrane form Secretory Vesicles One of the essential capabilities of many cells is secretion of particular chemical substances. Almost all such secretory substances are shaped by the endoplasmic reticulum� Golgi equipment system and are then launched from the Golgi equipment into the cytoplasm in the type of storage vesicles referred to as secretory vesicles or secretory granules. The proenzymes are secreted later via the outer cell membrane into the pancreatic duct and thence into the duodenum, where they turn out to be activated and carry out digestive functions on the meals in the intestinal tract. In addition, the inside cavity of the mitochondrion is crammed with a matrix that contains large quantities of dissolved enzymes which might be needed for extracting power from nutrients. These enzymes operate in affiliation with the oxidative enzymes on the cristae to trigger oxidation of the nutrients, thereby forming carbon dioxide and water and on the similar time releasing energy. Cells that are confronted with elevated energy demands-which occurs, for instance, in skeletal muscle tissue subjected to persistent exercise training-may enhance the density of mitochondria to supply the additional energy required. The cytoskeleton of the cell not solely determines cell form but additionally participates in cell division, permits cells to transfer, and offers a track-like system that directs the motion of organelles throughout the cells. Nucleus the nucleus, which is the management center of the cell, sends messages to the cell to develop and mature, to replicate, or to die. During mitosis, the chromatin materials organizes in the form of highly structured chromosomes, which may then be simply recognized utilizing the sunshine microscope, as illustrated in Chapter three. The nuclear membrane, also called the nuclear envelope, is actually two separate bilayer membranes, one inside the other. The outer membrane is Cell Cytoskeleton-Filament and Tubular Structures the cell cytoskeleton is a network of fibrillar proteins organized into filaments or tubules. These originate as precursor protein molecules synthesized by ribosomes within the cytoplasm. As an example, massive numbers of actin filaments incessantly happen in the outer zone of the cytoplasm, referred to as the ectoplasm, to form an elastic help for the cell membrane. A special sort of stiff filament composed of polymerized tubulin molecules is used in all cells to construct robust tubular buildings, the microtubules. Another instance of microtubules is the tubular skeletal construction within the middle of every cilium that radiates upward from the cell cytoplasm to the tip of the cilium. Also, each the centrioles and the mitotic spindle of the mitosing cell are composed of stiff microtubules. Large complexes of protein molecules are connected on the edges of the pores in order that the central space of every pore is simply about 9 nanometers in diameter. Even this size is massive enough to allow molecules up to 44,000 molecular weight to move through with reasonable ease. The nuclei of most cells comprise one or more extremely staining buildings called nucleoli. The nucleolus turns into significantly enlarged when the cell is actively synthesizing proteins. Formation of the nucleoli (and of the ribosomes in the cytoplasm outside the nucleus) begins within the nucleus. Correspondingly, the capabilities and anatomical group of the cell are additionally much more advanced than those of the virus. The important life-giving constituent of the small virus is a nucleic acid embedded in a coat of protein. Thus, the virus propagates its lineage from technology to technology and is subsequently a living structure in the identical way that the cell and the human being live constructions. As life evolved, other chemical compounds apart from nucleic acid and easy proteins grew to become integral parts of the organism, and specialized capabilities began to develop in several components of the virus. A membrane formed across the virus, and inside the membrane, a fluid matrix appeared.
Its anterior facet is rough medicine runny nose buy cyklokapron 500 mg overnight delivery, round and steady with the tibial inferior border treatment walking pneumonia cyklokapron 500 mg discount free shipping. The medial floor has a triangular articular aspect medicine for sore throat cyklokapron 500 mg discount otc, vertically convex symptoms 24 buy cyklokapron 500 mg low price, its apex distal, which articulates with the lateral talar floor. The posterior tibiofibular ligament and, more distally, the posterior talofibular ligament, are connected within the fossa. The ant erior talofibular ligament is connected to the anterior floor of the lateral malleolus; the calcaneofibular ligament is connected to the notch anterior to its apex. The tendons of fibularis brevis and longus groove its posterior aspect; the latter is superficial and lined by the superior fibular retinaculum. Muscle attachments Head the top of the fibula is irregular in form and tasks anteriorly, posteriorly and laterally. A spherical side on its proximomedial aspect articulates with a corresponding aspect on the inferolateral floor of the lateral tibial condyle. It faces proximally and anteromedially, and has an inclination which will vary among people from nearly horizontal to an angle of up to 45�. A blunt apex initiatives proximally from the posterolateral facet of the pinnacle and is often palpable roughly 2 cm distal to the