
Dutas
| Contato
Página Inicial
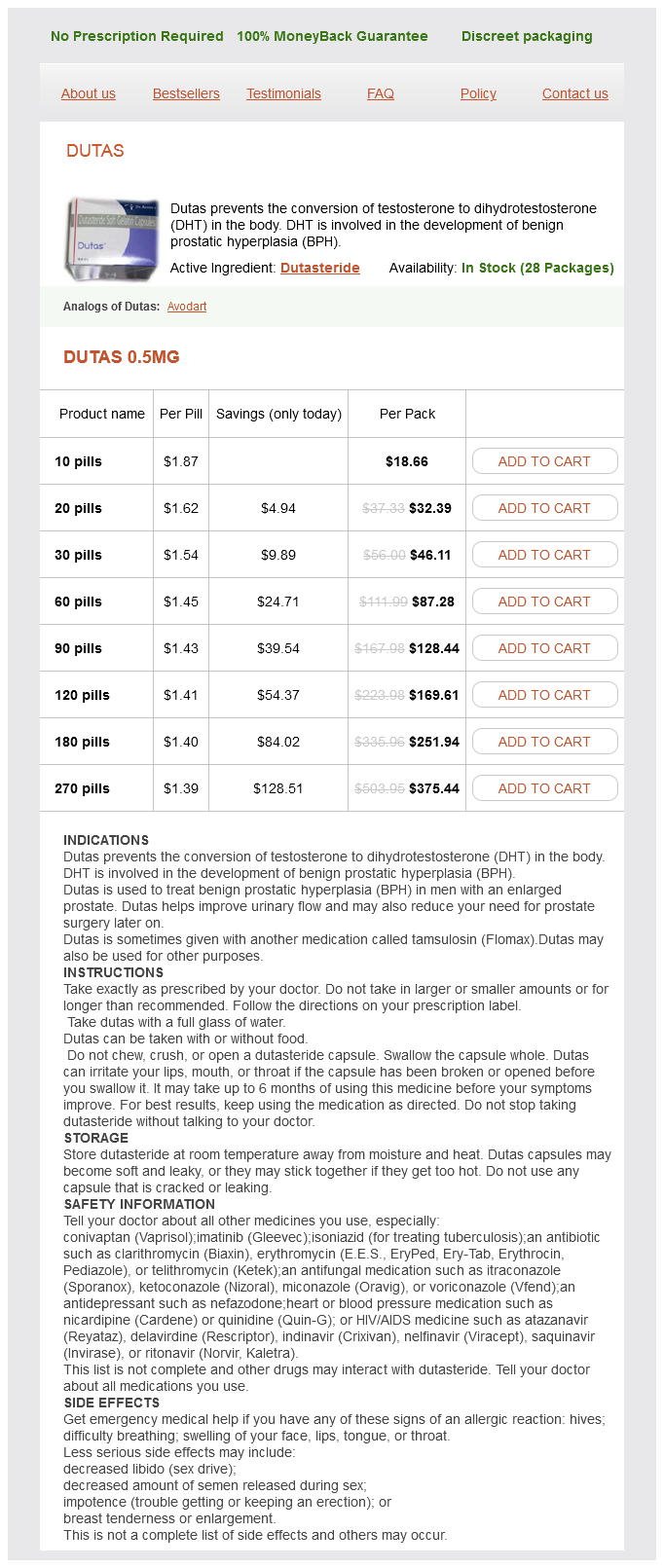
"Dutas 0.5 mg order line, hair loss 3 month old baby".
Y. Jensgar, M.B.A., M.D.
Associate Professor, University of Vermont College of Medicine
Patients with painful situations corresponding to arthritis may regularly change medicines in the hope of finding a better one hair loss cure x sinusite cheap 0.5 mg dutas. Essentially e-prescribing supplies an digital flow of information between the prescriber hair loss treatment australia dutas 0.5 mg order without prescription, middleman hair loss cure december 2013 generic dutas 0.5 mg online, pharmacy hair loss in men 2 piece dutas 0.5 mg on-line, and well being plan. Lack of transportation in addition to varied social or private beliefs about drugs are likewise barriers to compliance. The growth of enormous health maintenance organizations has greatly strengthened this growth of prescribing rights as a outcome of it presents these extraordinarily highly effective economic our bodies a method to reduce their expenses. As indicated in Table 65�2, many state boards have tried to reserve some measure of the primary accountability for prescribing to physicians by requiring that the ancillary skilled work with or beneath a physician in accordance with a particular protocol. Prescription drugs are controlled by the United States Food and Drug Administration as described in Chapter 5. The federal legend statement as properly as the package insert is a part of the packaging necessities for all prescribed drugs. The package deal insert is the official brochure setting forth the indications, contraindications, warnings, and dosing for the drug. Prescribers should move examinations, pay fees, and-in the case of some states and some professions- meet other requirements for relicensure corresponding to continuing schooling. If these requirements are met, the prescriber is licensed to order dishing out of medicine. Such drugs embrace opioids, hallucinogens, stimulants, depressants, and anabolic steroids. Moderate or low potential for bodily dependence and high potential for psychological dependence. Pharmacists collaborate with physicians to handle the drug remedy challenges in these high-use teams. These permitted (labeled) makes use of or indications are set forth within the package deal insert that accompanies the drug. Practitioners may submit stories on any suspected opposed drug (or medical device) effect using a easy kind obtainable from. For example, the brand name of a well-liked sedative is Valium, manufactured by Hoffmann-LaRoche. In most states and in most hospitals, pharmacists have the choice of supplying a generically equivalent drug product even when a proprietary name has been specified in the order. Some governmentsubsidized health care applications and many third-party insurance payers require that pharmacists dispense the most affordable generically equal product in the inventory (generic substitution). In spite of the proof, many practitioners keep away from generic prescribing, thereby increasing medical costs. In the case of life-threatening diseases, the benefits of generic substitution may be outweighed by the medical urgency so that the prescription should be filled as written. If outdoors a managed care group, the prescriber can generally override these controls by writing "dispense as written" on a prescription that requires a brand-named product. However, in such cases, the affected person may have to pay the difference between the allotted product and the cheaper one. Other Cost Factors the non-public pharmacy bases its costs on the price of the drug plus a charge for providing knowledgeable service. The prescriber controls the frequency of filling prescriptions by authorizing refills and specifying the quantity to be dispensed. However, for medications used for continual sicknesses, the amount covered by insurance coverage may be limited to the amount used in 1 month. This rise is occasioned by new technology, marketing prices, and stockholder expectations. The pharmaceutical industry usually posts profits of 10-15% yearly, whereas the retail enterprise sector reveals a 3% profit. The cost to the affected person for lots of new drugs similar to statins exceeds $1000 per year. Unfortunately, the complexity of the legislation and the ensuing confusing insurance policy with gaps in protection, formulary and quantity limits, and the favored economic treatment given the pharmaceutical business, prevent this plan from solving the high drug value downside. One of the factors that may alter the response to medication is the concurrent administration of other medicine. The common rules of