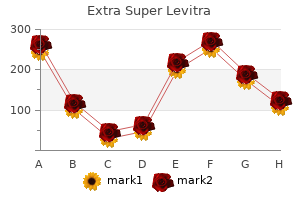
Extra Super Levitra
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Extra super levitra 100 mg with mastercard, impotence treatment options".
N. Kippler, MD
Vice Chair, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Titration is required erectile dysfunction after 60 discount extra super levitra 100 mg with mastercard, as treatments that enhance neurogenic orthostatic hypotension can also unmask or exacerbate supine hypertension what age does erectile dysfunction usually start proven extra super levitra 100 mg. The discovering of antibodies in opposition to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor within the autonomic ganglia in lots of of those sufferers has established autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy as a definable illness entity erectile dysfunction statin drugs 100 mg extra super levitra best. Autoimmune neuromyotonia is characterized by peripheral nerve hyperexcitability erectile dysfunction young adults treatment extra super levitra 100 mg buy fast delivery, insomnia, fluctuating delirium, and prominent dysautonomia with hyperhidrosis and orthostatic intolerance. Paraneoplastic autonomic neuropathies, which can predate the diagnosis of malignancy, are a uncommon epiphenomenon of malignancy, most regularly small cell lung carcinoma (Chapter 182),7 and may happen also in association with other cancers. Amyloidosis (Chapter 179) outcomes from the focal deposition of insoluble fibrillary proteins organized in -pleated sheet configurations within the extracellular space of varied tissues, which can embrace the vasculature of peripheral autonomic nerves and sympathetic ganglia. Amyloid neuropathy is often manifested as a painful distal small fiber sensory and extreme autonomic neuropathy. Among the infectious neuropathies, tetanus an infection (Chapter 280) causes sympathetic overactivity in a 3rd of sufferers because of the exotoxin tetanospasmin, which is taken up by peripheral nerve terminals and transported throughout synaptic junctions to attain the central nervous system. There it binds to gangliosides at presynaptic junctions to disinhibit preganglionic neurons and damages autonomic brain stem nuclei. Sympathetic hyperactivity ends in labile or persistent hypertension or hypotension, tachyarrhythmias, peripheral vasoconstriction, fever, and profuse sweating. Diphtheritic neuropathy (Chapter 276) causes bulbar weak spot and may be related to cardiovagal impairment but not normally with orthostatic hypotension. The acute cholinergic neuropathy of botulism (Chapter 280) occurs along with bulbar and generalized neuromuscular paralysis 12 to 36 hours after the ingestion of meals contaminated with the gram-positive anaerobic bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Botulinum toxin binds with high affinity to presynaptic receptors of cholinergic nerve terminals and inhibits the release of acetylcholine, thereby blocking neuromuscular and cholinergic autonomic transmission. Autonomic manifestations embrace anhidrosis, dry eyes, dry mouth, paralytic ileus, gastric dilation, urinary retention, and generally orthostatic hypotension with fluctuating blood strain and vasomotor tone. Human immunodeficiency virus infection commonly causes autonomic disturbances, notably in its advanced stages. Manifestations can embody orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, urinary dysfunction, impotency, diarrhea, and cardiac conduction defects. Perivascular mononuclear inflammatory infiltrates and neuronal degeneration in biopsy specimens of sympathetic ganglia recommend an autoimmune pathogenesis. Chagas disease (Chapter 326) causes a predominantly parasympathetic neuropathy characterised by megaesophagus, megaduodenum, and megacolon, in addition to sympathetic cardiovascular failure with cardiomegaly and conduction defects. The autonomic neuropathy develops years to a long time after major infection with Trypanosoma cruzi. Leprosy (Chapter 310), one of the most common causes of neuropathy worldwide, frequently causes peripheral autonomic neuropathy as a outcome of an immune reaction towards Mycobacterium leprae. Distal elements of the vagus nerve are affected early, and orthostatic hypotension may occur in additional superior levels. Subacute mixed degeneration from vitamin B12 deficiency (Chapter 205) ends in axonal degeneration and is often manifested as orthostatic hypotension. Autonomic neuropathy has been described in some circumstances of celiac disease (Chapter 131). Affected children cry without tears, feed poorly, lack lingual fungiform papillae, have depressed patellar reflexes, and are subject to orthostatic hypotension and autonomic storms owing to impaired baroreflex afferent neurons. Holmes-Adie syndrome, which consists of tonic pupils with asymmetrical or absent tendon reflexes, has been described in patients with Ross syndrome, a partial dysautonomia consisting of the scientific triad of unilateral or bilateral tonic pupils, tendon hyporeflexia, and segmental body anhidrosis. Some patients current with generalized autonomic failure, whereas others present with regional or system-selective autonomic dysfunction. Orthostatic hypotension and not utilizing a compensatory tachycardia (Chapter 56) is the hallmark of generalized autonomic failure. It is typically worse within the morning and aggravated by dehydration, deconditioning, prolonged standing, bodily exertion, heat, carbohydrate ingestion, or menstruation. Early symptoms typically embrace lightheadedness on arising in the morning or following a heat bathe, physical train, or a big meal. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is often accompanied by supine hypertension, and the traditional diurnal lower in blood strain throughout sleep is reversed. Other widespread symptoms embody male erectile dysfunction, decreased sweating, dry mouth, constipation, and bladder dysfunction. Gastroparesis (Chapter 127) could manifest as early satiety, nausea, anorexia, bloating, and sometimes pain and weight loss. In some cases, prescribed medicines or over-the-counter supplements are the trigger of autonomic signs and should be scrutinized fastidiously. Hyperhidrosis might improve with reduction or elimination of opioids or serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Anhidrosis could improve with the discontinuation of any medications with anticholinergic effects. In treating orthostatic hypotension, the first step is to scale back, or eliminate, if appropriate, antihypertensive, diuretic, or -receptor antagonist drugs. The objectives of treatment are to improve the time the affected person is prepared to stand without developing orthostatic signs, while concurrently avoiding extreme recumbent hypertension. Mild orthostatic hypotension usually responds to conservative measures similar to increasing oral hydration (2 to 2. Prolonged bedrest and drugs that would doubtlessly exacerbate orthostatic hypotension ought to be prevented if potential. Elevating the head of the bed by inserting 4-inch blocks beneath the head posts can improve orthostatic tolerance in some sufferers by lowering nocturnal natriuresis and stimulating the discharge of renin. Postprandial hypotension may be managed by dividing meals to avoid giant carbohydrate loads. For the therapy of extreme neurogenic orthostatic hypotension, two medication presently are accredited: midodrine (5 to 10 mg three times daily), which constricts capacitance vessels, A1 and droxidopa (100 to 600 mg thrice daily), which is an orally active artificial precursor of norepinephrine. A4 Pyridostigmine has a more modest pressor impact but is less problematic when it comes to supine hypertension. These pharmacologic measures are of variable profit, and a few patients cease taking them due to lack of symptomatic enchancment or the development of opposed reactions. A6 Nocturnal hypertension could also be minimized by avoiding pressor brokers within a number of hours of bedtime and by elevating the top of the bed. Paroxysmal hypertension in patients with arterial baroreflex denervation may improve on clonidine (0. Autonomic signs might or might not mirror a disorder of the autonomic nervous system. Panic dysfunction (Chapter 369), for instance, manifests its signs by way of a normally functioning autonomic nervous system. Some sufferers have a functional dysautonomia, by which a medical or psychosomatic condition impairs regular autonomic perform within the absence of a identified structural neurologic deficit. Examples embrace neurally mediated syncope (Chapter 56), irritable bowel syndrome (Chapter 128), and a few types of orthostatic intolerance and ache. Progressive or episodic phenomena should be distinguished from persistent and secure circumstances. Blood stress and coronary heart price should be measured with the patient resting supine and once more after standing for 1 to 3 minutes and correlated with signs. Orthostatic hypotension is outlined as a reduction in systolic blood stress of a minimum of 20 mm Hg or a discount in diastolic blood strain of no less than 10 mm Hg, with or without signs, inside 1 to 3 minutes of assuming an erect posture. Measurements taken instantly on standing may be deceptive, as a outcome of wholesome younger individuals with out orthostatic hypotension will typically exhibit transient hypotension that resolves within 30 seconds of standing. Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is often sustained with continued standing. Except in patients treated with -blockers, orthostatic hypotension with out reflex tachycardia is proof of generalized adrenergic failure. If reflex tachycardia occurs, dehydration or extreme venous pooling should be considered. Some sufferers with orthostatic intolerance on standing expertise an irregular rise in coronary heart fee rather than a drop in blood strain. Postural tachycardia syndrome9 is outlined as a sustained enhance in heart price by greater than 30 beats per minute in adults (40 beats per minute in adolescents) and infrequently higher than 120 beats per minute when standing. Appropriate laboratory testing depends on the kind and distribution of autonomic dysfunction.