knee joint. The fibular collateral ligament is attached in entrance of the apex, embraced by the primary attachment of biceps femoris. The common fibular nerve crosses posterolateral to the neck and could be rolled towards the underlying bone at this location. The shaft has three borders and surfaces, every associated with a particu lar group of muscles. The poste rior border, continuous with the medial margin of the posterior groove on the lateral malleolus, is usually distinct distally however often rounded in its proximal half. Over the proximal twothirds of the fibular shaft the two borders strategy each other, with the floor between the two being narrowed to 1 mm or much less. The lateral floor, between the anterior and posterior borders and associated with the fibular muscular tissues, faces laterally in its proximal three quarters. The distal quarter spirals posterolaterally to turn out to be continu ous with the posterior groove of the lateral malleolus. The anteromedial (sometimes merely termed anterior, or medial) floor, between the anterior and interosseous borders, normally faces anteromedially but usually instantly anteriorly. Though wide distally, it narrows in its proximal half and will become a mere ridge. The posterior surface, between the interosseous and pos terior borders, is the biggest and is related to the flexor muscular tissues. The remaining surface faces posteriorly in its proximal half; its distal half curves on to the medial facet. Distally, this space occupies the fibular notch of the tibia, which is roughened by the attachment of the principal interosseous tibiofibular ligament. The triangular space proximal to the lateral floor of the lateral malleolus is subcutaneous; muscle tissue cowl the the rest of the shaft. The anterior border is split distally into two ridges that enclose a triangular subcutaneous floor. The lateral end of the superior extensor retinaculum is attached distally on the anterior border of the triangular area and the lateral finish of the superior fibular retinaculum is attached distally on the posterior margin of the triangular space. The interosseous border ends on the proximal restrict of the rough space for the Shaft the main attachments of biceps femoris embrace the fibular collateral ligament in front of the apex of the fibular head. Extensor digitorum longus is attached to the head anteriorly, fibularis longus anterolat erally, and soleus posteriorly. Extensor digitorum longus, extensor hal lucis longus and fibularis tertius are connected to the anteromedial (extensor) floor. Fibularis longus is attached to the entire width of the lateral (fibular) floor in its proximal third, but in its middle third solely to its posterior part, behind fibularis brevis. Muscle attachments to the posterior surface, which is divided longi tudinally by the medial crest, are advanced. Tibialis posterior is attached throughout most (the proximal threequarters) of this area; an intramuscular tendon may ridge the bone obliquely. Flexor hallucis longus is hooked up distal to soleus on the posterior surface and almost reaches the distal end of the shaft. Vascular supply A little proximal to the midpoint of the posterior floor (14�19 cm from the apex), a distally directed nutrient foramen on the fibular shaft receives a branch of the fibular artery. An appreciation of the detailed anatomy of the fibular artery in relation to the fibula is prime to the raising of osteofasciocutaneous free flaps. Free vascularized diaphys ial grafts may also be taken on a fibular arterial pedicle. The proximal and distal ends receive metaphysial vessels from the arterial anastomo ses on the knee and ankle, respectively (Taylor and Razaboni 1994). Innervation the proximal and distal ends of the bone are provided by branches of nerves that innervate the knee and superior tibiofibular joint, and the ankle and inferior tibiofibular joints, respectively. The periosteum of the shaft is supplied by branches from the nerves that innervate the muscle tissue hooked up to the fibula. The process begins in the shaft at about the eighth week in utero; in the distal finish within the first year; and in the proximal end at about the third yr in females and the fourth year in males. A longitudinal radiographic examine of kids has shown that the proximal development plate of the fibula contributes extra to development than the proximal development plate of the tibia, their development contributions being 61% and 57%, respectively (Pritchett and Bortel 1997). Fibular dimelia is characterised by duplication of the fibula, tibial aplasia and partial duplication of the foot with mirror polydactyly, and could also be associated with ulnar dimelia and calcaneal duplication. It has been postulated that a reestablishment of limb polarity during embryogen esis might account for this situation (Bayram et al 1996, Ganey et al 2000). The larger bulk of the muscles within the calf is commensurate with the powerful propulsive position of the plantar flexors in walking and working. Attachments to the talus, first metatarsal head, base of the proximal phalanx of the hallux, and extensor retinaculum have been recorded. When acting from under, they pull the physique forwards on the fixed foot during walking. Two of the muscles, extensor digitorum longus and extensor hallucis longus, additionally extend the toes, and two muscles, tibialis anterior and fibularis tertius, have the extra actions of inversion and eversion, respectively. Relations