
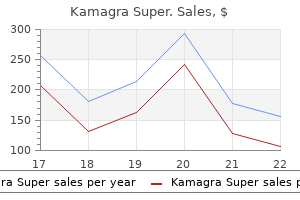
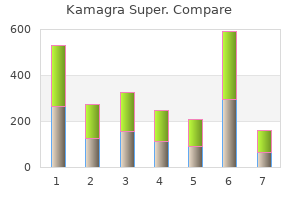
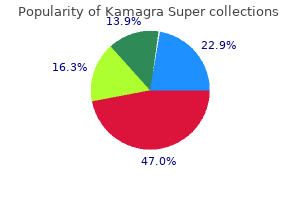
Kamagra Super
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Kamagra super 160 mg cheap line, erectile dysfunction doctor malaysia".
M. Basir, M.B.A., M.D.
Vice Chair, Keck School of Medicine of University of Southern California
Autophagy also is recognized as xenophagy (autophagy of infectious particles) erectile dysfunction insurance coverage kamagra super 160 mg cheap with amex, which also entails membrane site visitors and fusion erectile dysfunction risk factors kamagra super 160 mg order online. Typical donors of endosome membranes are endoplasmic reticulum impotence nitric oxide kamagra super 160 mg generic mastercard, Golgi apparatus erectile dysfunction gif 160 mg kamagra super order amex, mitochondrion, and plasma membrane. For physiological autophagy Rab1, 5, 7, 24, and 33B act in a regulated trend to type autophagolysosome, which is the stepwise fruits of the fusion of a double-membrane phagophore with endosome with S. A failure to keep low pH might differentially regulate virulence gene expression, which in flip might affect bacterial survival. Oxygen radical and nitric oxide collectively could kind reactive peroxynitrite, which may then target cysteine residues of the S. Endothelial cells additionally specific comparatively much less specific galectin-8 than galectin-3, which ends up in abrogation of xenophagic killing and intracellular multiplication of S. Cumulative studies have revealed that in HeLa cells, autophagy plays an necessary function within the intracellular degradation of type M6 S. This statement is attributed to the ability of the M1T1 strain to avoid the ubiquitination strategy of the autophagy protein. Although the direct function of galectin in autophagy is unknown, it has been found that larger expression of Gal-3 and decrease expression of Gal-8 in endothelial cells in comparison with epithelial cells might contribute to the noticed differential S. This examine additionally revealed that upon knockdown of Gal3 in endothelial cells, the colocalization of Gal8, ubiquitin E3-ligase (parkin), and ubiquitin-decorated S. Similarly, upon inhibition of Gal-8 in epithelial cells, recruitment of parkin, ubiquitin, and S. In particular, within the presence of this endogenous nitrated nucleotide, selective clearance of invasive S. The Lys-63-linked polyubiquitination has been discovered to be focused specifically to S-guanylated S. Interestingly, one of the guanylated and ubiquitinated surface proteins of intracellular S. Thus, the noticed differences in autophagy-mediated intracellular killing can be attributed to the intracellular expression ranges of deubiquitinase enzymes, in addition to the other components described above. Apoptosis is essential for proper organismal growth, maintenance of cell number homeostasis, and elimination of diseased or in any other case dangerous cells (267, 268). Apoptotic cell demise in response to bacterial infection is believed to delete infected and damaged epithelial cells and to restore epithelial integrity, which is distorted during an infection (269). The capability of host cells to endure apoptosis is considered the host protection strategy to maintain the pathogen at a disadvantage by not offering a target for adherence, invasion, and subsequent proliferation. However, the ability of the bacterium to direct the host cell to endure apoptotic cell death, thus allowing it to escape from phagocytic exercise, could also be an essential virulence issue. Caspase-9 activation and inhibition of apoptosis of those cells in the presence of caspase inhibitors indicate that caspase activation is probably going an necessary mediator which triggers apoptosis (265, 266). Global transcriptional regulation in neutrophils after phagocytosis of Borrelia hermsii, L. Phosphorylation of H3 performs a decisive function in transcription regulation during progress and growth (276�278). During pneumococcal meningitis, neuronal harm arises not directly from the micro organism and excessive immune response by the host. In experimental meningitis, concentrations of a number of caspases are considerably elevated, and active caspase3 is present within the dentate gyrus (286). However, intrathecal remedy with broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor rescues only around 50% of the neurons of experimental mice with acute pneumococcal meningitis (287). In a microglial neuronal cell tissue culture system, pneumococcal an infection leads to speedy injury of mitochondria followed by the discharge of cytochrome C and apoptosis-inducing factor (288). Anti-apoptosis-inducing factor