pharmacokinetics are discussed in Chapters three and 4; the final rules of pharmacodynamics in Chapter 2. Unfortunately, botanicals are much less properly studied than different medicine, so details about their interactions is scanty. Knowledge of the mechanism by which a given drug interaction occurs is commonly clinically helpful, because the mechanism might influence each the time course and the methods of circumventing the interaction. Pharmacokinetic Mechanisms the gastrointestinal absorption of medication may be affected by concurrent use of different agents that (1) have a large surface space upon which the drug can be adsorbed, (2) bind or chelate, (3) alter gastric pH, (4) alter gastrointestinal motility, or (5) affect transport proteins such as P-glycoprotein and natural anion transporters. Displacement from tissue binding sites would tend to transiently enhance the blood concentration of the displaced drug. Drug metabolism primarily occurs in the liver and the wall of the small gut, however different sites embody plasma, lung, and kidney. Whether or not the interaction occurs (precipitant drug produces a measurable change in the object drug) and produces an adverse impact is dependent upon each patient- and drug-specific factors. Drug-specific factors include dose, route of administration, drug formulation, and the sequence of drug administration. However, if the half-life of the affected (object) drug is lengthy, it may take per week or more (three to 4 half-lives) to attain a new steady-state serum focus. Drugs which will inhibit the cytochrome P450 metabolism of different drugs embody amiodarone, androgens, atazanavir, chloramphenicol, cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, clarithromycin, cyclosporine, delavirdine, diltiazem, diphenhydramine, disulfiram, enoxacin, erythromycin, fluconazole, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, furanocoumarins (substances in grapefruit juice), indinavir, isoniazid, itraconazole, ketoconazole, metronidazole, mexiletine, miconazole, nefazodone, omeprazole, paroxetine, propoxyphene, quinidine, ritonavir, sulfamethizole, verapamil, voriconazole, zafirlukast, and zileuton. The renal excretion of active drug may additionally be affected by concurrent drug remedy. This is due to changes in ionization of the drug, as described in Chapter 1 beneath Ionization of Weak Acids and Weak Bases; the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. For some medication, active secretion into the renal tubules is an important elimination pathway. P-glycoprotein, organic anion transporters, and natural cation transporters are concerned in active tubular secretion of some drugs, and inhibition of these transporters can inhibit renal elimination with attendant enhance in serum drug concentrations. Pharmacodynamic Mechanisms When medicine with comparable pharmacologic effects are administered concurrently, an additive or synergistic response is normally seen. In theory, drugs acting on the identical receptor or process are often additive, eg, benzodiazepines plus barbiturates. Conversely, drugs with opposing pharmacologic results may scale back the response to one or each medicine. In this way, the interactions can be anticipated and applicable countermeasures taken. Combined Toxicity the combined use of two or more drugs, every of which has poisonous results on the identical organ, can significantly improve the probability of organ harm. For instance, concurrent administration of two nephrotoxic medication can produce kidney injury, despite the precise fact that the dose of either drug alone may have been insufficient to produce toxicity. Drug or Drug Group Alcohol Properties Promoting Drug Interaction Chronic alcoholism leads to enzyme induction. Acute alcoholic intoxication tends to inhibit drug metabolism (whether person is alcoholic or not). Severe alcohol-induced hepatic dysfunction may inhibit capacity to metabolize medication. Antacids Antacids could adsorb medication in gastrointestinal tract, thus lowering absorption. Some antacids (eg, magnesium hydroxide with aluminum hydroxide) alkalinize the urine somewhat, thus altering excretion of medication delicate to urinary pH. Iron: [P] Decreased gastrointestinal absorption of iron with calcium-containing antacids. Itraconazole: [P] Reduced gastrointestinal absorption of itraconazole because of elevated pH (itraconazole requires acid for dissolution). Ketoconazole: [P] Reduced gastrointestinal absorption of ketoconazole because of elevated pH (ketoconazole requires acid for dissolution). Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole: [P] Inhibited warfarin metabolism; displaces from protein binding.
