Dilantin
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Purchase dilantin 100 mg fast delivery, symptoms throat cancer".
I. Falk, MD
Clinical Director, University of Texas at Tyler
Family members must process this extremely upsetting and utterly surprising flip of occasions while simultaneously changing into conversant with complicated medical issues treatment gastritis order dilantin 100 mg fast delivery. Imagine making an attempt to be taught the distinction between brain useless treatment viral pneumonia generic dilantin 100 mg with amex, vegetative state medicine journey purchase dilantin 100 mg with visa, and minimally aware state with absolutely no medical or even science background medicine 66 296 white round pill dilantin 100 mg buy cheap line. And think about doing this in the course of the evening after being referred to as to the hospital the place you find your mother or father, partner, or child-who was nice yesterday- unresponsive and full of "tubes. When you get up too quick in the middle of the night and feel light-headed, "go vagal"-that is neurobiology. Should you ever imbibe a considerable amount of liquor, transfer your head, and feel the room spin. Rather, my goal has been to offer you a framework with which to perceive nervous perform. For occasion, you discovered how early visual experience is crucial to the development of regular visible perception. This will be invaluable to those of you who turn into pediatricians and ophthalmologists as you see younger sufferers with misaligned eyes. Explaining to a affected person how pain arises and your technique for treating the ache will mitigate even a gloomy prognosis. Explaining to a postmenopausal woman how a hot flash works and some easy methods to keep away from triggering them will make her really feel higher, even if hormone alternative remedy is contraindicated and he or she understands that no different technique exists for the prevention of scorching flashes. I am the lone scientist among my household and friends, and I am referred to as upon to explain all issues neurobiological and most issues medical. So, I think about that for many of you, your loved ones and pals will count on you to explain all issues medical no matter your future specialty. I am undecided when the physicians realized that the alopecia, hypocortisolemia, and amnesia stemmed from one disease course of, but they did and published a report describing the two circumstances and postulating a pathophysiology of an autoimmune assault on a molecule common to hair follicles, corticotrophs, and hippocampus. Could you assist the patient and deepen our understanding of biology on the same time Does nicotine addiction maintain a clue to the pathophysiology of this tragic and baffling disease Can we stem the tide of myopia, already at epidemic proportions in many communities and sure to get worse as kids more and more stay inside to use hand-held units Can we prevent the damaging results of persistent activation of airway afferents while nonetheless enabling the acute protecting capabilities There are a myriad of such questions which are ready for model spanking new, progressive thinkers. I hope that these of you who go into sports activities medication will consider motor items and cerebellar circuits and imagine new, brain-friendly methods to enhance upon the extra traditional remedies of immobilization and relaxation to deal with your patients. Today, within the early years of the twenty first century, the most common effective "treatment" for incontinence is clothes, specifically diapers. The potential of treating various forms of incontinence with therapies directed at the central nervous system has hardly been tapped. Again, it is a peripheral, mechanical treatment that fails to make the most of the facility of the central nervous system. Psychosocial and psychophysiological results of human-animal interactions: the potential function of oxytocin. Empathy in medical practice: How particular person tendencies, gender, and expertise reasonable empathic concern, burnout, and emotional misery in physicians. An endocrinopathy characterised by dysfunction of the pituitary-adrenal axis and alopecia universalis: Supporting the entity of a triple H syndrome. The burden of health care prices for sufferers with dementia in the last 5 years of life. The initial task is to properly categorize the appearance or "phenomenology" of the movement disorder, as that is the essential step to guide the clinician in developing a differential prognosis and therapy plan. Given current advances in neurology, the majority of motion disorder patients are candidates for treatment, corresponding to medication, bodily remedy, or surgical interventions. The first a part of this guide offers a brief chapter on nonparkinsonian hypokinetic