When the trigeminal nerve is involved impotence husband extra super levitra 100 mg order visa, spread to the inside of the eye (uveitis) is more than likely if vesicles are current within the inside nook of the eyelids or on the nostril erectile dysfunction treatment south africa extra super levitra 100 mg discount amex, especially the tip of the nostril (Hutchinson sign) erectile dysfunction va disability purchase extra super levitra 100 mg on line. In sufferers with moderate to extreme skin involvement erectile dysfunction treatment in bangalore generic extra super levitra 100 mg line, treatment may be began with oral acyclovir (800 mg orally five occasions per day for 7 to 10 days) or valacyclovir (1 g three times a day for 10 to 14 days). Like herpes simplex virus, herpes zoster can have an effect on the cornea and sufferers ought to be monitored for recurrent illness. Chlamydial Conjunctivitis Adult inclusion conjunctivitis is a chronic conjunctivitis attributable to sexual transmission of Chlamydia trachomatis (Chapter 302). Oral erythromycin (500 mg orally, 4 occasions day by day for 7 days) or azithromycin (1 g orally twice day by day for 7 days) is required. It causes an entropion, inversion of the eyelashes (trichiasis), corneal vascularization, and opacification. Topical erythromycin or tetracycline, twice day by day for 3 to 4 weeks, can be effective, however surgical epilation or eyelid reconstruction may be required. Pseudomonal and Gonococcal Keratitis Keratitis, which is inflammation of the corneal stroma, may be caused by unfold of pathogens internally from a corneal ulcer. Small yellow choroidal lesions may be seen, and retinal periphlebitis could happen secondarily. To avoid intraocular spread, urgent and aggressive antibiotic treatment is necessary. Another gram-negative explanation for a virulent keratitis is Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Chapter 282), particularly in neonates. Corneal an infection is accompanied by copious tearing and a attribute hyperpurulent discharge. Prompt remedy with topical irrigation (normal saline to take away mucopurulent material) and penicillin G (100,000 units/kg/day given intravenously in four divided doses for 7 days) is essential to prevent corneal perforation. In tertiary syphilis, the miotic Argyll Robertson pupil reacts poorly to light however briskly to lodging. The presumptive prognosis is made on the characteristic intense, retinal, wedgeshaped response, with considerable exudates and hemorrhages, giving the phrases "pizza pie retinitis" and "hemorrhagic cottage cheese retinitis" to the entity. Treatment is with antiviral drugs: ganciclovir (5 mg/kg intravenously twice every day, two to three times per week), foscarnet (90 mg/kg intravenously twice daily, twice per week), or cidofovir (5 mg/kg intravenously, weekly for 3 weeks) with follow-up upkeep. Intravitreal injections with an appropriately lowered dose are also utilized in selected cases. When patients are examined early of their illness course, they might solely have a slight epitheliopathy and have ache out of proportion to findings on examination. Swimming or using fresh water with contact lens wear can often be elicited within the historical past. Using a confocal microscope, the acanthamebic parasite can be noticed clinically as a pearshaped cyst (11 to 15 �m). The lens doubles in quantity between start and age 70 years as new lens "fiber cells" are laid down on the exterior side of the lens cortex, beneath the lens capsule. As the process progresses, the lens loses its transparency, beginning at the heart of the lens (nuclear sclerosis). The concurrent change in density of the lens nucleus could alter the optical traits of the eye to cause acquired nearsightedness ("second sight"). Ultimately, the cataract might become so dense that cataract surgical procedure is important to restore vision. Prognosis for restoration of imaginative and prescient is excellent, depending on the operate of the retina. Glaucoma Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy in which progressive harm to retinal ganglion cells and their axons results in the attribute lack of optic nerve tissue and damage to the peripheral and central visual area. Aqueous humor is produced by the nonpigmented ciliary epithelium of the pars plicata of the ciliary physique. Aqueous fluid leaves the attention through the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral pathways into the venous circulation. If the elevated intraocular stress is high enough or is present lengthy enough, ganglion cells within the retina are damaged, inflicting loss of their axons. Loss of axons can greatest be appreciated clinically at their normal exit from the eye, the optic disc. Bulk lack of axons will lead to enlargement of the optic cup, which is recorded as increase in the cup-to-disc ratio. Intraocular stress is the principal