
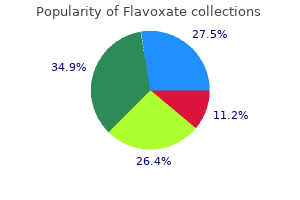
Flavoxate
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Generic flavoxate 200 mg with visa, xanax spasms".
H. Pranck, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Professor, Florida International University Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine
Affective regulation in trichotillomania: Evidence from a largescale internet study spasms prednisone buy 200 mg flavoxate overnight delivery. Optimizing psychological interventions for trichotillomania (hairpulling disorder): An update on current empirical status muscle relaxer kidney discount flavoxate 200 mg amex. A preliminary investigation of acceptance and commitment therapy as a treatment for continual pores and skin selecting spasms of the esophagus 200 mg flavoxate discount fast delivery. Disordered reward processing and useful connectivity in trichotillomania: A pilot examine muscle relaxant used during surgery proven 200 mg flavoxate. Sequential software of main habitreversal elements to deal with motor tics in kids. Bodyfocused repetitive behaviors are ordinary in nature, involving repetitive motor responses that often end in removing of a half of the physique. Body focused repetitive behaviors can start at any age, with some research suggesting bi or trimodal onset. Oral exploration or ingestion of picked or pulled hair, pores and skin, or nail is also frequent (Snorrason, Belleau, & Woods, 2012). Research in hair pulling and skin selecting means that most people have interaction in each types of behavior but can determine a dominant type (Flessner, Woods, et al. Emotion regulation is the ability to experience, differentiate between, and respond to the full range of emotions (Gratz & Roemer, 2004). Adaptive emotion regulation is believed to contain altering the Body-Focused Repetitive Behavior 311 period or depth of emotional arousal to match the context appropriately, sustaining aim directed behavior, and inhibiting impulsive conduct (Gratz & Roemer, 2004). In addition, they found that people with pathological pores and skin picking are generally more emotionally reactive and have issue with emotion regulation. Shusterman, Feld, Baer, and Keuthen (2009) found that those that pull skilled more problem controlling emotions than non pullers, and that this problem was correlated with severity of the disorder. This analysis can additionally be primarily based on relatively homogeneous samples which would possibly be predominantly grownup, female, and Caucasian. The behaviors are physically stimulating; this stimulation may be rewarding or pleasurable in those who are understimulated, or can provide distraction for individuals who are overstimulated (Penzel, 2002). Walther are at present getting used to test hypotheses about etiological elements such as genetic, neurochemical, and neurocircuitry vulnerabilities and mechanisms (Kalueff, La Porte, & Bergner, 2010). In help of this model, some analysis suggests that adults with hair pulling could have related functional connectivity and mind activation patterns to anticipated monetary reward as those with nicotine, alcohol, and cocaine dependence (White et al. These patterns indicated (a) overactivation to rewarding outcomes, suggesting that pulling could additionally be strengthened to an exaggerated degree, and (b) less deactivation to loss outcomes, suggesting that the unfavorable consequences of pulling bay be underrepresented. Finally, analysis on household history signifies considerably greater rates of substance use problems within the firstdegree family members of these with hair pulling in comparability with controls (Schlosser, Black, Blum, & Goldstein, 1994). Habit reversal remedy has three main components-awareness training, competing response coaching, and social assist coaching. Early habit reversal treatment manuals referred to as for a number of further elements. In some ways, monitoring and awareness training function an extension of functional evaluation by providing additional details about antecedents and penalties of the conduct. This knowledge can be essential for the subsequent stage of remedy, stimulus control (Mansueto et al. Approaches for stimulus management are selected primarily based on maintaining elements recognized in the useful evaluation. Strategies that block the onset of the behavior, corresponding to wearing gloves or using petroleum jelly. For example, since trying in mirrors typically cues hair pulling episodes, eradicating mirrors totally is usually a profitable technique to scale back pulling. Similarly, easy postural changes, corresponding to suggesting a shopper sit in the middle of a sofa if hair pulling typically occurs when leaning against the arm of the couch, could additionally be carried out. Once stimulus control procedures have been applied, competing response training can start. Several