antibody also inhibits apoptosis in a significant variety of cells contaminated with pneumococci, indicating that neuronal injury throughout pneumococcal meningitis occurs each as caspase-dependent and caspaseindependent (mitochondrial pathway) manners (287, 288). Unlike in neuronal cells, pneumococci induce apoptosis of human alveolar and broncho-epithelial cells by caspase-6 and noncaspase protease however not by caspase-3 (289). Inflammasome-associated cell demise (pyroptosis) and apoptosis are distinct but related phenomena and have interaction in bidirectional cross-talk in macrophages (296). Virulence issue regulation and regulatory networks in Streptococcus pyogenes and their impact on pathogen-host interactions. Regulation of virulence by environmental indicators in group A streptococci: affect of osmolarity, temperature, fuel trade, and iron limitation on emm transcription. Environmental regulation of virulence in group A streptococci: transcription of the gene encoding M protein is stimulated by carbon dioxide. Hertz�n E, Johansson L, Kansal R, Hecht A, Dahesh S, Janos M, Nizet V, Kotb M, Norrby-Teglund A. Intracellular Streptococcus pyogenes in human macrophages show an altered gene expression profile. Engagement of the pathogen survival response utilized by group A Streptococcus to avert destruction by innate host protection. Genome-wide protective response used by group A Streptococcus to evade destruction by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Discrimination between intracellular uptake and surface adhesion of bacterial pathogens. Subterfuge and sabotage: evasion of host innate defenses by invasive Gram-positive bacterial pathogens. However, latest research utilizing transgenic mice overexpressing the prosurvival Bcl2 protein discovered minimal impression on the clearance of S. The foundation of this dynamic course of is intracellular signaling occasions that finally decide the destiny of the targeted cell and subsequently that of adjacent cells. While collectively, these occasions allow streptococci to disseminate in tissues, the biochemical modifications resulting from cascades of signaling occasions in affected cells determine the scientific image of streptococcal disease. Limited attention has been given to the genetic basis of populations that are prone to develop frequent and severe S. Therapeutic concentrating on of the related host cell signaling occasions might maintain promise to counteract severe, invasive, and infrequently deadly S. Approaches to reprogramming mobile features have already been carried out for so much of septic shock and inflammatory ailments, despite persistent obstacles (301�306). Understanding how main bacterial pathogens subvert innate immunity to reveal novel therapeutic targets. Cell death during sepsis: integration of disintegration within the inflammatory response to overwhelming an infection. Septic shock in advanced age: transcriptome analysis reveals altered molecular signatures in neutrophil granulocytes. In defense of the oral cavity: structure, biosynthesis, and function of salivary mucins. Identification of the mucinbinding adhesin of Pseudomonas cepacia isolated from sufferers with cystic fibrosis. Structural and useful evaluation of a Streptococcus sanguis receptor for a human salivary glycoprotein. Aggregation of group A streptococci by human saliva and effect of saliva on streptococcal adherence to host cells. Group A streptococci bind to mucin and human pharyngeal cells through sialic acid-containing receptors. Streptococcus pyogenes glycoprotein-binding strepadhesin exercise is mediated by a surface-associated carbohydrate-degrading enzyme, pullulanase. Cloning and expression of the streptococcal C5a peptidase gene in Escherichia coli: linkage to the kind 12 M protein gene. Cysteine proteinase SpeB from Streptococcus pyogenes: a potent modifier of immunologically necessary host and bacterial proteins. Dohrman A, Miyata S, Gallup M, Li J-D, Chapelin C, Coste A, Escudier E, Nadel J, Basbaum C. The role of the service in remedy failures after antibiotic for group A streptococci within the higher respiratory tract. Biochemical and biophysical comparison of two mucins from human submandibular-sublingual saliva. The plasmin-binding protein Plr of group A streptococci is identified as glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