Therapy ought to be modified to an efficient oral agent as soon because the patient has improved and may tolerate oral drugs hair loss cure your own cancer order dutas 0.5 mg visa. Oral Treatment of Falciparum Malaria Quinine sulfate is suitable remedy for uncomplicated falciparum malaria besides when the an infection was transmitted in an area with out documented chloroquine-resistant malaria hair loss evaluation dutas 0.5 mg order free shipping. Quinine is commonly used with a second drug (most usually doxycycline or hair loss cure quick 0.5 mg dutas cheap free shipping, Contraindications & Cautions Quinine (or quinidine) should be discontinued if indicators of severe cinchonism hair loss cure propecia generic dutas 0.5 mg fast delivery, hemolysis, or hypersensitivity happen. It have to be used with nice caution in those with underlying cardiac abnormalities. Although toxicity is a priority, mefloquine is amongst the recommended chemoprophylactic medicine to be used in most malaria-endemic areas with chloroquine-resistant strains. Artesunate-mefloquine is the first-line therapy for uncomplicated malaria in a selection of countries in Asia and South America. Adverse Effects Weekly dosing with mefloquine for chemoprophylaxis may cause nausea, vomiting, dizziness, sleep and behavioral disturbances, epigastric ache, diarrhea, belly pain, headache, rash, and dizziness. Neuropsychiatric toxicities have acquired a good deal of publicity, but despite frequent anecdotal reports of seizures and psychosis, numerous managed research have found the frequency of significant opposed effects from mefloquine to be no higher than that with other widespread antimalarial chemoprophylactic regimens. Leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and aminotransferase elevations have been reported. The latter opposed effects are more widespread with the higher dosages required for treatment. These effects may be lessened by administering the drug in two doses separated by 6�8 hours. The incidence of neuropsychiatric symptoms appears to be about ten instances extra widespread than with chemoprophylactic dosing, with extensively various frequencies of up to about 50% being reported. It can only be given orally as a outcome of extreme local irritation happens with parenteral use. Mefloquine is very protein-bound, extensively distributed in tissues, and eliminated slowly, permitting a single-dose treatment regimen. Mefloquine and acid metabolites of the drug are slowly excreted, mainly within the feces. Mefloquine resistance appears to be related to resistance to quinine and halofantrine but not with resistance to chloroquine. Theoretical risks of mefloquine have to be balanced with the risk of contracting falciparum malaria. Available knowledge counsel that mefloquine is safe all through being pregnant, although expertise within the first trimester is proscribed. Mefloquine chemoprophylaxis should be discontinued if significant neuropsychiatric symptoms develop. Chemoprophylaxis Mefloquine is efficient in prophylaxis against most strains of P falciparum and possibly all other human malarial species. As with chloroquine, eradication of P vivax and P ovale requires a course of primaquine. Its three main metabolites seem to have less antimalarial activity however extra potential for inducing hemolysis than the parent compound. Antimalarial Action & Resistance Primaquine is active against hepatic stages of all human malaria parasites. Primaquine acts against erythrocytic stage parasites, however this exercise is simply too weak to play an necessary position. Some strains of P vivax in New Guinea, Southeast Asia, Central and South America, and different areas are relatively proof against primaquine. Liver forms of these strains may not be eradicated by a single standard treatment with primaquine and should require repeated therapy. Because of lowering efficacy, the standard dosage of primaquine for radical remedy of P vivax an infection was just lately doubled to 30 mg base daily for 14 days. Pneumocystis jiroveci Infection the mixture of clindamycin and primaquine is an alternative routine within the therapy of pneumocystosis, notably delicate to moderate illness. It occasionally causes nausea, epigastric pain, stomach cramps, and headache, and these signs are more common with larger dosages and when the drug is taken on an empty stomach. More serious but rare adverse results are leukopenia, agranulocytosis, leukocytosis, and cardiac arrhythmias. Therapy (Radical Cure) of Acute Vivax and Ovale Malaria Standard remedy for these infections includes chloroquine to eradicate erythrocytic types and primaquine to eradicate liver hypnozoites and prevent a subsequent relapse. Chemoprophylaxis of Malaria Primaquine has been studied as a daily chemoprophylactic agent. Gametocidal Action A single dose of primaquine (45 mg base) can be used as a control measure to render P falciparum gametocytes noninfective to mosquitoes. This therapy is of no clinical benefit to the affected person but will disrupt transmission. Its bioavailability is low and erratic, but absorption is elevated by fatty meals. Initial use of atovaquone to treat malaria led to disappointing results, with frequent failures, apparently as a result of the choice of resistant parasites throughout remedy. Atovaquone is another therapy for P jiroveci infection, though its efficacy is decrease than that of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Adverse results embrace fever, rash, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, and insomnia. Serious antagonistic effects seem to be minimal, although experience with the drug remains restricted. Neither drug is sufficiently gametocidal or efficient in opposition to the persistent liver phases of P vivax or P ovale. The mechanism of action of pyrimethamine and proguanil involves selective inhibition of plasmodial dihydrofolate reductase, a key enzyme in the pathway for synthesis of folate. At present, resistance seriously limits the efficacy of sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (Fansidar) for the therapy of malaria in most areas, however in Africa most parasites exhibit an intermediate degree of resistance, such that antifolates might proceed to provide some preventive efficacy towards malaria. Chemoprophylaxis Chemoprophylaxis with