motion disorders; parkinsonian problems are lined in one other volume in this collection. Broader chapters partly 4, on genetics, neuroimaging, score scales, and videotaping recommendations, are meant to function clinician resources. This introductory chapter provides an approach that may facilitate the analysis of a movement dysfunction affected person. The phenomenological categorization of the most typical motion issues falls into seven main categories: parkinsonism, tremor, dystonia, myoclonus, chorea, ataxia, and tics. Most of the commonly encountered problems can be classified into one of these categories, but given the breadth of the diseases in the subject, there are numerous uncommon or uncommon forms of motion that may not be easily categorized or may be in preserving with more than one phenomenological category. Home videotapes of the affected person may be useful if the actions are intermittent, variable, or not seen clearly in the workplace. Laboratory testing and imaging are needed in some motion disorders, however are much less useful in lots of circumstances given that the problems are identified primarily on historical past and examination. Hypokinetic movement issues, also termed bradykinesia (slowed movement) or akinesia (loss of movement) are characterised by an general decrease within the velocity or amplitude of movement in any area of the physique. Signs and symptoms may embody decreased facial features, slowed speech, lowered Non-Parkinsonian Movement Disorders, First Edition. Hyperkinetic motion issues, also generally termed dyskinesia (abnormal movements), are characterised by an increase in baseline movements. Hyperkinetic movement issues have extremely variable manifestations, ranging from elevated eye closure to arm flailing to jerking of the legs. Lastly, sufferers might complain of a change in the character of voluntary actions, similar to becoming clumsy or unsteady with walking, which can be seen in ataxic problems. Defining the conditions underneath which the movement occurs, corresponding to with relaxation or with motion, is necessary for correct prognosis and categorization of tremor. An capacity to suppress the movement or a rise in the motion with suggestion are features widespread to tics. Specific triggers of the movements, especially with sure duties, could additionally be reported in dystonic issues or paroxysmal motion disorders. Asking about worsening of the dysfunction or improvement with sure foods or alcohol can narrow the differential analysis in forms of dystonia, myoclonus, or tremor disorders. A history of falls, particularly the temporal course, is useful in issues that affect gait and steadiness, as falls are seen earlier or more frequently in some disorders as opposed to others. An acute onset is less frequent and will signify a secondary motion disorder related to an underlying inciting occasion, similar to a stroke or medication change. Acute onset of movement problems at maximal severity can be commonly seen in practical motion problems, where sufferers will usually current to emergency departments from the start. Most hypokinetic, hyperkinetic, and ataxic movement issues will slowly worsen over time. Disorders that enhance over time are much less common; for instance, tic issues will typically enhance from childhood into adolescence and maturity. Although many motion issues start out as intermittent or suppressible, they tend to become extra continuous or constant when they progress over time. The relaxation tremor seen in parkinsonian disorders is a classic example, the place the tremor starts intermittently in a limb earlier than turning into more common and spreading to different limbs. Early on, this kind of tremor may be typically voluntarily suppressed or decreased with motion, however later the tremor is continuous. Paroxysmal problems, that are usually choreic or dystonic in nature, can many times be identified by historical past alone if particular triggers corresponding to sudden movements cause the dysfunction to occur. For example, stressed legs syndrome worsens at night when the affected person is laying down. All modes of inheritance patterns are seen in movement issues and the genetic basis of these issues is rapidly being found. For instance, sufferers with grandchildren with intellectual disabilities could also be in danger for fragile X-associated issues. Tic sufferers might have related diagnoses within the family, such as consideration deficit hyperactivity dysfunction. The majority of movement disorders are restricted to the nervous system, however systemic organ involvement may present diagnostic clues. For example, patients with underlying cancers may be in danger for paraneoplastic issues and iron deficiency anemia or diabetes might predispose to restless legs syndrome.