research point out that the competing response is the ingredient most central to the efficacy of treatment. The competing response for mouth or cheek chewing often entails holding the jaw closed. Though Azrin and Nunn (1973) initially proposed a threeminute period for the competing response, Twohig and Woods (2001) discovered that a oneminute length is equally effective. The position of the social help particular person is to present reminders to use the competing response and to present reinforcement when the shopper has tried or applied the competing response. Though there have been significant limitations to this research in phrases of generalizability. Cognitive behavioral skills included stress administration, rest strategies, thought stopping, and cognitive restructuring. For example, those who pull hair privately in the toilet could also be encouraged to have interaction in behaviors according to their self recognized values in response to the urge to pull (call a good friend, be present with loved ones, etc. Furthermore, decreases in experiential avoidance had been associated with larger reductions in hair pulling severity, lending evidence to the notion that further techniques designed to handle the targeted components of hair pulling may be useful. All members benefited from remedy, with an average reduction in hair pulling severity of over 88%. At threemonth followup, two of the participants had maintained features, two skilled some return of symptoms, and the final participant demonstrated signs just like baseline. Consistent with Woods, Wetterneck, and Flessner (2006), decreases in experiential avoidance had been related to decreases in hair pulling severity. Furthermore, in those people that skilled a return of hair pulling symptoms, corresponding will increase in experiential avoidance were noticed. It must be famous that the aforementioned research used small pattern sizes and only one used a randomized examine design. A handbook describing this strategy for the remedy of hair pulling is on the market to clinicians (Woods & Twohig, 2008) and is at present being tested in a big randomized control trial (ClinicalTrials. All 5 participants experienced significant adjustments in pulling or selecting signs. Although individuals did expertise symptom discount throughout phases that concerned only one treatment part, most symptomatic change occurred during phases that included both treatment components. Significant decreases in hair pulling severity, impairment, anxiety, and melancholy had been reported at posttreatment. Furthermore, adjustments in emotion regulation had been related to modifications in hair pulling severity. Gains had been typically maintained at threemonth and 6 month followup (Keuthen et al. Thus, as in Woods, Wetterneck, and Flessner (2006), preliminary knowledge were supportive of the notion that addressing "targeted" or emotion regulation elements of hair pulling with extra techniques may be beneficial. Body-Focused Repetitive Behavior 317 Preliminary proof in hair pulling means that styles may be influenced by developmental factors. In that study, kids exhibited a larger proportion of computerized pulling relative to centered pulling. Automatic pulling remained relatively stable across cohorts, however focused pulling elevated dramatically in the adolescent group and remained high in the different cohorts, with the exception of the middle to late adulthood cohort (aged 49�69) cohort, where the proportion of automated to targeted pulling was equal. Thus, though the research was limited because of its crosssectional as opposed to a longitudinal design, preliminary evidence means that pulling types might change over time. Authors hypothesized that biological components, such because the onset of puberty and the perimenopause window, may contribute to changes in pulling style. In a examine examining hair pulling in younger youngsters (aged 10 and below), Walther et al. Children within the pattern also skilled decrease rates of antecedent pressure and ensuing gratification/relief, according to a extra computerized pulling style. Furthermore, kids experienced much less impairment and fewer cooccurring psychiatric situations than older samples. Not surprisingly, some researchers have instructed that treatment choice should be dictated, partially, by developmental components. Developmental concerns may factor into whether using these additional techniques is advisable. Thus, developmentally applicable modifications may be required if such methods are attempted. Adaptations to functional assessment to rely less completely on the shopper could also be helpful. For instance, the clinician can incorporate structured practical evaluation measures. Walther video), or create situations in which the problem behavior is more and fewer likely to happen to check hypotheses about maintaining elements.