single folate antagonists is no longer really helpful because of frequent resistance, however a variety of brokers are used in mixture regimens. Intermittent Preventive Therapy A new technique for malaria control is intermittent preventive remedy, in which high-risk sufferers receive intermittent remedy for malaria, regardless of their infection standing, typically with Fansidar, which benefits from easy dosing and extended activity. Chemistry & Pharmacokinetics Pyrimethamine is a 2,4-diaminopyrimidine related to trimethoprim (see Chapter 46). Typical schedules embrace single doses of Fansidar during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy and monthly doses whenever kids present for scheduled immunizations or, in areas with seasonal malaria, monthly doses in the course of the transmission season. Treatment of Chloroquine-Resistant Falciparum Malaria Fansidar is usually used to deal with uncomplicated falciparum malaria and until recently it was a first-line remedy for this indication in some tropical countries. Advantages of Fansidar are ease of administration (a single oral dose) and low price. However, charges of resistance are rising, and Fansidar is now not a recommended remedy. A new antifolate-sulfone mixture, chlorproguanildapsone (Lapdap), was until just lately available in some African international locations for the therapy of uncomplicated falciparum malaria, and the combination of chlorproguanil-dapsone and artesunate (Dacart) was under growth. Toxoplasmosis Pyrimethamine, in combination with sulfadiazine, is first-line therapy in the therapy of toxoplasmosis, together with acute infection, congenital an infection, and disease in immunocompromised patients. The replacement of sulfadiazine with clindamycin provides an efficient alternative regimen. Pneumocystosis P jiroveci is the cause for human pneumocystosis and is now acknowledged to be a fungus, however this organism is discussed on this chapter as a end result of it responds to antiprotozoal drugs, not antifungals. Standard remedy contains high-dose intravenous or oral therapy (15 mg trimethoprim and seventy five mg sulfamethoxazole per day in three or 4 divided doses) for 21 days. Trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole can be the standard chemoprophylactic drug for the prevention of P jiroveci an infection in immunocompromised individuals. Adverse Effects & Cautions Most patients tolerate pyrimethamine and proguanil well. Fansidar is not recommended for chemoprophylaxis due to unusual however severe cutaneous reactions, including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Severe reactions seem to be a lot much less frequent with single-dose or intermittent remedy, and use of the drug has been justified by the dangers associated with falciparum malaria. Maloprim is now not recommended for chemoprophylaxis because of unacceptably excessive charges of agranulocytosis.
0.5 mg dutas discount with visa. HIMS // 3 Month Update.
In some folks hair loss cure jak inhibitor buy dutas 0.5 mg without prescription, the painul deviation is so large that the great toe overlaps the 2nd toe hair loss in men we trust dutas 0.5 mg generic on-line. Oten hair loss keppra 0.5 mg dutas discount overnight delivery, the surrounding tissues swell and the resultant stress and riction in opposition to the shoe cause a subcutaneous bursa to orm; when tender and infamed hair loss 2 year old dutas 0.5 mg lowest price, the bursa is called a bunion. Oten, onerous corns (infamed areas o thick skin) also orm over the proximal interphalangeal joints, particularly o the little toe. Hammer Toe Hammer toe is a oot deormity in which the proximal phalanx is completely and markedly dorsilexed (hyperextended) on the metatarsophalangeal joint and the center phalanx strongly plantarlexed at the proximal interphalangeal joint. This deormity o one or more toes may end result rom weakness o the lumbrical and interosseous muscular tissues, which lex the metatarsophalangeal joints and prolong the interphalangeal joints. A callosity or callus, exhausting thickening o the keratin layer o the pores and skin, oten develops the place the dorsal surace o the toe repeatedly rubs on the shoe. Claw Toes Claw toes are characterized by hyperextension o the metatarsophalangeal joints and fexion o the distal interphalangeal joints. Callosities or corns develop on the dorsal suraces o the toes as a end result of o strain o the shoe. They can also orm on the plantar suraces o the metatarsal heads and the toe suggestions as a outcome of they bear extra weight when claw toes are present. Pes Planus (Flat Feet) the fat appearance o the solely real o the oot beore age three is normal; it outcomes rom the thick subcutaneous at pad within the sole. As kids become old, the at is lost, and a standard medial longitudinal arch turns into seen. The more frequent fexible fats eet outcome rom unfastened or degenerated intrinsic ligaments (inadequate passive arch support). Flexible fat eet is common in childhood however usually resolves with age because the ligaments develop and mature. The condition often persists into maturity and may or may not be symptomatic. Rigid fats eet with a historical past that goes back to childhood are more doubtless to end result rom a bone deormity (such as a usion o adjoining tarsal bones). Acquired fats eet ("allen arches") are likely to be secondary to dysunction o the tibialis posterior (dynamic arch support) owing to trauma, degeneration with age, or denervation. In the absence o regular passive or dynamic support, the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament ails to support the pinnacle o the talus. As a outcome, some fattening o the l medial part o the longitudinal arch happens, together with lateral deviation o the oreoot. Flat eet are common in older folks, particularly i they undertake much unaccustomed standd ing or gain weight quickly, adding stress on the muscles and growing the strain on the ligaments supporting the arches. Talipes equinovarus, the common kind (2 per 1,000 neonates), involves the subtalar joint; boys are aected twice as oten as women. The oot is inverted, the ankle is plantarfexed, and the oreoot is adducted (turned towards the midline in an irregular manner). The main abnormality is shortness and tightness o the muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joint capsules on the medial facet and posterior facet o the oot and ankle. Its stability outcomes rom (1) the mechanical strength o its ball and (deep) socket building, allowing in depth articular surace contact, (2) its sturdy joint capsule, and (3) its many surrounding muscles. However, it remains susceptible, especially in older age, as a end result of o the angle o the emoral neck (inclination) and shut association o the blood provide o the emoral head to the neck. Major movements o the hip joint embrace exion and extension, attainable over a broad range; medial and lateral rotation with abduction are part o every step o normal, bipedal walking. Knee joint: the knee is a hinge joint with a wide range o movement (primarily exion and extension, with rotation increasingly attainable with exion). Compensation is tried by a quantity of eatures, together with (1) sturdy intrinsic, extracapsular, and intracapsular ligaments, (2) splinting by many surrounding tendons (including the iliotibial tract), and (3) menisci that fll the spatial void, offering cellular articular suraces. Tibiobular joints: the tibiofbular joints embrace a proximal synovial joint, an interosseous membrane, and a distal tibiofbular syndesmosis, consisting o anterior, interosseous, and posterior tibiofbular ligaments. Together, these joints make up a compensatory system that enables a slight upward movement o the fbula owing to orced transverse enlargement o the malleolar mortise (deep square socket) during maximal dorsiexion o the ankle. All fbrous tibiofbular connections run downward rom tibia to fbula, permitting this slight upward motion whereas strongly resisting the downward pull utilized to the fbula by the contraction o eight o the 9 muscles connected to it. The ankle joint is maintained medially by a robust, medial (deltoid) ligament and a a lot weaker lateral ligament. The lateral ligament (specifcally its anterior talofbular ligament component) is essentially the most requently injured ligament o the body. Injury happens primarily by inadvertent inversion o the plantarexed, weight-bearing oot. About 70� o dorsiexion and plantarexion is feasible on the ankle joint, in addition to which small quantities o wobble happen in the less steady plantarexed place. Joints o oot: Functionally, there are three compound joints in the oot: (1) the scientific subtalar joint between the talus and the calcaneus, the place inversion and eversion occur about an oblique axis; (2) the transverse tarsal joint, where the midoot and oreoot rotate as a unit on the hindoot round a longitudinal axis, augmenting inversion and eversion; and (3) the remaining joints o the oot, which permit the pedal platorm (oot) to orm dynamic longitudinal and transverse arches. The arches provide the resilience essential or strolling, working, and leaping and are maintained by our layers o passive, fbrous assist, plus the dynamic assist provided by the intrinsic muscle tissue o the oot and the long fbular, tibial, and exor tendons. It is the control and communications middle in addition to the "loading dock" or the physique. The head additionally consists of special sensory receivers (eyes, ears, mouth, and nose), broadcast units or voice and expression, and portals or the intake o uel (ood), water, and oxygen and the exhaust o carbon dioxide. The head consists o the mind and its protecting coverings (cranial vault and meninges), the ears, and the ace. The ace contains openings and passageways, with lubricating glands and valves (seals) to shut some o them, the masticatory (chewing) units, and the orbits that home the visible equipment. Disease, malormation, and trauma o buildings in the head orm the bases o many specialties, together with dentistry, maxilloacial surgery, neurology, neuroradiology, neurosurgery, ophthalmology, oral surgery, otology, rhinology, and psychiatry. The neurocranium is the bony case o the brain and its membranous coverings, the cranial meninges. It also incorporates proximal components o the cranial nerves and the vasculature o the mind. The neurocranium in adults is ormed by a series o eight bones: our singular bones centered on the midline (rontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and occipital), and two units o bones occurring as bilateral pairs (temporal and parietal). The neurocranium has a dome-like roo, the calvaria (skullcap), and a foor or cranial base (basicranium). The bones orming the calvaria are primarily fat bones (rontal, 1 There is conusion about exactly what the term cranium means. It could mean the cranium (which consists of the mandible) or the half o the cranium excluding the mandible. There has also been conusion as a outcome of some individuals have used the time period skull or solely the neurocranium. In the anatomical position, the inerior margin o the orbit and the superior margin o the exterior acoustic meatus lie in the identical horizontal orbitomeatal (Frankort horizontal) airplane. The neurocranium and viscerocranium are the two primary unctional elements o the skull. The unpaired sphenoid and occipital bones make substantial contributions to the cranial base. The spinal cord is continuous with the brain through the oramen magnum, the massive opening within the basal part o the occipital bone. The viscerocranium, housing the optical apparatus, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and oral cavity, dominates the acial aspect o the skull. The mandible is a major component o the viscerocranium, articulating with the rest o the skull by way of the temporomandibular joint. The broad ramus and coronoid course of o the mandible provide attachment or powerul muscular tissues succesful o generating great orce in relationship to biting and chewing (mastication). The supra-orbital notch, the inra-orbital oramen, and the psychological oramen, giving passage to main sensory nerves o the ace, are approximately in a vertical line. The bones contributing to the cranial base are primarily irregular bones with substantial fats parts (sphenoidal and temporal) ormed by endochondral ossication o cartilage (chondrocranium) or rom a couple of sort o ossication. The ethmoid bone is an irregular bone that makes a relatively minor midline contribution to the neurocranium but is primarily part o the viscerocranium.