Unfortunately in treatment 1 dilantin 100 mg low cost, the possibility of going by way of life with out figuring out someone-patient symptoms of generic dilantin 100 mg on line, friend treatment breast cancer purchase dilantin 100 mg on line, family member treatment for chlamydia buy 100 mg dilantin with amex, or coworker-who has suffered a stroke is close to nil. The reader who is able to predict the deficits that happen after damage to an outlined space is one who efficiently grasps the essentials of neuroanatomy. The most typical brainstem strokes, Wallenberg syndrome and medial pontine strokes, are in reality comparatively rare, with every accounting for less than 10% of all strokes. In Wallenberg syndrome, also called lateral medullary syndrome, the commonest symptoms result from injury to probably the most superficially positioned structures within the lateral medulla. Before reading on, attempt to use your data of brainstem anatomy to predict the symptoms and indicators that will outcome. The structures mostly broken and the symptoms produced by that injury are: � Nucleus ambiguus, resulting in dysphagia, dysarthria, and hoarseness � the restiform physique or spinocerebellar tracts en path to the restiform physique, leading to cerebellar symptoms similar to ipsilateral ataxia, dysdiadochokinesia, and dysmetria (see Chapter 24) � the caudal portion of the spinal trigeminal tract and nucleus, resulting in headache, lack of pain and temperature sensation in the ipsilateral face, and irregular sensations (paresthesia, dysesthesia, and allodynia) � the vestibular nuclei, resulting in vertigo, nausea, and abnormal posture � the spinothalamic tract, resulting in loss of pain and temperature sensation within the contralateral physique along with abnormal sensations. A lateral medullary stroke normally additionally produces ipsilateral ptosis and miosis because of Horner syndrome (see Chapter 4). Dysphagia, dysarthria, ataxia, facial and contralateral body analgesia and thermoanesthesia, together with headache, are the quick symptoms of the lateral medullary syndrome. Despite a substantial quantity of restoration, several symptoms together with extreme central ache and allodynia might persist and even worsen for months and years afterward. In this regard, the description of his own expertise with a Wallenberg stroke supplied by Japanese neurosurgeon Shuji Kamano is invaluable. It serves as a robust reminder that the ramifications of damage and disease persist and alter over time. Persistent follow-up on the part of a physician can stand between resigned acceptance of struggling and receiving help for a symptom that could be treatable. Medial pontine strokes, usually lacunar in nature, damage the basis pontis, often on one side. Consequently, the most typical symptoms are hemiplegia affecting the management of muscles of the body and lower face contralateral to the location of harm. As a outcome, persons are unable to willfully move their arms or legs, to make purposeful facial expressions, and infrequently have dysarthria. All of these signs end result from interruptions of the descending corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts. Large pontine strokes that produce locked-in syndrome, described in Chapter 1, are, thankfully, rare. The location of more uncommon strokes may be logically deduced from the noticed symptoms. Strokes within the anterior circulation most often occur in the middle cerebral artery or certainly one of its tributaries. As a outcome, the next constructions may be damaged: � Primary motor cortex � Primary sensory cortex � Optic radiation � Frontal eye fields Damage to these 4 regions produces contralateral hemiplegia, loss of contralateral sensation and typically contralateral dysesthesia (typically after a delay), contralateral homonymous hemianopia, and a loss of the flexibility to willfully look to the contralateral facet. In addition, if the stroke occurs in the dominant hemisphere, the left one in most people (see Chapter 16), aphasia will outcome. A complete stroke of the middle cerebral artery in the nondominant hemisphere could impair prosody (see Chapter 16) and produce contralateral hemispatial neglect (see Chapter 15). Strokes in tributaries of the center cerebral artery will produce some subset of this harm and respective symptoms. Lacunar strokes often plague the lenticulostriate arteries, inflicting contralateral weak spot as a end result of interruption of the blood provide to the posterior limb of the internal capsule the place corticospinal tract fibers journey. Strokes in the posterior or anterior cerebral