danger factor for the onset and development of glaucoma. Additional threat components for glaucoma embrace African ancestry, older age, low blood strain, genetic predisposition, disc hemorrhage, myopia, and anterior section abnormalities and systemic associations. The most typical kind of glaucoma in elderly people is main open-angle glaucoma. For many patients, the primary symptom may be problem studying, loss of contrast sensitivity, or glare. Peripheral visual fields may be decreased significantly before the patient notes lack of operate. Most circumstances of main open-angle glaucoma are identified during routine eye examinations, either Toxoplasmic Retinitis Toxoplasma gondii (Chapter 328) causes both a congenital and an acquired retinochoroiditis, which is extra widespread in immunosuppressed patients. The lesions begin as an acute retinitis that atrophies centrally and pigments peripherally because it heals. When energetic lesions are within the macula or a severe vitreitis causes a minimum of a two-line lower in vision, four to 6 weeks of quadruple therapy (pyrimethamine, 200 mg oral loading dose, then 25 mg orally day by day; folinic acid, 10 mg orally every other day; sulfadiazine, 2 g oral loading dose, then 1 g four instances daily; and oral corticosteroids. Alternative regimens might include trimethroprimsufamethoxazole (800/160 mg orally twice daily), clindamycin (150 to 450 mg orally three to 4 occasions daily), or atovaquone (1 g oral loading dose, then 500 mg daily). Fungal Endophthalmitis Fungal endophthalmitis is infrequent (7% of microbial endophthalmitis) but is a doubtlessly disastrous infection of the within of the eye, typically resulting in blindness. The major organisms are Candida, Coccidioides, and Aspergillus species, which may gain access inside the attention both by traumatic introduction or by way of hematogenous unfold. Multiple abscesses are most likely to be brought on by fungi, whereas a solitary abscess is extra probably brought on by bacteria. Average intraocular stress is usually at or under 21 mm Hg, however exceptions exist relying on corneal thickness (causing artifacts of measurement in patients with excessively thin or thick corneas) and genetic disposition. The diagnosis of glaucoma is confirmed by characteristic visible area loss as decided by automated perimetry. The therapy objective is to reduce intraocular pressure, initially with pharmacologic agents: -blockers. Applying energy to the buildings of the trabecular meshwork with a laser (laser trabeculoplasty) usually leads to years of management of intraocular pressure, and this procedure could turn out to be first-line therapy because it might possibly maintain normal stress without drugs. A7 In resistant instances, mechanical filtration is accomplished surgically by bypassing the trabecular meshwork either by creating a fistula (trabeculectomy) between the anterior chamber and the episcleral tissue or by implanting an artificial filtration system (a tube-shunt) A8 from the anterior chamber via the sclera into a group reservoir positioned on the equator of the eye within the gentle tissues of the orbit. Secondary causes of elevated intraocular stress also can lead to glaucomatous nerve damage. The most typical is pseudoexfoliation syndrome, a genetically determined biochemical abnormality of the basement membrane protein, fibrillin. The syndrome occurs amongst people all through the world but is very outstanding in Scandinavians and Saudi Arabians. Affected people are identified by accumulation of irregular fibrillogranular materials (exfoliative material) on the surface of the crystalline lens, most simply seen within the pupillary house or pupillary border. Pseudoexfoliative glaucoma tremendously will increase the chance for developing open-angle glaucoma. Alternatively, symptoms may develop over a protracted period of time with few specific symptoms. The threat components for angle-closure glaucoma are based on the anatomic configuration of the components of anterior chamber. As the crystalline lens increases in volume with time, the iris is displaced anteriorly. At some level, the posterior floor of the iris may are out there in relatively tight contact with the anterior floor of the lens. Aqueous flow is restricted, and fluid accumulates within the posterior chamber, the place it displaces the diaphanous peripheral iris anteriorly. When the peripheral iris is out there in contact with the posterior cornea, the anterior chamber angle is all of a sudden occluded. The intraocular pressure could increase from 21 mm Hg to 50 to 70 mm Hg (nearly equaling diastolic arterial pressure). The symptoms of acute angle closure might include extreme pain, which may be poorly localized to the eye, nausea, and vomiting. Most sufferers require a laser iridectomy prophylactically within the second eye to prevent angle-closure glaucoma.