Tibialis anterior overlaps the anterior tibial vessels and deep fibular nerve within the higher a part of the leg. Vascular provide the primary physique of tibialis anterior is supplied by a series of medial and anterior branches of the anterior tibial artery; the branches might happen in two columns. The tendon is provided by the anterior medial malleolar artery and community, dorsalis pedis artery, medial tarsal arteries, and by the medial malleolar and calcaneal branches of the posterior tibial artery. It arises from the lateral condyle and proximal onehalf to twothirds of the lateral floor of the tibial shaft; the adjoining anterior surface of the interosseous membrane; the deep surface of the deep fascia; and the intermuscular septum between itself and extensor digitorum longus. The muscle descends vertically and ends in a tendon on its anterior surface within the decrease third of the leg. The tendon passes through the medial compartments of the supe rior and inferior retinacula, inclines medially, and is inserted on to the medial and inferior surfaces of the medial cuneiform and the adjoining part of the bottom of the first metatarsal. Tibialis anterior Innervation Tibialis anterior is innervated by the deep fibular nerve, L4 and L5. Its tendon can be seen through the skin lateral to the anterior border of the tibia and can be traced downwards and medially across the front of the ankle to the medial side of the foot. Tibialis anterior elevates the primary meta tarsal base and medial cuneiform, and rotates their dorsal elements laterally. The muscle is normally quiescent while standing, for the explanation that weight of the body acts by way of vertical strains that move anterior to the ankle joints. Superior medial genicular artery Superior lateral genicular artery Testing Tibialis anterior could be seen to act when the foot is dorsiflexed in opposition to resistance. It arises from the center half of the medial surface of the fibula, medial to extensor digitorum longus, and from the adjoining anterior floor of the interosseous membrane. Its fibres run distally and end in a tendon that varieties on the anterior border of the muscle.
They can be positioned both upstream or downstream of the gene that they regulate 5 medications related to the lymphatic system 500 mg cyklokapron order with visa. It is estimated that there are a hundred and ten in treatment 2 buy cyklokapron 500 mg with amex,000 gene enhancer sequences within the human genome medicine 1975 proven cyklokapron 500 mg. In the group of the chromosome symptoms 10 days post ovulation cheap 500 mg cyklokapron overnight delivery, you will want to separate lively genes which are being transcribed from genes which are repressed. This separation may be difficult as a result of a number of genes could additionally be positioned shut together on the chromosome. These insulators are gene sequences that present a barrier so that a particular gene is olated in opposition to transcriptional influences from surrounding genes. A promoter is incessantly controlled by transcription elements situated elsewhere within the genome. That is, the regulatory gene causes the formation of a regulatory protein that in flip acts either as an activator or a repressor of transcription. Occasionally, many different promoters are managed at the identical time by the same regulatory protein. In some instances, the identical regulatory protein functions as an activator for one promoter and as a repressor for another promoter. Even then, particular transcriptor factors control the actual rate of transcription by the promoter within the chromosome. The gene management techniques are particularly essential for controlling intracellular concentrations of amino acids, amino acid derivatives, and intermediate substrates and products of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism. Thus, enzyme regulation represents a second class of mechanisms by which cellular biochemical capabilities can be controlled. Some chemical substances shaped or inhibited, and likewise, the enzyme methods could be both activated or inhibited. However, on occasion, substances from without the cell (especially a few of the hormones mentioned all through this text) additionally control the intracellular biochemical reactions by activating or inhibiting a quantity of of the intracellular control systems. Almost always the synthesized product acts on the primary enzyme in a sequence, somewhat than on the following enzymes, normally binding immediately with the enzyme and inflicting an allosteric conformational change that inactivates it. The genes and their regulatory mechanisms determine the expansion characteristics of the cells and likewise when or whether or not these cells will divide to form new cells. In this manner, the all-important genetic system controls every stage in the development of the human being, from the singlecell fertilized ovum to the entire functioning body. Enzymes which are normally inactive Life Cycle of the Cell the life cycle of a cell is the period from cell copy to the following cell reproduction. It is terminated by a collection of distinct physical occasions referred to as mitosis that trigger division of the cell into two new daughter cells. The precise stage of mitosis, nevertheless, lasts for under about half-hour, and thus more than ninety five percent of the life cycle of even rapidly reproducing cells is represented by the interval between mitosis, called