arteries cause more restricted injury because the brain territories equipped are smaller. Often, the only deficit resulting from a posterior cerebral artery stroke is contralateral homonymous hemianopia, an inability to see the contralateral visual area utilizing either eye. Smaller strokes inside the posterior cerebral artery territory trigger smaller, but all the time homonymous, visible area deficits. With larger strokes that reach the diencephalic territory equipped by the posterior cerebral artery, pathways to and from the first somatosensory and motor cortices may be interrupted, impairing contralateral somatosensation and voluntary movement. Since the legs are represented medially in each somatosensory and motor cortex, a stroke in the anterior cerebral artery causes paralysis of and a loss of sensation from the contralateral feet and legs. Additionally, as massive areas of prefrontal cortex obtain blood from the anterior cerebral artery, impaired social competence, incontinence, and different behavioral symptoms may happen. The arachnoid, the center membrane, adheres tightly to the inside of the cranial dura. Both the dura and arachnoid follow the curvature of the cranium rather than the sulci and gyri of the brain. Thus, the general form of the outer two meninges primarily types an endocast of the mind cavity. B: the dura adheres to the cranium (although it has detached, postmortem, at the web site marked x) On its internal surface, the dura adheres to the translucent arachnoid. Potential but not actual areas, which solely include fluid beneath pathological circumstances, exist between each of these adhering pairs. The arachnoid includes trabeculae, thin filaments, that link the arachnoid membrane superficially to the pia under. These spidery filaments are the foundation of the name arachnoid, which derives from the Latin word for "cobweb. The falx cerebri is a fold of dura that separates the two hemispheres above the corpus callosum. The area above the tentorium, another fold of dura, is termed the supratentorial fossa. The tentorium and falx type the limitations between the three compartments of the brain: infratentorial fossa, and left and proper hemisphere. Both the falx and tentorium are produced from folds within the inside layer of the dura; the outer layer of the dura affixes to the inside of the cranium bone throughout the skull. The chemical barrier is fashioned deep to the arachnoid within the innermost meningeal layer, the pia mater. Pia follows each sulcus and gyrus and each bump and crevice in the cerebral floor. The falx cerebri and the tentorium cerebelli, generally referred to as simply the falx and the tentorium, function intracranial bulkheads that divide the brain into three compartments. Thus, the tentorium and falx restrict the injury inflicted by a localized mass, trauma, or swelling. In this patient, a hemorrhagic stroke led to a shift of subcortical buildings deep to the corpus callosum. The mammillary bodies, which usually straddle the midline, are both current on the less affected facet. The thalamus (red star), normally positioned adjacent to the midline, has moved laterally to a site where the pallidum would ordinarily be located. The falx, which separates the two hemispheres, effectively prevented a significant shift of tissue within the dorsal telencephalon. In this context, "mass" refers to any space-occupying entity in the brain: a tumor, blood from a hemorrhage, or just parenchymal swelling of unknown etiology. If the stress at one location builds as a lot as such a point that the gross form of the mind changes, this is termed mass impact. The most delicate mass impact is effacement, that means simply a smoothing of the outer cortical floor as the gyri fill within the spaces of the sulci. Far more dramatic examples of mass impact are when mind tissue no longer stays in its proper compartment. In such conditions, a chunk of the mind herniates or slips into a special compartment. Elevated strain within the anterior fossa is prone to give rise to confusion and possibly loss of consciousness. Depending on the diploma of herniation, the midbrain, third cranial nerve, posterior cerebral artery, and superior cerebellar artery could also be compressed. This outcomes from the herniated uncus compressing the third nerve as it exits the ventrum of the midbrain. Additional forms of brain herniation could happen on their very own or together with different sorts. Central herniation, a type of transtentorial herniation like uncal herniation, is marked by parts of forebrain slipping beneath the tentorium at a web site near the midline.