Blood macrophages start to reach the infarcted tissue erectile dysfunction protocol guide 100 mg extra super levitra discount overnight delivery, and neovascularization peaks after about 2 weeks erectile dysfunction kya hai discount 100 mg extra super levitra otc. Macrophagemediated elimination of cellular debris peaks at about three to 4 weeks after the infarct erectile dysfunction pills in india extra super levitra 100 mg purchase amex. Because the mind has no reserve power provide erectile dysfunction hypertension drugs extra super levitra 100 mg order on-line, energy-dependent neuronal and glial processes stop soon after acute deprivation of blood and oxygen. Calcium ions enter depolarized neurons and glia, the place they activate second messengers, including lipases and proteases, thereby releasing free fatty acids and generating free radicals that degrade cellular organelles and membranes. Depolarized neurons also launch high ranges of excitatory neurotransmitters, similar to glutamate into synapses, which outcomes in additional neuronal depolarization and calcium entry. Once this cascade has been initiated, neurons should degenerate over time by apoptosis (programmed cell death) even if blood circulate is restored. Although promising in the laboratory, all attempts to block the ischemic cascade pharmacologically have failed in medical trials to date. Subarachnoid hemorrhage, which is bleeding between the pial and arachnoid coverings over the mind, is most commonly related to a ruptured aneurysm (Chapter 380). Cerebral aneurysms may happen spontaneously or be acquired because of an infection or trauma. Noninfectious aneurysms are typically located at department points of major cerebral arteries: anterior cerebral artery�anterior communicating artery, inside carotid artery�posterior communicating artery, center cerebral artery bifurcation, basilar artery tip. Initial mind damage could be caused by an acute improve in intracranial stress, with delayed ischemic damage associated to the event of vasospasm after 7 to 10 days. Interference with the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid although the arachnoid granulations can lead to speaking hydrocephalus. Clot within the third or fourth ventricle or cerebral aqueducts may cause obstructive hydrocephalus. The most common causes of intracerebral parenchymal mind hemorrhages are hypertension (Chapter 70) and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Myriad different potential vascular and nonvascular causes, together with vascular malformations, vasculitis (Chapter 254), venous sinus thrombosis, and coagulopathies (Chapters 163, 164, and 165), are much less widespread. Hypertension-related intracerebral hemorrhage occurs in typical areas of the mind. In distinction, intracerebral hemorrhage related to cerebral amyloid angiopathy is usually lobar and located nearer to the cortical floor. Without sequential neuroimaging studies exhibiting an preliminary area of ischemic injury, lobar hemorrhages could also be difficult to distinguish from a hemorrhagic infarction. Symptoms are usually present when the Pao2 abruptly falls to lower than 40 mm Hg. Increases in cerebral blood move can partially compensate for slow declines in Pao2, which can still trigger symptoms with further or rapid reductions. The brain on this area, termed the penumbra, is electrically quiescent and contributes to the ensuing neurologic deficit. Because the pH of the extracellular fluid in the penumbral zone is low, vessels are maximally dilated and the cerebral autoregulatory response is inoperative. When neurons and glia are injured by ischemia, power metabolism fails and the cells can no longer preserve regular ion gradients between the intracellular and extracellular compartments. Vasogenic edema, which may happen because of disruption of the blood-brain barrier because of damage to the endothelium, permits giant molecules to move by way of the blood-brain barrier and acquire entry to the mind. In sufferers with ischemic stroke, the event of cytotoxic edema can result in a rise in intracranial stress and, when extreme, herniation. In chosen sufferers, craniotomy could be thought of to relieve the stress until the edema subsides. Neurons, glia, and endothelial cells are also broken within the setting of intracerebral hemorrhage. The hemorrhage itself is a space-occupying lesion that may additionally be associated with each cytotoxic and vasogenic edema. Mass effect from cerebellar hemorrhages can compress the fourth ventricle (thereby leading to obstructive hydrocephalus), compress the mind stem (thereby compromising the reticular activating system and impairing consciousness), or trigger herniation. Emergent evacuation of cerebellar hemorrhages