interphase. Except in special situations of rapid mobile reproduction, inhibitory elements nearly all the time sluggish or cease the uninhibited life cycle of the cell. Therefore, different cells of the physique actually have life cycle periods that change from as little as 10 hours for highly stimulated bone marrow cells to a complete lifetime of the human physique for many nerve cells. Another interesting instance of both enzyme inhibition and enzyme activation occurs in the formation of the purines and pyrimidines. When purines are shaped, they inhibit the enzymes which are required for formation of further purines. Conversely, the pyrimidines inhibit their own enzymes however activate the purine enzymes. This uncoiling is achieved by enzymes that periodically cut every helix along its entire size, rotate each segment sufficient to cause separation, and then resplice the helix. Even throughout this period, preliminary modifications that may lead to the mitotic process are starting to take place. Because of restore and proofreading, mistakes are not often made within the transcription process. The mutation causes formation of some irregular protein in the cell rather than a needed protein, usually leading to abnormal mobile perform and generally even cell dying. Yet given that 30,000 or extra genes exist in the human genome and that the period from one human era to another is about 30 years, one would expect as many as 10 or many extra mutations within the passage of the genome from mother or father to youngster. As an additional protection, however, each human genome is represented by two separate sets of chromosomes with virtually similar genes. Therefore, one practical gene of every pair is almost always obtainable to the child regardless of mutations. Several nonhistone proteins are additionally major components of chromosomes, functioning both as chromosomal structural proteins and, in connection with the genetic regulatory machinery, as activators, inhibitors, and enzymes. The two newly formed chromosomes stay connected to one another (until time for mitosis) at a degree known as the centromere located near their center. The complicated of microtubules extending between the 2 new centriole pairs is known as the spindle, and the whole set of microtubules plus the two pairs of centrioles is identified as the mitotic apparatus. While the spindle is forming, the chromosomes of the nucleus (which in interphase encompass loosely coiled strands) turn into condensed into well-defined chromosomes. At the identical time, a quantity of microtubules from the aster connect to the chromatids on the centromeres, the place the paired chromatids are nonetheless sure to each other; the tubules then pull one chromatid of every pair toward one cellular pole and its partner towards the other pole. This pushing is believed to occur as a end result of the microtubular spines from the 2 asters, the place they interdigitate with one another to kind the mitotic spindle, truly push each other away. Minute contractile protein molecules known as "molecular motors, that are perhaps " composed of the muscle protein actin, lengthen between the respective spines and, using a stepping action as in muscle, actively slide the spines in a reverse course along one another. Simultaneously, the chromatids are pulled tightly by their hooked up microtubules to the very heart of the cell, lining as a lot as kind the equatorial plate of the mitotic spindle. All 46 pairs of chromatids are separated, forming two separate sets of 46 daughter chromosomes. One of these units is pulled towards one mitotic aster and the other is pulled toward the opposite aster as the two respective poles of the dividing cell are pushed still farther apart. Then the mitotic apparatus dissolutes, and a new nuclear membrane develops around every set of chromosomes. This membrane is formed from parts of the endoplasmic reticulum which are already present within the cytoplasm. This pinching is attributable to formation of a contractile ring of microfilaments composed of actin and probably myosin (the two contractile proteins of muscle) at the juncture of the newly creating cells that pinches them off from each other. Once each chromosome has been replicated to kind the 2 chromatids, in lots of cells, mitosis follows routinely within 1 or 2 hours. One of the primary events of mitosis takes place within the cytoplasm; it happens during the latter a part of interphase in or around the small structures known as centrioles. Each pair of centrioles, together with connected pericentriolar materials, is called a centrosome. Shortly earlier than mitosis is to take place, the 2 pairs of centrioles start to transfer aside from one another. This motion is attributable to polymerization of protein microtubules rising between the respective centriole pairs and truly pushing them apart. At the same time, different microtubules grow radially away from each of the centriole pairs, forming a spiny star, known as the aster, in every finish of the cell. Many other cells, however, similar to easy muscle cells, could not reproduce for many years. In sure tissues, an insufficiency of some forms of cells causes them to grow and reproduce rapidly till applicable numbers of these cells are again obtainable. For instance, in some younger animals, seven eighths of the liver may be removed surgically, and the cells of the remaining one eighth will grow and divide until the liver mass returns to almost normal. The same phenomenon happens for many glandular cells and most cells of the bone marrow, subcutaneous tissue, intestinal epithelium, and almost another tissue except extremely differentiated cells similar to nerve and muscle cells. The mechanisms that keep correct numbers of the different sorts of cells in the physique are nonetheless poorly understood. However, experiments have shown no less than 3 ways during which progress could be managed. First, growth often is controlled by progress elements that come from other parts of the physique.