Several noncatecholamine dopamine receptor agonists have additionally been developed and should result in hair loss cure for dogs dutas 0.5 mg discount amex clinical benefit hair loss cure cnn 0.5 mg dutas generic fast delivery, as mentioned in the textual content that follows hair loss cure book dutas 0.5 mg cheap visa. The benefits of dopaminergic antiparkinsonism medicine appear to rely mostly on stimulation of the D2 receptors hair loss specialist discount dutas 0.5 mg. However, D1- receptor stimulation may also be required for maximal profit and one of many newer drugs is D3 selective. Moreover, certain amino acids from ingested meals can compete with the drug for absorption from the intestine and for transport from the blood to the mind. Plasma concentrations normally peak between 1 and a pair of hours after an oral dose, and the plasma half-life is often between 1 and 3 hours, though it varies significantly among people. Indeed, concomitant administration of a peripheral dopa decarboxylase inhibitor corresponding to carbidopa might scale back the daily necessities of levodopa by approximately 75%. The advantages of coadministration of carbidopa include discount of the amount of levodopa required for profit and of the absolute quantity diverted to peripheral tissues and a rise within the fraction of the dose that reaches the mind. This is sometimes as a outcome of the day by day dose of levodopa should be decreased over time to avoid adverse effects at doses that were properly tolerated initially. Most sufferers finally require carbidopa 25 mg, levodopa 250 mg three or four times every day. A formulation of carbidopa-levodopa (10/100, 25/100, 25/250) that disintegrates within the mouth and is swallowed with the saliva (Parcopa) is now available commercially and is finest taken about 1 hour earlier than meals. Finally, remedy by intraduodenal infusion of levodopacarbidopa appears to be secure and is superior to a variety of oral combination therapies in sufferers with response fluctuations. Behavioral Effects A broad variety of opposed mental results have been reported, together with depression, anxiety, agitation, insomnia, somnolence, confusion, delusions, hallucinations, nightmares, euphoria, and different modifications in temper or persona. The character of dopa dyskinesias varies between patients however tends to stay constant in individual sufferers. Certain fluctuations in medical response to levodopa happen with increasing frequency as remedy continues. The vomiting has been attributed to stimulation of the chemoreceptor set off zone positioned in the brainstem but outside the blood-brain barrier. Antiemetics similar to phenothiazines ought to be avoided because they reduce the antiparkinsonism results of levodopa and should exacerbate the disease. When levodopa is given together with carbidopa, antagonistic gastrointestinal results are much much less frequent and troublesome, occurring in lower than 20% of circumstances, so that patients can tolerate proportionately higher doses. The incidence of such arrhythmias is low, even in the presence of established cardiac disease, and could also be lowered still further if the levodopa is taken in combination with a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor. Furthermore, a drug vacation carries the risks of aspiration pneumonia, venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and depression ensuing from the immobility accompanying extreme parkinsonism. It can additionally be contraindicated in patients with angle-closure glaucoma, however those with chronic open-angle glaucoma could also be given levodopa if intraocular stress is nicely managed and may be monitored. Patients with lively peptic ulcer should also be managed carefully, since gastrointestinal bleeding has sometimes occurred with levodopa. In consequence, dopaminergic therapy may finest be initiated with a dopamine agonist. In either case, the dose of the dopamine agonist is constructed up steadily relying on response and tolerance. Moreover, drugs selectively affecting sure (but not all) dopamine receptors may have more limited opposed effects than levodopa. The older dopamine agonists (bromocriptine and pergolide) are ergot (ergoline) derivatives (see Chapter 16), and are rarely-if ever- used to deal with parkinsonism. The product was recalled in the United States in 2008 due to crystal formation on the patches, affecting the provision and efficacy of the agonist. Dyskinesias Abnormal movements just like these introduced by levodopa may happen and are reversed by lowering the entire dose of dopaminergic medicine being taken. Mental Disturbances Confusion, hallucinations, delusions, and different psychiatric reactions are potential issues of dopaminergic treatment and are extra widespread and severe with dopamine receptor agonists Pramipexole Pramipexole is quickly absorbed after oral administration, reaching peak plasma concentrations in roughly 2 hours, and is excreted largely unchanged within the urine. Disorders of impulse management might result in compulsive gambling, shopping, betting, sexual activity, and other behaviors (see Chapter 32). Miscellaneous Headache, nasal congestion, elevated arousal, pulmonary infiltrates, pleural and retroperitoneal fibrosis, and erythromelalgia are different reported opposed results of the ergot-derived dopamine agonists. Erythromelalgia consists of red, tender, painful, swollen ft and, sometimes, arms, at occasions related to arthralgia; signs and signs clear within a couple of days of withdrawal of the causal drug. Contraindications Dopamine agonists are contraindicated in patients with a history of psychotic sickness or latest myocardial infarction, or with lively peptic ulceration. Neither selegiline nor rasagiline ought to be taken by sufferers receiving meperidine, tramadol, methadone, propoxyphene, cyclobenzaprine, or St. Monoamine oxidase A metabolizes norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine; monoamine oxidase B metabolizes dopamine selectively. It is subsequently used as adjunctive remedy for patients with a declining or fluctuating response to levodopa. Studies in animals counsel that it may scale back illness progression, but trials to test the impact of selegiline on the development of parkinsonism in people have yielded ambiguous results. The findings in a big multicenter research were taken to recommend a beneficial impact in slowing illness development but may simply have reflected a symptomatic response. Levodopa clearance is