The expression of poisonous merchandise erectile dysfunction premature ejaculation treatment proven kamagra super 160 mg, using massive fragments or high-copynumber plasmids erectile dysfunction gnc discount kamagra super 160 mg on-line, and sequence-specific effects unrelated to promoter activity appear to be more doubtless causes erectile dysfunction doctors in san fernando valley 160 mg kamagra super effective. Insertion-duplication mutagenesis has been the classical technique to knock out genes in S erectile dysfunction caused by medications 160 mg kamagra super generic overnight delivery. In vitro mariner transposon mutagenesis has proven to be a helpful technique (72, 165). The latter method allows the development of libraries for the screening of important genes (165). It is feasible to introduce in-frame deletions, insertions, and single nucleotide substitutions in the bacterial chromosome (167). Introduction of unmarked mutations in encapsulated strains with low levels of competence is completed using gene replacement methods involving a negative selection (168). The Janus cassette, which contains a selectable kanamycin-resistance marker and counterselectable rpsL, which confers dominant streptomycin sensitivity in a streptomycin-resistant background, is first introduced by homologous recombination at the site of interest. The Sweet Janus cassette incorporates a counterselectable marker that confers sucrose sensitivity and allows a reduction of the false-positive mutants which are isolated (169). The cassette is flanked by the recombinasespecific recognition sequence and is launched by transformation within the goal gene. Upon addition of fucose in the development medium, the recombinase gene is expressed and the cassette is excised (170). Duplication of the target fragment occurs, and the gene is disrupted by the plasmid insertion, resulting in an insertion-duplication mutation. Both genes ought to be practical, unless they form part of an operon, during which case the plasmid insertion could be polar on the downstream gene. The figure exhibits a selectable erythromycin-resistance gene (erm) and a promoterless chloramphenicol-resistance reporter gene (cat). Nomenclature of major antimicrobial-resistant clones of Streptococcus pneumoniae defined by the pneumococcal molecular epidemiology network. A functional genomics approach to establish the complement of carbohydrate transporters in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Comparative genomic analyses of seventeen Streptococcus pneumoniae strains: insights into the pneumococcal supragenome. Structure and dynamics of the pan-genome of Streptococcus pneumoniae and carefully associated species. Comparative genomics for identification of clone-specific sequence blocks in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Organization and transfer of heterologous chloramphenicol and tetracycline resistance genes in pneumococcus. This work is dedicated to the memory of Susan Hollingshead, who so significantly contributed to our understanding of pneumococcal pathogenesis. Marker discrimination in deoxyribonucleic acid-mediated transformation of various Pneumococcus strains. Competence for genetic transformation in encapsulated strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae: two allelic variants of the peptide pheromone. Annotated draft genomic sequence from a Streptococcus pneumoniae sort 19F clinical isolate. Bacteriophage-associated gene transfer in pneumococcus: transduction or pseudotransduction Genomics and Genetics of Streptococcus pneumoniae tuning of competence development. Diversification of bacterial genome content material by way of distinct mechanisms over completely different timescales. Blomberg C, Dagerhamn J, Dahlberg S, Browall S, Fernebro J, Albiger B, Morfeldt E, Normark S, Henriques-Normark B. Pattern of accessory regions and invasive disease potential in Streptococcus pneumoniae. A locus contained within a variable area of pneumococcal pathogenicity island 1 contributes to virulence in mice. A variable area within the genome of Streptococcus pneumoniae contributes to strain-strain variation in virulence. Nucleotide sequence analysis of integrative conjugative element Tn5253 of Streptococcus pneumoniae. New insights into the classification and integration specificity of Streptococcus integrative conjugative elements through extensive genome exploration. Regulation of the transformability of pneumococcal cultures by macromolecular cell products. An unmodified heptadecapeptide pheromone induces competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Genetic and molecular characterization of capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae type three. Pherotype polymorphism in Streptococcus pneumoniae has no obvious results on inhabitants construction and recombination. Interconnection of competence, stress and CiaR regulons in Streptococcus pneumoniae: competence triggers stationary section autolysis of ciaR mutant cells. Development of competence in Streptococcus pneumonaie: pheromone autoinduction