However medicine syringe 500 mg cyklokapron purchase otc, blood circulate within the coronary heart treatment 1860 neurological cyklokapron 500 mg cheap on line, kidneys symptoms 2 weeks after conception cyklokapron 500 mg online buy cheap, gastrointestinal tract medications emt can administer 500 mg cyklokapron order with visa, and skeletal muscle also increases with weight achieve because of increased metabolic price and development of the organs and tissues in response to their elevated metabolic demands. As the hypertension is sustained for many months and years, total peripheral vascular resistance may be increased. Sympathetic nerve exercise, especially in the kidneys, is increased in obese sufferers. There is also evidence for reduced 240 sensitivity of the arterial baroreceptors in buffering increases in blood stress in obese topics. If imply arterial strain in the important hypertensive individual is 150 mm Hg, acute reduction of imply arterial strain to the conventional value of 100 mm Hg (but with out in any other case altering renal function apart from the decreased pressure) will trigger virtually complete anuria; the individual will then retain salt and water till the strain rises back to the elevated worth of 150 mm Hg. Eventually uncontrolled hypertension associated with obesity can result in severe vascular harm and full loss of kidney perform. The curves of this determine are called sodium-loading renal function curves as a result of the arterial strain in each instance is elevated very slowly, over many days and even weeks, by steadily rising the extent of sodium intake. The sodium-loading sort of curve may be determined by growing the level of sodium consumption to a model new level each few days, then ready for the renal output of sodium to come into stability with the consumption, and at the similar time recording the modifications in arterial strain. Analysis of arterial strain regulation in (1) saltinsensitive important hypertension and (2) salt-sensitive essential hypertension. Vasodilator medicine normally cause vasodilation in many different tissues of the physique, as well as in the kidneys. Different ones act in one of many following methods: (1) by inhibiting sympathetic nervous signals to the kidneys or by blocking the action of the sympathetic transmitter substance on the renal vasculature and renal tubules, (2) by instantly relaxing the smooth muscle of the renal vasculature, or (3) by blocking the motion of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system on the renal vasculature or renal tubules. Drugs that scale back reabsorption of salt and water by the renal tubules embrace, in particular, medicine that block lively transport of sodium via the tubular wall; this blockage in flip also prevents the reabsorption of water, as defined earlier within the chapter. These natriuretic or diuretic medication are discussed in larger element in Chapter 32. The purpose for the difference between salt-insensitive important hypertension and salt-sensitive hypertension is presumably associated to structural or practical differences in the kidneys of these two kinds of hypertensive sufferers. For example, salt-sensitive hypertension might happen with different sorts of chronic renal disease due to the gradual loss of the functional units of the kidneys (the nephrons) or due to normal getting older, as discussed in Chapter 32. Abnormal perform of the renin-angiotensin system can even trigger blood stress to become salt delicate, as discussed previously on this chapter. For instance, when an individual bleeds severely so that the pressure falls suddenly, two problems confront the stress control system. The first is survival; the arterial pressure must be rapidly returned to a high enough degree that the particular person can live by way of the acute episode. The second is to return the blood quantity and arterial pressure ultimately to their normal levels in order that the circulatory system can reestablish full normality, not merely back to the levels required for survival. In Chapter 18, we saw that the primary line of protection against acute changes in arterial pressure is the nervous control system. The rapidly appearing traces for treating hypertension recommend, as a first step, lifestyle modifications which are aimed toward increasing physical activity and weight reduction in most sufferers. Unfortunately, many sufferers are unable to shed weight, and pharmacological therapy with antihypertensive medication have to be initiated. They are (1) the baroreceptor suggestions mechanism, (2) the central nervous system ischemic mechanism, and (3) the chemoreceptor mechanism. After any acute fall in pressure, as may be caused by extreme hemorrhage, the nervous mechanisms mix to trigger (1) constriction of the veins and transfer of blood into the guts, (2) elevated coronary heart fee and contractility of the heart to provide greater pumping capability by the