Syndromes
- Loss of short-term memory (recent events)
- Allergic reaction (such as allergic rhinitis, hay fever, or a bee sting)
- Clumsiness
- Swallowing difficulty
- Echocardiogram
- End-stage kidney disease
- Breast cancer
Multidimensional assessment of emotion dysregulation: Development spasms during sleep discount flavoxate 200 mg with visa, issue construction spasms while eating flavoxate 200 mg line, and preliminary validation of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale muscle relaxant shot 200 mg flavoxate discount mastercard. Antecedent and response centered emotion regulation: Divergent penalties for experience muscle relaxant over the counter buy flavoxate 200 mg mastercard, expression, and physiology. Transdiagnostic treatment of bipolar dysfunction and comorbid nervousness with the Unified Protocol: A clinical replication sequence. Experiential avoidance and behavioral problems: A useful dimensional strategy to analysis and treatment. Inefficiency of emotion regulation as vulnerability marker for bipolar dysfunction: Evidence from healthy people with hypomanic character. Induced ruminative and mindful consideration in everyday life: An experimental ambulatory evaluation research. Childhood maltreatment will increase danger for personality disorders during early maturity. Age of onset of in affective dysfunction: Its correlation with hereditary and psychosocial components. Bipolar and unipolar despair: A comparison of clinical phenomenology and psychosocial predictors. Causal relationship between annoying life events and the onset of main melancholy. Dialectical habits therapy for borderline personality dysfunction: A metaanalysis using combined results modeling. Metaanalysis of the affiliation between two polymorphisms within the serotonin transporter gene and affective issues. Severe temper dysregulation, irritability, and the diagnostic boundaries of bipolar in youths. Association of anxietyrelated traits with a polymorphism within the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Social rhythm disruption and tense life events in the onset of bipolar and unipolar episodes. Poorer sleep quality is related to lower emotionregulation ability in a laboratory paradigm. The affiliation between meditation apply and therapy outcome in mindfulnessbased cognitive remedy for bipolar dysfunction. The therapy of maladaptive shame in borderline character dysfunction: A pilot examine of "reverse motion. Transdiagnostic remedy of borderline personality dysfunction with comorbid disorders: A medical replication sequence. The function of adverse affectivity and adverse reactions to emotions in predicting outcomes in the unified protocol for the transdiagnostic remedy of emotional problems. Comparing mindfulness based mostly intervention methods: Sitting meditation, physique scan, and mindful yoga. Mindfulnessbased cognitive therapy for melancholy: A new approach to preventing relapse. The impact of the cognitive type of acceptance on negative mood in a recovered depressed sample. Effects of the dialectical behavioral therapymindfulness module on attention in patients with borderline persona disorder. Mood dysregulation throughout developmental psychopathology: General ideas and disorder particular expressions. A pilot examine of cognitive�behavioral remedy of insomnia in individuals with delicate melancholy. Crosssectional and longitudinal relations between affective instability and despair. The on a regular basis experience of adults with main depressive disorder: Examining emotional instability, inertia, and reactivity. Affective instability: Measuring a core function of borderline persona disorder with ecological momentary assessment. Cognitive reappraisal and acceptance: An experimental comparison of two emotion regulation strategies. Unfortunately, entry to and dissemination of enough evaluation and treatment practices are lacking (Cohen et al. To do that in an approachable and instructive method, we must first understand the theoretical foundation of those behaviors and the potential functions that hair pulling would possibly serve. For instance, hair pulling has broadly been theorized to be impacted by and to serve a wide selection of functions together with cognitive, affective, motoric, sensory, and environmental (Mansueto, Golomb, Thomas, & Stemberger, 1999). Further, two disparate styles of pulling-automatic and focused- may serve differing features each between and within people (Christenson & Crow, 1995; Du Toit, van Kradenburg, Niehaus, & Stein, 2001; Flessner, Conelea, et al. Neuroanatomical and Neuropsychological Bases Several notable neuroanatomical anomalies. For occasion, dysregulation such as decreased response monitoring (Roberts, Stanley, Franklin, & Simons, 2014) may be implicated within the occurrence of automated pulling, while variations in inhibitory control may be intrinsic to pulling normally (Brennan, Francazio, Gunstad, & Flessner, 2015). Rather, several elements may interweave to both create and perpetuate such abnormalities in neurological functioning and behavioral presentations. Often people continue to pull their hair regardless of significant psychosocial repercussions. Moreover, behavioral reports from case studies have suggested that pulling perpetuates even under solitary conditions. For instance, reduction from pulling in response to rigidity exemplifies successful avoidance of disagreeable stimuli, a type of robust automatic adverse reinforcement. For example, focused pulling, specifically, may provide negative reinforcement and relief via distraction from disagreeable thoughts or emotional experiences. Automatic pulling, contrarily, is instead most related to states similar to boredom (Shusterman, Feld, Baer, & Keuthen, 