and control of quorum sensing by the oligopeptide permease. Competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae: organization of a regulatory locus with homology to two lactococcin A secretion genes. Antibiotic-induced replication stress triggers bacterial competence by increasing gene dosage close to the origin. Competence-induced cells of Streptococcus pneumoniae lyse competence-deficient cells of the same pressure throughout cocultivation. Membrane location of a deoxyribonuclease implicated within the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. A membrane-bound nuclease required for transformation of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Transformation and deoxyribonucleic acid dimension: extent of degradation on entry varies with size of donor. Identification of the most important protein part of the pneumococcal eclipse advanced. Purification and characterization of the RecA protein from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Competence-specific induction of recA is required for full recombination proficiency throughout transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Sensor domain of histidine kinase ComD confers competence pherotype specificity in Streptoccoccus pneumoniae. Constitutive competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae attributable to mutation of a transmembrane histidine kinase. Identification of a model new regulator in Streptococcus pneumoniae linking quorum sensing to competence for genetic transformation. Competence for genetic transformation in pneumococcus is determined by synthesis of a small set of proteins. ComX is a singular link between multiple quorum sensing outputs and competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Identification of ComW as a model new component within the regulation of genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Genetic and physiological research of the CiaH-CiaR two-component signal-transducing system involved in cefotaxime resistance and competence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. A two-component signal-transducing system is involved in competence and penicillin susceptibility in laboratory mutants of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Cross-regulation of competence pheromone production and export in the early management of transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. The Streptococcus pneumoniaecia regulon: CiaR target sites and transcription profile evaluation. Regulation of Streptococcus pneumoniae clp genes and their position in competence improvement and stress survival. Global transcriptional evaluation of clpP mutations of type 2 Streptococcus pneumoniae and their effects on physiology and virulence. Bacillus subtilis CinA is a stationary phase-induced protein that localizes to the nucleoid and performs a minor position in competent cells.
Perform a chi-square evaluation utilizing the number of individuals noticed and anticipated in every blood-type category erectile dysfunction treatment in pune buy cheap kamagra super 160 mg line, and state whether or not the sample is in H-W equilibrium (see pages 50 and fifty one for the chi-square formula and table) erectile dysfunction treatment chicago kamagra super 160 mg purchase without a prescription. The alleles exhibit an incomplete dominance relationship by which C1C1 produces black rabbits erectile dysfunction drug approved to treat bph symptoms 160 mg kamagra super generic overnight delivery, C1C2 tan-colored rabbits what do erectile dysfunction pills look like 160 mg kamagra super discount amex, and C2C2 rabbits with white fur. If the assumptions of the Hardy�Weinberg principle apply to the rabbit inhabitants, what are the anticipated frequencies of black, tan, and white rabbits What are the frequencies of the wild-type (bA) and mutant (bS) alleles on this inhabitants Epidemiologic information on the inhabitants within the earlier downside reveal that before the applying of modern medical remedy, pure choice performed a major role in shaping the frequencies of alleles. In population A, sixty four p.c of persons are tasters (an autosomal dominant trait) and 36 p.c are nontasters. Assuming that Hardy�Weinberg conditions apply, determine the genotype frequencies in every inhabitants. Despite its invariably deadly impact, Tay�Sachs disease happens at very high frequency in some Central and Eastern European (Ashkenazi) Jewish populations. Population biologists believe the excessive frequency is a consequence of genetic bottlenecks attributable to pogroms (genocide) which have decreased the inhabitants a quantity of occasions up to now a number of hundred years. Explain how a genetic bottleneck and