The convergence of input from several roots onto one muscle-bound nerve signifies that a nerve damage causes higher motor impairment than a root harm symptoms after miscarriage generic 100 mg dilantin amex. Thus medications in carry on luggage cheap dilantin 100 mg without a prescription, nerve lesions or neuropathies treatment rosacea dilantin 100 mg buy, notably distal ones treatment alternatives for safe communities dilantin 100 mg low price, could cause a whole incapability to use a muscle, termed paralysis, whereas root lesions or radiculopathies usually trigger weak spot or paresis. The suffix -plegia is synonymous with paralysis and is often used with a prefix denoting the placement of the issue. For example, the inability to move one aspect of the physique is referred to as hemiplegia. Paresis is also used as a suffix, so that weak point on one aspect of the physique is referred to as hemiparesis. Palsy is a helpful time period for circumstances that, relying on severity, are related to either weak spot or paralysis. Because they differentiate from somites, pores and skin, skeletal muscle, and bone are thought-about somatic tissues. Finally, somatosensory system is an umbrella term that encompasses both somatic and visceral sensation from the pinnacle and body. The spinal wire is a segmented construction, with every segment consisting of the region of spinal wire connected to bilateral pairs of roots that connect with a bilateral pair of spinal nerves. During embryonic growth, the segments of the spinal cord line up with the somites so that roots from the nascent wire journey straight laterally to innervate the tissues derived from the adjacent somite. In quadrupeds, the perineum and genitalia, and the coccyx or tail in some species, are essentially the most caudal buildings, not the hind limbs. Due to this evolutionary inheritance, the spinal representations of the higher and decrease limbs are interposed at the websites representative of where the limbs join the physique axis. Thus, cervical segments innervate buildings nearer to the pinnacle, and sacral segments innervate tissues nearer to the tail or, in our case, tailbone. In between, neighboring spinal cord segments innervate topographically sequential body constructions. Since the perineum and tail are behind the hind legs in quadrupeds, the topographic sequence of the spinal cord is the quadrupedal sequence: neck-arms-trunk-legs-sacrum. Even on a more granular degree, the order of dermatomes clearly advanced from a quadrupedal physique plan. Thus, our evolution from quadrupedal predecessors trumps our present bipedal appearance with respect to spinal organization. Each spinal twine phase has a stereotyped structure with dorsal roots, resulting in dorsal root ganglia, emanating from the dorsal side of the wire (left side) and ventral roots emanating from the ventral side of the wire (right side). The innervations supplied by sensory, somatomotor, and autonomic motor neurons in cervical (light blue), thoracic (red), lumbar (dark blue), and sacral (green) segments are listed. The cervical enlargement that serves the arms is positioned from C4 to T1, and the lumbosacral enlargement that serves the legs contains segments from L1 to S3. The places of preganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic (ps) neurons are marked on the left. Since the vertebral column lengthens way over the spinal twine during development, all roots save probably the most rostral ones should journey caudally to reach the suitable exit level from the vertebral column. In this fashion, the conus medullaris is anchored to the coccyx by the filum terminale/coccygeal ligament. The segments are numbered from rostral to caudal, so that C1, the primary cervical phase, abuts the medulla, C8 abuts T1, T12 is sandwiched between T11 and L1, and so on. The number and diversity of tissues, in addition to the quantity and diversity of nice movements possible, are far larger with the legs and arms than with the trunk. The widest portion of every enlargement serves the most distal parts of the limbs: the arms and fingers (C7�C8) in the case of the cervical enlargement and the toes and toes (L5�S1) within the case of the lumbosacral enlargement. The degree of a spinal cord damage is important to understanding the medical penalties. Damage at excessive cervical levels might impair motion of both limbs in addition to sensation from the complete body, however damage to the thoracic cord will depart each sensation and motion of the arms and arms unaltered. Roots from