298 E. Other theories have also been discussed, incorporating alexithymia (difficulty in identifying, describing, tolerating, and regulating emotional arousal;. The brief review above, nevertheless, also clearly presents the case that too little research has been carried out inside these domains to present definitive conclusions concerning models or mechanisms of the disorder. Such a sophisticated and interwoven etiology could help to clarify the tenacious nature of the disorder and its relative resistance to extinction. The following part supplies a thoughtful review of these therapies, expounding the core mechanisms underlying every. Alternatively, proprioceptive cues, such as hand and physique positioning, movements, or tactile sensations, can also pair alongside reinforcement schedules to turn out to be conditioned triggers for pulling (Mansueto, Stemberger, Thomas, & Golomb, 1997; Skinner, 2014). For example, feedback from sensorymotor methods similar to pleasurable tactile sensations. Therefore, the following evaluation of the core Mechanisms of Treatments for Trichotillomania 299 remedy parts draws primarily from singlesubject research and groupbased research. As such, the inclusion of competing response training-the practice of behaviors incompatible with pulling. For example, emotions or cognitions could serve as antecedents for targeted pulling, while premonitory urges and tactile sensations may be the stimuli of interest for automatic pulling (Franklin, Edson, Ledley, & Cahill, 2011). Extinction of undesirable behaviors is then targeted via methods to interrupt and eventually stop urges or precise pulling. Participant Factors ated with longterm upkeep of features (Falkenstein, Rogers, Malloy, & Haaga, 2014; Keijsers et al. Also of importance to consider is the potential impact of the familial setting. For example, Falkenstein and colleagues (2014) observed fewer positive aspects in grownup clients from ethnic minorities than nonminority purchasers when using webbased interventions-a discrepancy which disappeared following the initiation of in person therapy. The effect of behavioral therapies can also be contingent on therapeutic dosing and specific treatment parts. Further, clinicians ought to provide and encourage motivational enhancements tailor-made specifically to individual purchasers. Sequencing Treatment for Hair Pulling Disorder It is imperative to account for particular person client elements and situational influences each time 302 E. To this must be paired a stable understanding of the proof behind the components of profitable therapy, along with the flexibility to apply them as greatest wanted for a given shopper. For instance, although analysis has but to systematically look at differential intervention response based mostly on pulling fashion, proof means that proposed functions. What follows is an outline of these practical mechanisms and their potential impact on the remedies and therapy predictors described beforehand, in addition to instructed modifications to handle potential challenges. Emotion Regulation Deficits As discussed previously, present literature additionally suggests that emotion may drive and/or be pushed by hair pulling behavior (in explicit, targeted pulling; Diefenbach et al.
Syndromes
- No genetic or chromosome problems were seen in your baby
- H. pylori tests
- Convallarin
- Skin sore (ulcer)
- Medicines to raise blood pressure if it drops too low
- From another part of your body (usually around your pelvic bone). This is called an autograft. Your surgeon will make a small cut over your hip and remove some bone from the back of the rim of the pelvis.
- Left arm?
- Bleeding or blood pooling where the catheter is inserted
Expectancy learning and evaluative learning in human classical conditioning: Affective priming as an oblique and unobtrusive measure of conditioned stimulus valence muscle relaxant walgreens discount flavoxate 200 mg visa. Testing the disgust conditioning principle of foodavoidance in adolescents with recent onset anorexia nervosa muscle relaxant veterinary flavoxate 200 mg discount mastercard. A preliminary investigation of the efficacy of disgust exposure strategies in a subclinical population with blood and injection fears muscle relaxant triazolam flavoxate 200 mg purchase visa. Beyond fear and disgust: the function of (automatic) contaminationrelated associations in spider phobia muscle relaxant hamstring flavoxate 200 mg purchase fast delivery. Domainspecific and generalized disgust sensitivity in blood� injection�injury phobia: the applying of behavioral approach/avoidance duties. Fear is fast in phobic individuals: Amygdala activation in response to fearrelevant stimuli. The connection between disgust and obsessions and compulsions in a nonclinical pattern. Looking past fear: the extinction of different feelings implicated in anxiety disorders. Distinct neural correlates of washing, checking, and hoarding symptom dimensions in obsessive�compulsive dysfunction. Embracing the repulsive: the case for disgust as a functionally central emotional state in the theory, follow, and dissemination of cognitive�behavioral remedy. Interoceptive publicity for disgust in the therapy of emetophobia: A case series. Disgust and interpersonal experiences: the advanced emotional experience of rejection. Emotional responses to meals, body dissatisfaction and different eating disorder options in kids, adolescents and young adults. Voluntary hyperventilation within the remedy of panic disorder�functions of hyperventilation, their implications for respiratory training, and proposals for standardization. Disgust sensitivity as a predictor of obsessive� compulsive contamination signs and related cognitions. Assessment