decreased, and relative bioavailability of levodopa is thus elevated. Neither the time to reach peak focus nor the maximal focus of levodopa is elevated. By contrast, entacapone (200 mg) must be taken with every dose of levodopa, as a lot as five instances day by day. It is usually necessary to lower the day by day dose of levodopa by about 30% in the first forty eight hours to keep away from or reverse such problems. Other adverse effects include diarrhea, abdominal pain, orthostatic hypotension, sleep disturbances, and an orange discoloration of the urine. A commercial preparation named Stalevo consists of a mixture of levodopa with each carbidopa and entacapone. Use of this preparation simplifies the drug regimen and requires the consumption of a lesser number of tablets than otherwise. It has been reported to antagonize the results of adenosine at adenosine A2A receptors, that are receptors which will inhibit D2 receptor function. The plasma half-life is between 2 and four hours, a lot of the drug being excreted unchanged in the urine. Amantadine ought to be used with caution in sufferers with a historical past of seizures or heart failure. It is quickly taken up within the blood after which the brain, leading to clinical benefit that begins inside about 10 minutes of injection and persists for as much as 2 hours. The optimal dose is identified by administering rising take a look at doses until sufficient benefit is achieved or a maximum of 10 mg is reached. Most patients require a dose of 3�6 mg, and this ought to be given no more than about three times every day. Nausea is often troublesome, particularly at the initiation of apomorphine therapy; accordingly, pretreatment with the antiemetic trimethobenzamide (300 mg thrice daily) for 3 days is recommended before apomorphine is launched and is then continued for at least 1 month, if not indefinitely. Other opposed effects include dyskinesias, drowsiness, chest pain, sweating, hypotension, and bruising at the injection website. Drug Benztropine mesylate Biperiden Orphenadrine Procyclidine Trihexyphenidyl Usual Daily Dose (mg) 1�6 2�12 150�400 7. All trials involved infusion into the striatum of adeno-associated virus type 2 because the vector for the gene. Adverse Effects Antimuscarinic medication have a variety of undesirable central nervous system and peripheral results (see Chapter 8) and are poorly tolerated by the aged. Acute suppurative parotitis generally occurs as a complication of dryness of the mouth. Stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus by an implanted electrode and stimulator has yielded good outcomes for the administration of the medical fluctuations occurring in advanced parkinsonism. Such procedures are contraindicated in patients with secondary or atypical parkinsonism, dementia, or failure to reply to dopaminergic medication.
Doxercalciferol and paricalcitol are accredited for the therapy of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients with persistent kidney illness hair loss quotes dutas 0.5 mg purchase amex. Vitamin D and its metabolites circulate in plasma tightly bound to the vitamin D-binding protein hair loss 6 months after pregnancy generic 0.5 mg dutas otc. Ergosterol undergoes similar transformation to vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) hair loss questions order dutas 0.5 mg line, which hair loss cure products generic dutas 0.5 mg online, in turn, is metabolized to 25-hydroxyvitamin D2, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2, and 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2. In people, corresponding D2 and D3 derivatives have equal results although they differ in pharmacokinetics. The metabolic clearance of calcitriol in humans signifies a fast turnover, with a terminal half-life measured in hours. Such analogs have much less of the hypercalcemic, hypercalciuric effects of calcitriol, an important side of their use for the management of conditions similar to psoriasis and hyperparathyroidism. The mechanism of motion of the vitamin D metabolites remains beneath energetic investigation. Such drugs are proving useful within the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism accompanying chronic kidney disease and may be useful in chosen instances of primary hyperparathyroidism. Salmon calcitonin has an extended half-life, making it extra enticing as a therapeutic agent. However, long-term use of estrogen has fallen out of favor as a end result of concern about opposed effects. Newer Therapies for Osteoporosis Newer Therapies for Osteoporosis Bone undergoes a steady transforming process involving resorption and formation. Raloxifene shares some of the beneficial results of estrogen on bone with out rising the risk of breast or endometrial cancer (it may very well cut back the risk of breast cancer). Nonhormonal types of therapy for osteoporosis with proven efficacy in lowering fracture threat have also been developed. Bisphosphonates corresponding to alendronate, risedronate, and ibandronate have been conclusively proven to enhance bone density and scale back fractures over no less than 5 years when used continuously at a dosage of 10 mg/d or 70 mg/wk for alendronate; 5 mg/d or 35 mg/wk for risedronate; or 2. Its efficacy in stopping fractures appears to be no much less than as nice as that of the bisphosphonates. Additional promising new treatments present process scientific trials embrace an antibody towards sclerostin (a protein produced by osteocytes that inhibits bone formation), that has been shown to stimulate bone formation, and inhibitors of cathepsin K, an enzyme in osteoclasts that facilitates bone resorption. Currently obtainable bisphosphonates embody etidronate, pamidronate, alendronate, risedronate, tiludronate, ibandronate, and zoledronate. With the development of the more potent bisphosphonates, etidronate is seldom used. The portion of drug retained in bone is determined by the speed of bone turnover; drug in bone typically is retained for months if not years. The mevalonate pathway effects range depending on the bisphosphonate (ie, only amino bisphosphonates have this property), and may account for a few of the scientific differences noticed within the effects of the varied bisphosphonates on bone mineral homeostasis. More lately, concern has been raised about over-suppressing bone turnover, and case stories have appeared describing uncommon subtrochanteric (femur) fractures in sufferers on long-term bisphosphonate treatment. It is a minimal of as effective as the