its aftermath may end in a population that carries a lethal allele in excessive frequency. In the mouse, Mus musculus, survival in agricultural fields that are frequently sprayed with a herbicide is set by the genotype for a cleansing enzyme encoded by a gene with two alleles, F and S. Why will this pattern of natural choice lead to a steady equilibrium of frequencies of F and S In a inhabitants of flowers growing in a meadow, C1 and C2 are autosomal codominant alleles that control flower colour. Flowers which may be C1C1 are yellow, orange flowers are C1C2, and C2C2 flowers are red. A storm blows a model new species of hungry bugs into the meadow, and so they begin to eat yellow and orange flowers however not red flowers. The predation exerts sturdy pure selection on the flower inhabitants, resulting in relative health values of C1C1 = zero. Assuming the inhabitants begins in H-W equilibrium, what are the allele frequencies after one generation of pure selection Assuming random mating takes place amongst survivors, what are the genotype frequencies within the second generation If predation continues, what are the allele frequencies when the second generation mates Assume that the flower inhabitants described within the previous downside undergoes a special sample of predation. Flower shade willpower and the beginning Problems 755 frequencies of C1 and C2 are as described above, but the new bugs assault yellow and pink flowers, not orange flowers. Assuming Hardy�Weinberg circumstances apply, what are the frequencies of genotypes, and what are the blood group frequencies on this inhabitants A pattern of 500 area mice incorporates 225 individuals which would possibly be D1D1, 175 which would possibly be D1D2, and one hundred which might be D2D2. Is inbreeding a potential genetic explanation for the noticed distribution of genotypes Determine the frequency of genotypes for each gene and the frequency of every phenotype. What are the anticipated frequencies of the four potential phenotype combos: dimpled tasters, undimpled tasters, dimpled nontasters, and undimpled nontasters Albinism, an autosomal recessive trait characterised by an absence of skin pigmentation, is present in 1 in 4000 people in populations at equilibrium. Brachydactyly, an autosomal dominant trait producing shortened fingers and toes, is present in 1 in 6000 individuals in populations at equilibrium. The family contains a quantity of inbred people and a variety of inbreeding pathways. In distinction, a quantity of alleles decreasing eumelanin manufacturing have been present in European populations. Achromatopsia is a uncommon autosomal recessive form of complete colour blindness that impacts about 1 in 20,000 people in most populations. People with this disorder see solely in black and white and have excessive sensitivity to light and poor visual acuity. On Pingelap Island, considered one of a cluster of coral atoll islands within the Federated States of Micronesia, roughly 10 percent of the 3000 indigenous Pingelapese inhabitants have achromatopsia. Achromatopsia was first recorded on Pingelap in the mid-1800s, about four generations after a typhoon devastated Pingelap and decreased the island population to about 20 folks. All Pingelapese with achromatopsia trace their ancestry to one male who was one of the 20 storm survivors. Provide a genetic rationalization for the origin of achromatopsia on Pingelap, and explain the most probably evolutionary mannequin for the high frequency there of achromatopsia. If hybridization occurs between a diploid plant species with 2n = 14 and a second diploid species with 2n = 22, the new allopolyploid would have 36 chromosomes. Is it doubtless that sexual copy between the allopolyploid species and either of its diploid ancestors would yield fertile progeny What sort of isolation mechanism is most probably to prevent hybridization between the allopolyploid and the diploid species What pattern of speciation is illustrated by the development of the allopolyploid species Draw a separate hypothetical pedigree identifying the inbred individuals and the inbreeding pathways for each of the following inbreeding coefficients: a. The issues in this part are greatest done in small teams of three to six folks, if potential. Divide the contents of a big bag of various coloured candies randomly and approximately equally among the members of the group. Do not decide particular candy colors, but simply empty the contents of the bag onto a table and rapidly divide the pile. Have each particular person depend the variety of candies of each colour in his or her pile and calculate the frequency of each color within the pile. Tabulate the entire number of candies of every