of disgust sensitivity in children with an age downward version of the Disgust Emotion Scale. Developing an implicit measure of disgust propensity and disgust sensitivity: Examining the position of implicit disgust propensity and sensitivity in obsessive�compulsive tendencies. Fears, phobias, and preparedness: towards an advanced module of concern and worry studying. Alleviation of moral disgust, disgrace, and guilt in posttraumatic stress reactions: An evaluation of complete distancing. Evaluative studying and emotional responding to fearful and disgusting stimuli in spider phobia. Risk and resiliency in posttraumatic stress disorder: Distinct roles of anxiety and disgust sensitivity. The Disgust Propensity and Sensitivity Scale�Revised: Psychometric properties and specificity in relation to nervousness disorder signs. Is disgust associated with Disgust in Psychopathology: Mechanisms and Treatment 501 psychopathology Specificity of disgust sensitivity in the prediction of worry and disgust responding to a quick spider exposure. Core, animal reminder, and contamination disgust: Three kinds of disgust with distinct persona, behavioral, physiological, and clinical correlates. Multimodal assessment of disgust in contaminationrelated obsessive� compulsive dysfunction. Disgust: Characteristic features, social manifestations, and clinical implications. Examination of the decline in concern and disgust throughout exposure to threatrelevant stimuli in blood� injection�injury phobia. The relation between fearfulness, disgust sensitivity and religious obsessions in a nonclinical sample. The structure of disgust: Domain specificity in relation to contamination ideation and excessive washing. The Disgust Scale: Item analysis, factor structure, and ideas for refinement. The disgusting self: Perspectives on the psychological, social, and clinical implications of selfdirected disgust. Individual variations in disgust sensitivity: Comparisons and evaluations of paperandpencil versus behavioral measures. Disgust and implicit selfconcept in girls with borderline personality disorder and posttraumatic stress dysfunction. Blood phobia and spider phobia: Two particular phobias with different autonomic cardiac modulations. Exposure to disgustevoking imagery and knowledge processing biases in blood� injection�injury phobia. Disgust sensitivity and contamination fears in spider and blood� injection�injury phobias. The connection between disgust sensitivity and bloodrelated fears, faintness symptoms, and obsessive�compulsiveness in a nonclinical sample. Subtypes of obsessive�compulsive dysfunction: Implications for specialised cognitive behavior therapy. Neural mechanisms of computerized and direct processing of phobogenic stimuli in particular phobia. Change in disgust reactions following cognitive�behavioral remedy for childhood Disgust in Psychopathology: Mechanisms and Treatment 503 anxiety issues. Implicit associations for fearrelevant stimuli among people with snake and spider fears. Studies on the role of disgust within the acquisition and maintenance of specific phobias. Behavioral avoidance checks and disgust in contamination fears: Distinctions from trait nervousness. Microbes, mating, and morality: individual variations in three functional domains of disgust. The Disgust Propensity and Sensitivity Scale�Revised: Its predictive value for avoidance conduct. Disgust propensity and disgust sensitivity: Separate constructs that are differentially associated to particular fears. The relationship between disgust sensitivity and avoidant conduct: Studies of medical and nonclinical samples. Rapee the Nature of the Problem Internalizing disorders are widespread, affecting approximately one in seven schoolaged kids (Sawyer et al. Specifically, at any given cut-off date, anxiety issues have an result on round 5% of youth and melancholy affects approximately 2% (Breton et al. Lifetime prevalence rates are considerably greater, with nervousness problems affecting well over 20% of the inhabitants and depression greater than 15% (Kessler, Berglund, Demler, Jin, & Walters, 2005). Internalizing problems in youth have a negative influence across a quantity of domains, including peer relations and faculty engagement, and are associated with ongoing problems with psychological well being, relationships, and employment into maturity (Kessler et al. In this chapter, we give consideration to the connection between temperament and internalizing disorders in kids and adolescents, and the implications of this body of labor for prevention and early intervention. We begin by reviewing theoretical models that emphasize the position of kid temperament in internalizing problems and the evidence for these models. We shut with a important reflection on the potential of this strategy and directions for future research in this area. It is usually accepted that people present some consistency of their behavior, ideas, and response types across situations. In adults, these particular person variations are usually referred to as character, whereas in young youngsters the term "temperament" is extra commonly used (Prior, 1992). This has led to some fragmentation of the literature, though that is maybe exaggerated by the use of different phrases rather than by dramatic variations in constructs (Tackett, 2006). Most temperament nosologies include a broad typology that reflects withdrawal/emotional reactivity/negative affectivity Treatments for Psychological Problems and Syndromes, First Edition. Temperament in Youth Internalizing Disorders 505 and approach/reward seeking/positive emotionality (Muris & Ollendick, 2005). Rothbart and colleagues additionally suggest a regulatory dimension, which they term "effortful control.