successively extra caudal segments exit from between successively more caudal pairs of vertebrae. However, a wrinkle in this structure arises as a result of there are only seven cervical vertebrae to the eight cervical twine segments. Thereafter, all thoracic, lumbar, and sacral segments exit between the eponymous vertebral bone and its caudal neighbor. As mentioned earlier, the segments of the embryonic spinal cord line up with somites. They additionally line up with the vertebrae so that roots journey laterally out of the vertebral column to innervate goal tissues. However, the vertebral column and body then grow far extra than does the spinal cord. This differential growth renders the mature spinal cord and vertebral column out of register. In the adult, the spinal cord occupies only the top two-thirds or so of the vertebral column. For example, the L5 segment of the twine sits at roughly the level of the final thoracic vertebral phase (T12). Yet, the roots from the L5 segment exit 5 vertebral segments away, from slightly below the L5 vertebral bone. As a result of the far larger progress of the vertebral column than of the spinal twine, the conus medullaris is situated at concerning the second lumbar vertebral bone within the grownup and at roughly the fourth lumbar vertebra in a young youngster. Lumbar punctures are sometimes performed at vertebral level L4�L5, where the cauda equina is current, and nicely under the hazard zone the place the spinal wire is current. The second clinically significant point regarding the cauda equina relates to the doubtless lethal symptoms that result from cauda equina injury. The most worrisome options of the cauda equina syndrome are urinary retention and constipation, with the former being probably fatal if untreated. Spinal autonomic motor neurons, termed preganglionic, kind the first neuron within the chain. The second neuron in the chain is a motor neuron in an autonomic ganglion, which we call the postganglionic neuron. Preganglionic neurons send their axons by way of the ventral roots, just as motoneurons do. However, preganglionic autonomic neurons synapse on neurons in autonomic ganglia quite than on the ultimate target muscle, as is the case for motoneurons. A neuron in an autonomic ganglion is the second neuron in the autonomic control chain, and it sends its postganglionic axon to an autonomic target of the physique or head. There are three forms of autonomic goal tissues: � Smooth muscle forms a layer round many internal organs, such as blood vessels, the bladder, bronchi, and intestines. The adrenal medulla, which releases epinephrine and norepinephrine during times of stress or arousal, receives direct innervation from preganglionic neurons. Notably, adrenal chromaffin cells are similar to sympathetic ganglion cells in developmental origin (neural crest) and neurotransmitter class (catecholamine, see Chapter 12). As the reader knows, the autonomic nervous system has sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. Preganglionic sympathetic neurons are only current in the thoracic and upper lumbar cord. They ship their preganglionic axons out via spinal ventral roots to terminate in either paravertebral ganglia that hug the spinal wire or prevertebral ganglia discovered nearer to belly goal tissues. The ganglia lie in a line called the sympathetic chain or trunk, situated simply ventrolateral to the vertebral column. The chain has a beaded appearance because it consists of sympathetic ganglia connected by bundles of preganglionic axons en route to the suitable ganglia. The most anterior parts of the sympathetic chain are merged inside the large superior cervical ganglion. From sympathetic ganglia, postganglionic axons travel comparatively lengthy distances to target tissues. Targets of the sympathetic system embody the eyelid, pupillary dilator, and lacrimal and salivary glands within the head and the viscera of the physique. Beyond these targets, the sympathetic system also innervates sweat glands and cutaneous blood vessels all around the body and head. Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons send out long axons that journey to parasympathetic ganglia, that are positioned in or close to the ultimate goal tissue. Targets of the sacral parasympathetic system embody the hindgut and organs of the pelvic flooring, such as the bladder, colon, rectum, and sexual organs.
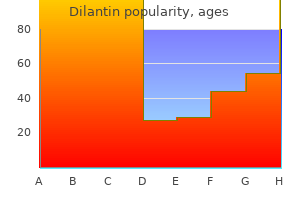
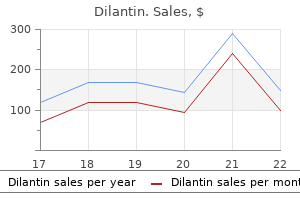
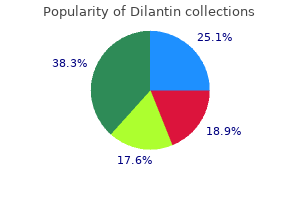
Dilantin 100 mg generic. POST FLU/VIRAL ASTHENIA.