colour within the original bag by combining the numbers from each particular person. Have every person examine the frequencies of each colour in his or her pile with the frequencies within the authentic bag. Put all the candies utilized in Problem 40 into a single mound after which divide them into 4 equal piles, this time being certain that the frequency of every colour is the same in each pile. Determine the frequency of every sweet colour within the whole of 25 draws (a whole of fifty candies) and examine these frequencies with the original frequencies of the colours within the pile. Explain any noticed differences in frequencies in terms of the evolutionary mechanism the results greatest emulate. Put all of the candies used in Problem forty one back into a single mound after which divide them into two piles, being certain that the frequencies of each colour are the same in each pile. Have one particular person blindly draw one sweet from the male pile and one candy from the female pile. If the 2 colors are another combination, together with yellow with some other color, put the candies back into their respective piles. Repeat this strategy of blindly drawing one male and one feminine sweet 12 to 15 instances for each individual within the group. When all choice rounds have been completed, combine the 2 piles and decide the frequency of each colour. Describe the noticed variations and identify the evolutionary mechanism this train finest emulates. Sort the candies by shade, and in case your bag has greater than four colors, eat the least frequent color or colours. Assume these frequencies represent 4 alleles of a gene, and use the outline of the H-W equilibrium for more than two alleles for assistance (Section 20.
Pbp2x localizes separately from Pbp2b and other peptidoglycan synthesis proteins during later phases of cell division of Streptococcus pneumoniae D39 impotence 2 purchase 160 mg kamagra super overnight delivery. Cellular localization of choline-utilization proteins in Streptococcus pneumoniae utilizing novel fluorescent reporter techniques erectile dysfunction cpt code buy cheap kamagra super 160 mg line. Construction of improved instruments for protein localization studies in Streptococcus pneumoniae erectile dysfunction latest medicine 160 mg kamagra super cheap fast delivery. In Tomasz A (ed) impotence treatment after prostate surgery kamagra super 160 mg buy discount online, Streptococcus pneumoniae: Molecular Biology & Mechanisms of Disease. Structure of the complex polysaccharide C-substance from Streptococcus pneumoniae sort 1. Cross-reactions between pneumococci and different streptococci because of C polysaccharide and F antigen. Lipoteichoic acid deficiency permits regular growth however impairs virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Choline within the cell wall of a bacterium: novel type of polymer-linked choline in pneumococcus. Choline-containing teichoic acid as a structural component of pneumococcal cell wall and its role in sensitivity to lysis by an autolytic enzyme. In Tomasz A (ed), Streptococcus pneumoniae: Molecular Biology and Mechanisms of Disease. Defective cell wall synthesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae R6 depleted for the important PcsB putative murein hydrolase or the VicR (YycF) response regulator. Influences of capsule on cell form and chain formation of wild-type and pcsB mutants of serotype 2 Streptococcus pneumoniae. Rico-Lastres P, D�ez-Mart�nez R, Iglesias-Bexiga M, Bustamante N, Aldridge C, Hesek D, Lee M, Mobashery S, Gray J, Vollmer W, Garc�a P, Men�ndez M. Substrate recognition and catalysis by LytB, a pneumococcal peptidoglycan hydrolase concerned in virulence. Hakenbeck R, K�nig A, Kern I, van der Linden M, Keck W, Billot-Klein D, Legrand R, Schoot B, Gutmann L. Acquisition of five high-Mr penicillin-binding protein variants throughout switch of high-level beta-lactam resistance from Streptococcus mitis to Streptococcus pneumoniae. Isolation and separation of the glycan strands from murein of Escherichia coli by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. In vitro reconstitution of peptidoglycan assembly from the Gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae. Co-inactivation of GlnR and CodY regulators impacts pneumococcal cell wall physiology. Schweizer I, Bl�ttner S, Maurer P, Peters K, Vollmer D, Vollmer W, Hakenbeck R, Denapaite D. Structure of pneumococcal peptidoglycan hydrolase LytB reveals insights into the bacterial cell wall transforming and pathogenesis. Purification and polar localization of pneumococcal LytB, a putative endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase: the chaindispersing murein hydrolase. Changes in