guts, and (3) constriction of most peripheral arterioles to impede flow of blood out of the arteries. All these results happen nearly immediately to raise the arterial stress back into a survival range. When the strain abruptly rises too high, as might happen in response to fast transfusion of extra blood, the same management mechanisms function in the reverse course, once more returning the pressure back towards normal. Several strain control mechanisms Renal�b isc he m ic sterone Aldo quantity lood pr e controssure l semi-acute means for increasing the arterial stress when this is needed. The stress-relaxation mechanism is demonstrated by the next instance: When the strain within the blood vessels turns into too high, they become stretched and keep on stretching increasingly more for minutes or hours; as a result, the strain within the vessels falls toward regular. This continuing stretch of the vessels, referred to as stress-relaxation, can serve as an intermediate-term strain "buffer. Conversely, when the capillary pressure rises too excessive, fluid is lost out of the circulation into the tissues, thus reducing the blood quantity, in addition to just about all the pressures throughout the circulation. These three intermediate mechanisms turn out to be mostly activated inside half-hour to several hours. During this time, the nervous mechanisms often turn into much less and fewer effective, which explains the importance of those non-nervous, intermediate time strain management measures. The goal of this chapter has been to clarify Maximum feedback achieve at optimum strain exhibit vital responses only after a few minutes following acute arterial stress change. We have already described at length the function of the renin-angiotensin vasoconstrictor system to provide a the role of the kidneys in long-term management of arterial stress. Yet, it eventually develops a suggestions achieve for control of arterial pressure almost equal to infinity. This implies that this mechanism can finally return the arterial pressure nearly all the greatest way back, not merely partway back, to the stress level that provides regular output of salt and water by the kidneys. By now, the reader ought to be conversant in this idea, which has been the major level of this chapter. Many components can have an effect on the pressure-regulating degree of the renal�body fluid mechanism. A decrease in arterial pressure leads inside minutes to an increase in aldosterone secretion, and over the subsequent hour or days, this effect plays an necessary role in modifying the strain control traits of the renal�body fluid mechanism. Especially important is interaction of the reninangiotensin system with the aldosterone and renal fluid mechanisms. We have seen in this chapter that salt consumption can lower to as little as one-tenth regular or can increase to 10 to 15 instances regular and but the regulated stage of the mean arterial pressure will change just a few mm Hg if the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system is totally operative. Thus, arterial strain control begins with the lifesaving measures of the nervous stress controls, then continues with the sustaining traits of the intermediate stress controls, and, finally, is stabilized on the long-term pressure level by the renal�body fluid mechanism. This long-term mechanism, in turn, has multiple interactions with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, the nervous system, and a number of other different factors that present special blood pressure control capabilities for special functions. Seventh Report of the Joint National Committeeonprevention,detection,analysis,andtreatmentof highbloodpressure. Venous return is the quantity of blood flowing from the veins into the right atrium each minute. The venous return and the cardiac output must equal each other aside from a couple of heartbeats at a time when blood is quickly saved in or faraway from the center and lungs. The cardiac index rises rapidly to a degree higher than four L/min/m2 at age 10 years and declines to about 2. We clarify later within the chapter that the cardiac output is regulated all through life virtually directly in proportion to overall metabolic activity. Therefore, the declining cardiac index is indicative of declining activity or declining muscle mass with age. When one considers the issue of age as well- as a end result of with increasing age, physique exercise and mass of some tissues. Cardiac Index Experiments have proven that the cardiac output will increase roughly in proportion to the surface space of the physique. Therefore, cardiac output is incessantly said by way of the cardiac index, which is the cardiac output per sq. meter of body surface space. The common human being who weighs 70 kilograms has a physique surface space of about 1. Cardiacindexforthehumanbeing(cardiacoutputper sq. meter of floor area) at completely different ages. Therefore, it follows that cardiac output regulation is the sum of all the local blood flow rules. Note that at every growing stage of work output throughout exercise, oxygen consumption and cardiac output enhance in parallel to each other. To summarize, cardiac output is often decided by the sum of all the various components all through the body that management native blood move. All the local blood flows summate to type the venous return, and the center automatically pumps this returning blood back into the arteries to flow around the system once more.