could be life-saving and depart surviving patients with little or no long-term useful impairment. Effect of routine low-dose oxygen supplementation on demise and disability in adults with acute stroke: the stroke oxygen research randomized medical trial. Effect of therapeutic hypothermia on survival and neurological end result in adults suffering cardiac arrest: a scientific evaluate and meta-analysis. Effect of prehospital induction of delicate hypothermia on survival and neurological status amongst adults with cardiac arrest: a randomized scientific trial. Cognitive perform in survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest after target temperature management at 33 degrees C versus 36 degrees C. Defining optimum brain health in adults: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Which of the following arteries is often the primary intradural department of the interior carotid artery The recurrent cerebral artery is generally a department of the anterior cerebral artery. Which of the following conditions is associated with the best populationattributable risk of stroke Sedentary life-style Answer: C Each of the listed circumstances and life-style components is associated with a rise within the risk for stroke. The left frequent carotid artery mostly arises from which of the following constructions Thyrocervical trunk Answer: C the left common carotid artery mostly arises instantly from the aortic arch. In some people, it might come up from the proximal portion of the brachiocephalic trunk ("bovine" anatomy). The definition of ischemic stroke is brain, spinal twine, or retinal cell demise attributable to ischemia with neuropathologic, neuroimaging, or clinical evidence of permanent damage. Overall, roughly 85% of strokes are related to ischemic illness, with 44% attributable to atherosclerosis, 21% to cardiogenic embolism, and 20% to small-vessel illness. Stroke (ischemic and hemorrhagic) is the second main explanation for demise worldwide and the fifth main explanation for dying in the United States. In addition to age, race or ethnicity, and family history, certain lifestyle factors and medical circumstances enhance the chance of stroke (Chapter 378; Table 379-1). Of these, hypertension is the one most necessary (Chapter 70; Table 379-1), and the chance of stroke increases with increasing blood pressure with no threshold impact. Diabetes (Chapter 216) is associated with a doubling of the chance of stroke (Table 379-1). Atrial fibrillation (Chapter fifty eight; Table 379-1) is associated with up to 25% of ischemic strokes, with absolutely the threat varying by concomitant danger factors. Extracranial carotid artery stenosis is present in 5 to 10% of people older than sixty five years and is associated with about 10% of all ischemic strokes. Untreated asymptomatic carotid stenosis carries solely a 1 to 2% annual threat of stroke, and the risk is decreased to as low as zero. Stroke can also be a complication of sickle cell disease (Chapter 154), with threat dramatically decreased with transfusion remedy in high-risk kids. Unlike with coronary coronary heart disease, the general association between high cholesterol focus and the danger of stroke is less certain. Ischemic stroke danger is associated with larger ranges of total ldl cholesterol, whereas the danger of hemorrhagic stroke is elevated with decrease cholesterol levels. Other factors related to the risk of stroke include migraine headaches with aura (Chapter 370), notably in ladies who smoke and are receiving oral contraceptives; elevated homocysteine level; excessive lipoprotein (a) stage; postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy (Chapter 227); coagulation issues (Chapter 73); systemic an infection (Chapter 67); renal impairment (Chapter 121); low vitamin D levels (Chapters 205 and 231); and environmental factors, together with excessive ranges of air air pollution. The damage could also be focal (related to occlusion of a single artery), multifocal (related to occlusion of several arteries), or diffuse. In the absence of an inflammatory illness such as vasculitis or different uncommon circumstances, simultaneous involvement of multiple vascular distribution suggests a proximal source of embolism. Involvement of a single vascular territory may be because of either local steno-occlusive illness. Guidelines for the first prevention of stroke: a suggestion for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Secondary prevention is geared toward basic risk components and particular therapies depending on stroke etiology. The ischemia could also be triggered when progressive stenosis at the website of an atherosclerotic plaque results in hemodynamic compromise affecting distal mind tissue.