composition of peptidoglycan during maturation of the cell wall in pneumococci. The pgdA gene encodes for a peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Structure and metal-dependent mechanism of peptidoglycan deacetylase, a streptococcal virulence issue. Development of screening assays and discovery of preliminary inhibitors of pneumococcal peptidoglycan deacetylase PgdA. Peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase, a putative virulence consider Streptococcus pneumoniae. Attenuation of penicillin resistance in a peptidoglycan O-acetyl transferase mutant of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Peptidoglycan O-acetylation is functionally related to cell wall biosynthesis and cell division in Streptococcus pneumoniae. From models to pathogens: how much have we realized about Streptococcus pneumoniae cell division Functional analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae MurM reveals the region liable for its specificity in the synthesis of branched cell wall peptides. Mutational evaluation of the Streptococcus pneumoniae bimodular class A penicillin-binding proteins. Autolysis and cell wall degradation in a choline-independent strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Abnormal physiological properties and altered cell wall composition in Streptococcus pneumoniae grown within the presence of clavulanic acid. Structure of the pneumococcal l,D-carboxypeptidase DacB and pathophysiological effects of disabled cell wall hydrolases DacA and DacB. Sortase, a universal target for therapeutic brokers against Gram-positive micro organism Molecular characterization of the pneumococcal teichoic acid phosphorylcholine esterase. Penicillin-binding proteins of multiply antibiotic-resistant South African strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. A organic price of antibiotic resistance: main adjustments within the peptidoglycan construction of penicillin-resistant pneumococci. Distribution of the mosaic structured murM genes among pure populations of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Non-penicillin-binding protein mediated high-level penicillin and cephalosporin resistance in a Hungarian clone of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Separation of abnormal cell wall composition from penicillin resistance via genetic transformation of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Drastic changes in the peptidoglycan composition of penicillin resistant laboratory mutants of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Chemical and immunological properties of a species-specific carbohydrate of pneumococci. Structural reevaluation of Streptococcus pneumoniae lipoteichoic acid and new insights into its immunostimulatory potency. Biosynthesis of teichoic acids in Streptococcus pneumoniae and carefully related species: lessons from genomes. The aqueous solution construction of a lipoteichoic acid from Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R6 containing 2,4diamino-2,four,6-trideoxy-galactose: proof for conformational mobility of the galactopyranose ring. Muramic acid phosphate as a component of the mucopeptide of Gram-positive bacteria. Purification and characterization of the autolytic glycosidase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. The essential tacF gene is answerable for the choline-dependent growth phenotype of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Attachment of capsular polysaccharide to the cell wall in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharide is linked to peptidoglycan via a direct glycosidic bond to b-D-N-acetylglucosamine. Kov�cs M, Halfmann A, Fedtke I, Heintz M, Peschel A, Vollmer W, Hakenbeck R, Br�ckner R. A useful dlt operon, encoding proteins required for incorporation of D-alanine in teichoic acids in Gram-positive micro organism, confers resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Roles of the essential protein FtsA in cell growth and division in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Suppression and synthetic-lethal genetic relationships of DgpsB mutations point out that GpsB mediates protein phosphorylation and penicillin-binding protein interactions in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39. Cell division in cocci: localization and properties of the Streptococcus pneumoniae FtsA protein. Remodeling of the Z-ring nanostructure during the Streptococcus pneumoniae cell cycle revealed by photoactivated localization microscopy. A new FtsZ-interacting protein, YlmF, enhances the exercise of FtsA throughout development of cell division in Bacillus subtilis.
Generic 160 mg kamagra super visa. Alcohol & Erectile Dysfunction | Erection Problems.