potent bisphosphonates in inhibiting bone resorption and has recently been accredited for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis and some cancers (prostate and breast). The latter software is to limit the development of bone metastases or bone loss resulting from the utilization of medication suppressing gonadal function. Denosumab is administered subcutaneously each 6 months, which avoids gastrointestinal unwanted effects. Both therapeutic applications originated from epidemiologic observations that subjects residing in areas with naturally fluoridated water (1�2 ppm) had much less dental caries and fewer vertebral compression fractures than topics living in nonfluoridated water areas. Fluoride accumulates in bones and teeth, the place it may stabilize the hydroxyapatite crystal. There is little additional benefit to giving fluoride after the everlasting teeth are fully fashioned. Results of earlier studies indicated that fluoride alone, without enough calcium supplementation, produced osteomalacia. Cinacalcet is permitted for the remedy of secondary hyperparathyroidism in continual kidney illness and for the treatment of parathyroid carcinoma. With the development of other much less poisonous medication for these functions, the medical use of plicamycin is seldom indicated. Unlike bisphosphonates, denosumab, or teriparatide, this drug increases bone formation markers while inhibiting bone resorption markers. With the attainable exception of hypervitaminosis D, the latter problems seldom require emergency reducing of serum calcium. Saline Diuresis In hypercalcemia of enough severity to produce symptoms, fast discount of serum calcium is required. In many subjects, saline diuresis suffices to scale back serum calcium to some extent at which more definitive diagnosis and treatment of the underlying situation could be achieved. Biochemical markers of skeletal involvement embrace modifications in serum levels of the skeletal isoenzyme of alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin, and N- and C- terminal propeptides of sort I collagen (reflecting osteoblastic activity), and serum and urine levels of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase and collagen breakdown products (reflecting osteoclastic activity). The kidney becomes involved when the calcium � phosphate product in serum rises above the purpose at which ectopic calcification happens (nephrocalcinosis) or when the calcium � oxalate (or phosphate) product in urine exceeds saturation, resulting in nephrolithiasis. The diploma of the ensuing renal failure is finest followed by monitoring the decline in creatinine clearance. Bisphosphonates Pamidronate, 60�90 mg, infused over 2�4 hours, and zoledronate, four mg, infused over a minimal of quarter-hour, have been approved for the therapy of hypercalcemia of malignancy and have largely changed the less effective etidronate for this indication. Calcitonin by itself seldom restores serum calcium to regular, and refractoriness incessantly develops. Calcimar (salmon calcitonin) is available for parenteral and nasal administration. Its main causes (other than thiazide therapy) are hyperparathyroidism and cancer, with or without bone metastases. Because of potential nephrotoxicity, patients must be nicely hydrated and have good renal output earlier than beginning the infusion. However, when different forms of remedy fail, 25�50 mcg/kg of plicamycin given intravenously often lowers serum calcium considerably inside 24�48 hours. The most harmful toxic effect is sudden thrombocytopenia adopted by hemorrhage. An motion of glucocorticoids to reduce vitamin D-mediated bone resorption has not been excluded, nevertheless. Glucocorticoids have also been proven to inhibit the secretion or effectiveness of cytokines elaborated by multiple myeloma and associated cancers that stimulate osteoclastic bone resorption. Phosphate is out there in oral and intravenous types as sodium or potassium salts. Amounts required to provide 1 g of elemental phosphorus are as follows: Intravenous: In-Phos: forty mL Hyper-Phos-K: 15 mL Oral: Fleet Phospho-Soda: 6. Calcium A number of calcium preparations are available for intravenous, intramuscular, and oral use. Calcium carbonate is commonly the preparation of selection due to its excessive proportion of calcium, ready availability (eg, Tums), low price, and antacid properties. In achlorhydric sufferers, calcium carbonate must be given with meals to increase absorption, or the affected person must be switched to calcium citrate, which is considerably higher absorbed. Prednisone in oral doses of 30�60 mg daily is mostly used, although equivalent doses of different glucocorticoids are efficient. Less severe hypocalcemia is greatest treated with oral forms enough to present roughly 400�1200 mg of elemental calcium (1�3 g calcium carbonate) per day. The combined effects of calcitriol and all different vitamin D metabolites and analogs on both calcium and phosphate make cautious monitoring of those mineral levels especially essential to forestall ectopic calcification secondary to an abnormally excessive serum calcium � phosphate product. Since the selection of the appropriate vitamin D metabolite or analog for long-term remedy of hypocalcemia is dependent upon the nature of the underlying illness, additional dialogue of vitamin D remedy is discovered underneath the headings of the precise diseases. The long-term effects of hypophosphatemia include proximal muscle weak point and irregular bone mineralization (osteomalacia). Therefore, hypophosphatemia should be avoided when using forms of remedy that may lead to hypophosphatemia (eg, phosphate binders, sure forms of parenteral nutrition) and handled in situations that trigger hypophosphatemia, similar to the varied forms of hypophosphatemic rickets. Emergency treatment of hyperphosphatemia is seldom needed however may be achieved by dialysis or glucose and insulin infusions. In basic, control of hyperphosphatemia involves restriction of dietary phosphate plus phosphatebinding gels similar to sevelamer and calcium supplements. Because of their potential to induce aluminum-associated bone illness, aluminum-containing antacids should be used sparingly and only when other measures fail to control the hyperphosphatemia. The principal therapeutic concern is to restore normocalcemia and normophosphatemia. Vitamin D (25,000�100,000 models three times per week) and dietary calcium dietary supplements have been used prior to now.
Additional information: