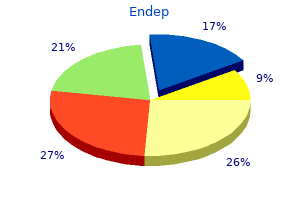
Endep
| Contato
Página Inicial

"25 mg endep discount, medicine vending machine".
M. Quadir, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Program Director, Donald and Barbara School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell
If the titration endpoint is confounded medications safe while breastfeeding cheap endep 25 mg online, then these may lead to medicine grand rounds buy generic endep 10 mg on-line misguided values for the target analyte pKa medications in mothers milk generic 50 mg endep visa. However medicine 4h2 buy endep 25 mg with visa, the impact of an natural eluent modifier on the analyte ionization must even be thought-about. It has been shown that increase of the organic content material in hydro-organic mixture leads to suppression of the basic analyte pKa and results in an increase in the acidic analyte pKa compared to their potentiometric pKa values decided in pure water [74]. This apply results in faster method development, rugged methods, and an accurate description of the analyte retention as a perform of pH at varying organic compositions. The concentration of organic within the mobile phase must be chosen to elute essentially the most hydrophilic species (ionized form) with a k > 1. If the compound is acidic, the elution of the fully ionized species shall be obtained at 2 pH models higher than the analyte pKa. If the compound is basic, the elution of the fully ionized species will be obtained at 2 pH units less than the analyte pKa. The organic composition chosen must also have the power to elute the neutral species within an affordable retention time. If the goal analyte is a fundamental compound, then the lowest pH mobile phase could presumably be run first, to acquire the retention of the ionized species. At least 25 column volumes (1 column quantity = � radius of column2 � length of column � 0. Multiple injections of the analyte ought to be made; and once a secure retention is obtained at a particular pH, the subsequent pH could be evaluated. The retention issue (or retention) is then plotted versus the s spH of the cellular phase. Using nonlinear regression analysis software program, the spKa of the analyte can be decided. Knowing the s pKa of the analyte and the sort and focus of s organic modifier used, the w pKa of the analyte could be calculated. Accounting for the pH shift of the cell section and analyte pKa shift upon the addition of natural modifier is necessary for the chromatographer to analyze the ionogenic samples at their optimal pH values. Therefore, one should account for the pH shift of the cellular part upon the addition of the organic modifier for a correct description of the ionogenic analyte retention course of. However, the effect of organic eluent modifier on the analyte ionization must also be thought of. It has been proven that enhance of the natural content in hydro-organic combination results in suppression of the fundamental analyte pKa and a rise within the acidic analyte pKa in comparability with their potentiometric pKa values determined in pure water [74, 79]. Accounting for the pH shift of modifier within the cellular section and analyte pKa shift upon the addition of organic modifier, this can permit the chromatographer to analyze the ionogenic samples at their optimal pH values. Moreover, a theoretical curve of the retention dependence versus pH of the cellular section was constructed for aniline, based mostly on its potentiometric pKa of four. The inflection point of the dependence of k versus pH corresponds to the analyte pKa at a selected hydro-organic composition. The pKa difference between these two curves is actually the mixture of two individual shifts occurring in opposing instructions: acidic mobile-phase upward pH shift and the fundamental analyte downward w pKa shift. The difference between the wpH and s pH curve is as a end result of of the pH shift s of the aqueous portion of the acidic mobile part which is caused by a change within the dissociation in the acidic buffer in the explicit hydro-organic eluent. The distinction between the s pH curve and the theoretis cal curve could probably be attributed to a change of the fundamental analyte ionization state at a particular hydro-organic composition upon addition of acetonitrile in the mobile section, and that is denoted as the basic analyte pKa shift. In the graph for all natural compositions a sigmoidal dependence of retention issue versus s pH is obtained and the plateau regions are the limiting factors s for the totally ionized and impartial types of the analyte. Retention Volume of Aniline as a Function of s pH (10�50 v/v% s Acetonitrile) s s pH 50 1. Similar adverse slopes for different monosubstituted aromatic amines have been determined (0. The analyte pKa shift upon addition of acetonitrile may be estimated by utilizing the slope of this dependence (0. This shall be denoted as the fundamental analyte pKa shift for additional discussions in the book. The decrease in the analyte pKa for primary compounds in acetonitrile/water has been attributed to the breaking of the water construction by addition of organic solvent which consequently modifications its ionization equilibria [79, 76, 94]. Therefore, particular solvation effects for sure classes of compounds could lead to different slopes of the change in the pKa as a function of the sort and concentration of organic composition. Similar parameters have been decided for this household of compounds for methanol/water mixtures [80]. Using these parameters for each household of compounds for a specific type of organic, the as and bs phrases could presumably be determined and the following empirical equation was determined: s s pKa = as w pKa + bs w (4-25) this empirical equation could be used to estimate the analyte s pKa values for s completely different classes of acidic and fundamental compounds specifically acetonitrile/water or methanol/water compositions. The inflection level of the dependence of k versus pH corresponds to the analyte s pKa at a selected hydro-organic coms place. The overall distinction between the theoretical curve and s pH curve is due to the pKa shift of the acidic analyte. The differs ence between the s pH curve and the theoretical curve is due to a change of s the acidic analyte ionization state at a selected hydro-organic composition upon addition of acetonitrile in the cellular part. In this graph a sigmoidal dependence of retention issue versus pH is obtained and the plateau regions are the limiting factors for the absolutely ionized and impartial types of the analyte. The inflection level of the dependence of k versus s pH corresponds to the acidic s analyte pKa at a particular hydro-organic composition. Also for weakly acidic analytes similar to mono- and disubstituted phenols [74, 76], increases of 0. However, since the natural eluent does result in adjustments within the mobilephase pH and analyte pKas, changes in selectivity could additionally be observed at certain pH values. In a perfect case, the plot of the logarithm of the retention factor versus the acetonitrile composition ought to give a linear dependence. Different slopes of retention dependence are obtained at a certain eluent pH versus eluent composition. Due to the upward pH shift of the acidic modifier, the s pH s of the eluent at 20% and 50%, respectively, is three. On the other hand, for the essential analyte because of downward pKa shift upon increase of the organic focus from 20% to 50%, the s pKa decreases from 4. Therefore, with a rise of natural concentration at w pH three w the analyte is being analyzed more progressively in its neutral state. The s spKa of aniline at acetonitrile compositions from 10 to 50 v/v% is shown in Table 4-14. An improve of the acetonitrile focus in general leads to an exponential decrease of the analyte retention. However, aniline is changing into much less ionized upon improve of organic content material within the eluent. Therefore, growing organic content material at a certain aqueous pH has a supposition of two reverse results on the general analyte retention: (1) a rise in analyte retention because of a decrease in an analyte ionization since analyte pKa decreases with enhance of natural content material, which outcomes in evaluation of analyte in a extra neutral state, and (2) a decrease in analyte retention because of decreased analyte interaction with the stationary section, which decreases hydrophobic interaction. The separation selectivity may be significantly affected because of totally different pH shift of different buffers even on the same natural composition. For instance, if two buffers are ready on the similar pH, one using an acidic buffer similar to phosphate and one other utilizing a fundamental buffer similar to ammonia, both at w wpH eight, the separation of a mixture of ionizable elements might be totally different. This might be attributed to the completely different mobile-phase s pH after the s aqueous is mixed with the natural. At this acetonitrile composition the wpH of the s ammonia buffer is estimated to be about 7. This estimation may assist to avoid unusual analyte retention behavior during further methodology optimization and variation of the mobile-phase composition. Below we include a number of examples the place the methodology of the combined pH and pKa shift evaluation is outlined. What should the pH of the phosphate buffer be in order to get hold of the fundamental analyte in its fully ionized type First account for the downward pKa shift for the basic analyte upon addition of organic. For each 10 v/v% increase in acetonitrile, the s pKa of s the analyte decreases by zero.
This retention model based on adsorption was first proposed by Snyder [2�5] to describe retention on silica and alumina adsorbents and later prolonged to explain retention on polar bonded phases symptoms pancreatitis endep 10 mg buy lowest price, similar to diol- medications you cant take with grapefruit endep 25 mg order with mastercard, cyano- treatment pneumonia discount endep 50 mg free shipping, and amino-bonded silica medications zoloft purchase 50 mg endep otc. Snyder assumed a homogeneous floor in order that adsorption energies for solute and solvent molecules are constant. The stoichiometry of solute�solvent competitors could be given by Sm + nEa Sa + nEm (5-1) m and a check with solute (S) and solvent (E) molecules within the mobile and adsorbed phases, respectively. For a binary mobile-phase system consisting of a weak nonpolar solvent and a robust polar solvent, adsorption of the weak solvent could be ignored. The stationary-phase floor consists of a layer of solute and/or solvent molecules, however, in contrast to the previous, the latter model assumes an energetically heterogeneous floor where adsorption happens totally at the high-energy active websites, resulting in discrete, one-to-one complexes of the form Sm + qEa -A* S - A* + qEm (5-3) A* is an lively floor site and q refers to the variety of substituents on a solute molecule that are able to simultaneously interacting with the lively website. In follow, it was discovered that equations (5-1) and (5-2) are most dependable for much less polar solvents and solute molecules on alumina or silica stationary phases only. Neither of the models is totally satisfactory in the varieties offered, particularly for predicting retention behavior on bonded stationary phases. These effects, corresponding to hydrogen bonding, give rise to a few of the most useful adjustments in retention and infrequently are an necessary supply of chromatographic selectivity [7, 8]. Another experimental deviation from equations (5-1) or (5-2) was determined to be as a result of the localization of solvent molecules onto the adsorption sites of stationary phase resulting from silanophilic interactions. An necessary consequence of solvent localization is the apparent change in the solvent power value of a polar solvent. There is competition between the two solvents for the lively sites of the adsorbent and the stronger solvent will preferentially adsorb, leading to a more concentrated adsorbed layer of the stronger solvent. For occasion, the dependence of solvent strength for several binary mixtures on alumina as adsorbent exhibits a big improve in solvent strength as a end result of a small enhance in the focus of a polar solvent at low concentrations. But at the different excessive, a relatively giant change within the focus of the polar solvent affects the solvent power of the cellular part to a lesser extent. In the case of low focus of polar solvent earlier than the localization on the surface of stationary phase reaches saturation, a small change of the polar solvent focus can greatly affect the variety of polar energetic websites on the column packing. Once the polar lively websites of the stationary section are localized fully, change of polar solvent concentration will have a smaller influence on analyte retention. Equation (5-7) has been discovered helpful to understand the elemental principles governing the retention habits as far as solute, solvent, and bonded-phase properties are concerned. Ideally, the mobile-phase power should be chosen to maintain analyte retention issue within the optimum range of 1 k 5 with selectivity values adequate to reach a satisfactory resolution. Snyder has developed a helpful scheme to classify solvents (nonelectrolytic solvents) nature primarily based on their interactions with solutes and the stationary part [9]. The property of a solvent is characterized by the three most important parameters, which are its protonacceptor (Xe), proton-donor (Xd), and dipole-donor (Xn) affinity. Each of those contributes to the overall polarity of the solvent, which in turn is related to its chromatographic energy. Rohrschneider determined the values of these parameters from distribution coefficients of take a look at solutes such as ethanol, dioxane, and nitrobenzene [10]. Solvents inside every class ought to show related selectivity for a set of parts, while the character of solvents from different courses are quite completely different and may impart differences in selectivity for a similar set of elements. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to choose solvents that are placed near the apices of the triangle for maximum selectivity. Solvent mixtures having the identical elution energy however different selectivities are referred to as isoelutropic cell phases. Binary mixtures, nevertheless, have only restricted skills for controlling mobilephase selectivity. Therefore, ternary and even quaternary cellular phases that include two or extra different polar solvents along with a nonpolar solvent are sometimes used to obtain the required selectivity. On the opposite hand, if the sum of the two polar solvents stays fixed but the ratio is variable, bigger effects on the selectivity of separation are observed than in the system where the ratio is fixed. This is attributable to changes in dipole�dipole and proton�donor� acceptor interactions between polar solvents and the analytes. Two other binary mixtures, particularly, hexane-dichloromethane and hexanechloroform, having the composition with the identical solvent energy, are then examined. Next, separations are performed with three different ternary mobile-phase methods produced by mixing an equal volume of each of the binary solvents. Finally, the evaluation is carried out by mixing in the three binary mixtures in equal ratio. Furthermore, optimum solvent composition can be obtained by regression analysis with knowledge obtained from the seven runs experiment [14]. On the opposite hand, molecules with other positions of useful groups could have weaker or absent a quantity of websites interplay with the stationary section. The mostly used stationary phases in normal-phase chromatography are both (a) inorganic adsorbents such as silica and alumina or (b) reasonably polar chemically bonded phases having functional teams similar to aminopropyl, cyanopropyl, nitrophenyl, and diol which are chemically bonded on the silica gel help [16]. Since the stationary part in regular part chromatography is more polar than the cell part, analyte retention is enhanced as the relative polarity of the stationary phase will increase and the polarity of the cellular section decreases. Retention also will increase with growing polarity and number of adsorption websites within the column. This means that retention is stronger on adsorbents with larger particular floor areas (surface space divided by the mass of adsorbents). Generally, the energy of interplay with analytes increases within the following order: cyanopropyl < diol < aminopropyl < silica alumina sta< tionary phases. Basic analytes are typically very strongly retained by the silanol groups in silica gel, and acidic compounds show increased affinities to aminopropyl silica columns. Aminopropyl and diol-bonded stationary phases choose compounds with proton�acceptor or proton�donor functional teams as in alcohols, esters, ethers, and ketones, whereas dipolar compounds are often extra strongly retained on cyanopropyl silica than on aminopropyl or diol silica. Alumina part has distinctive utility in the separation of compounds with different numbers or spacing of unsaturated bonds. This is because alumina favors interaction with electrons and often yields higher selectivity than silica [16]. Despite the numerous desirable properties of silica, its restricted pH stability (between 2 and 7. Hence, other inorganic supplies corresponding to alumina, titania, and zirconia, which not only have the specified physical properties of silica but in addition are secure over a large pH range, have been studied. Recently, Unger and associates [22] have chosen a completely new approach where they use mesoporous particles based mostly not solely on silica but in addition on titania, alumina, zirconia, and alumosilicates. However, predicting solute retention on bonded stationary phases is harder than when silica is used. This is essentially due to the complexity of associations potential between solvent molecules and the chemically and physically heterogeneous bonded phase floor. Several models of retention on bonded phases have been advocated, but their validity, significantly when blended solvent techniques are used as mobile part, may be questioned. Several research have shown that this model is applicable for diol- [23, 24], cyano- [23, 25], and aminopropyl-bonded silica [26, 27]. A main concern in benorylate manufacturing is the potential formation of impurities suspected of inflicting allergic unwanted side effects; therefore monitoring of this step is crucial to high quality management. However, an analytical technique primarily based on the use of normal-phase chromatography with alkylnitrilebonded silica because the stationary phase supplied an ideal solution to the analysis. Optimal selectivity was achieved with a ternary solvent system: hexane�dichloromethane�methanol, containing zero. The method was validated and decided to be reproducible based on precision, selectivity, and repeatability. Anthraquinone is an important intermediate within the manufacturing of varied dye merchandise but additionally is used as a catalyst in the isomerization of vegetable oils. It is produced in great amount by Friedel�Crafts reaction of phthalic anhydride with benzene within the presence of AlCl3 catalyst. The technique was successfully utilized to monitor the reaction conversion and likewise to determine the steadiness of 9,10-anthraquinone on the specified storage circumstances. Typical chromatogram of a reaction mixture collected in the course of the course of response of phthalic anhydride with benzene within the presence of AlCl3, as catalyst. Peaks: 1, benzene; 2, anthraquinone; three, phthalic anhydride; 4, maleic anhydride; 5, unknown. In the synthesis of leukotriene D4 antagonist, accurate quantitation of mesylate intermediate is essential for course of optimization. Owing to its inherent instability, analysis of mesylate intermediate have to be carried out beneath normal-phase conditions with nonprotic solvents; however, significant cyclization of mesylation was nonetheless observed in such condition at room temperature. The authors concluded that the on-column response of the mesylate was silicacatalyzed cyclization.