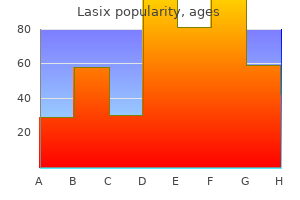
Lasix
| Contato
Página Inicial
"40 mg lasix purchase amex, blood pressure chart age 35".
Q. Irmak, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Clinical Director, Louisiana State University School of Medicine in New Orleans
The commonest location o dehiscence blood pressure chart log excel lasix 100 mg cheap mastercard, and likewise the most common web site o iatrogenic injury throughout center ear surgical procedure blood pressure drop 100 mg lasix overnight delivery, is the tympanic segment adjacent to the oval window blood pressure herbs 40 mg lasix purchase with visa. History � Any palsy demonstrating progression past 3 weeks or lack o any sign o restoration a er 6 months ought to be considered as a end result of arteria iliaca externa lasix 40 mg purchase with visa an underlying neoplasm until confirmed in any other case. Physical Examination � The initial analysis should decide i the weak spot is complete or partial. Remember that eyelid elevation is a unction o the levator palpebrae muscle, which is innervated by the oculomotor nerve, and can remain intact despite a total acial nerve paralysis. Central unilateral acial paralysis often entails solely the lower ace, because the innervation o the higher ace is derived rom bilateral upper acial motor neurons. In addition, the presence o emotional acial expression as well as lacrimation, style, and salivation on the ipsilateral side suggest a central lesion. Imaging Studies � The need or radiologic evaluation is predicated on the history and clinical course o each individual case. Gross Pa rt 2: Otology/Neurotology/Audiology Slight weakness noticeable on close inspection. Moderate dys unction Gross Obvious, however not dis guring di erence between the 2 sides. Electrophysiologic tests will reveal speedy and complete degeneration 72 hours a er damage. As lengthy because the endoneurium is preserved, there shall be full recovery with return o regular unction. Characterized by wallerian degeneration, an unpredictable regeneration potential, and the likelihood o signi cant resultant dys unction and synkinesis. Results rom a single axon or a small group o axons innervating motor end items o numerous and separated muscle tissue. Commonly used examples include the Schirmer take a look at, the submandibular ow check, and the stapedial re ex check. These exams have been ound to correlate poorly with the location o damage and are unreliable in predicting restoration. The electrodes are then positioned in corresponding locations on the concerned side, and the same procedure is per ormed. Cha pter 21: Fa cial Nerve Paralysis 373 � A suprathreshold electrical stimulus is used to elicit acial contraction on the traditional and paralyzed side. Lacrimation (Schirmer Test) � Evaluates larger super cial petrosal nerve unction (ie, tear production). Stapedial Re ex � The stapedius muscle contracts re exively in both ears when one ear is stimulated with a loud tone. This alters the reactive compliance o the center ear, which could be measured with impedance audiometry. Salivary Flow Testing � By cannulating Wharton papillae, a measurement o salivary ow to gustatory stimulation can be obtained. Idiopathic Facial Paralysis (Bell Palsy) � � � � � � � � The most common trigger o acute acial paralysis, accounting or 70% o instances. Recurrent paralysis occurs in approximately 10% to 12% o patients and is extra widespread on the contralateral facet. The viral in ection induces an in ammatory response that leads to neural edema and vascular compromise o the acial nerve throughout the allopian canal. This entrapment neuropathy is most evident in the labyrinthine section o the acial nerve where the allopian canal is narrowest in diameter. Presents with unilateral acial weakness o sudden onset, involving all branches o the nerve, which can progress to complete paralysis in two-thirds o sufferers over the course o 3 to 7 days. However, minimal diagnostic criteria or Bell palsy embody the ollowing: (a) Paralysis or paresis o all muscle groups on one facet o the ace (b) Rapid onset within seventy two hours (c) Absence o indicators o central nervous system disease, ear disease, or cerebellopontine angle disease Additional traits: viral prodrome (60%); ear pain (60%), numbness or ache o the ear, ace, or neck (60%); dysguesia (57%); hyperacusis (30%); and decreased tearing (17%). An audiogram is obtained to present a good basic screening o the auditory system although hearing loss is unlikely with Bell palsy. I full paralysis is identi ed, electrophysiologic tests must be per ormed to prognosticate restoration. Absence o onset o clinical recovery 6 months a er onset o paralysis, progressive paralysis beyond 3 weeks, and the presence o acial twitching also represent medical indicators or imaging o the acial nerve. In patients with complete paralysis, over two-thirds have a complete restoration and 15% have a great medical restoration with gentle residual palsy. The remaining 15% have a air to poor restoration and is the group that would bene t most rom aggressive medical or surgical intervention. Gastrointestinal complaints are the most typical facet e ects associated with antiviral medications. In people with good listening to, a center cranial ossa approach is used or surgical decompression o the acial nerve. In those with poor or no hearing in the a ected ear, a translabyrinthine strategy is used. Iatrogenic Injury � Facial nerve harm during mastoid or middle ear surgery is uncommon (~1%-3%). Usually, these injuries are identi ed at the time o surgical procedure and applicable repair (ie, end-to-end anastomosis or cable gra ing) is per ormed. Local anesthetics (ie, lidocaine) could result in residual weak spot or paralysis and ought to be given acceptable time to wear-o (ew hours). I paralysis persists, center ear and mastoid packing that might be compressing a dehiscent segment o the nerve ought to be eliminated. I no voluntary motor unit motion potentials are detected, a extreme contusion or disruption o the nerve can be in erred and surgical exploration is warranted. Systemic steroids may be administered to reduce the extent o neural edema related to the traumatic injury. Noniatrogenic Intratemporal Injury � Results rom temporal bone ractures, that are classi ed as longitudinal or transverse with respect to the long axis o the petrous ridge. They virtually all the time involve the center ear, however only 20% could have concomitant acial nerve injury. Common shows embody bleeding rom the middle or external ear, laceration o the tympanic membrane, and conductive listening to loss. Facial nerve harm, i present, is normally the end result o compression and ischemia versus neural disruption. Common shows embody hemotympanum, vestibular signs, and extreme sensorineural or blended listening to loss. In addition, blast accidents are o en accompanied by signi cant central nervous system or vascular harm. Delayed-onset acial paralysis related to temporal bone trauma can be more likely to get well without surgical intervention. Cha pter 21: Fa cial Nerve Paralysis 377 � Serial examination is essential to assess or any progressive paralysis and electrical testing ought to be per ormed i complete paralysis occurs. I degeneration o greater than 90% is identi ed on the a ected facet inside 2 weeks a er the harm, surgical decompression o the acial nerve on the a ected site should be considered. I surgical exploration o the acial nerve is undertaken, the decompression ought to prolong beyond this region. A center cranial ossa approach ought to be employed in a patient with intact listening to. O en, this process may be mixed with a transmastoid approach i decompression o the distal tympanic and mastoid segments is indicated. In instances o complete transection, the choice to reanastomose the nerve must be based on the ability to approximate the nerve edges with negligible rigidity on the anastamotic web site. Noniatrogenic Extratemporal Injury � The extracranial nerve is vulnerable to trauma, particularly penetrating accidents, and a direct evaluation ought to be carried out to evaluate the status o nerve unction, the extent o so tissue harm, and the quantity o contamination. A transected or severely injured nerve will present no response to stimulation proximal to the harm. In addition, electrical testing is instrumental in identi ying nerve branches intraoperatively. Because o the intensive community o branching and anastomoses, peripheral accidents are associated with much less morbidity.
Malignant tumors o the sinonasal tract comprise lower than 1% o all cancers and 3% o cancers involving with upper aerodigestive tract hypertension diagnosis code generic lasix 100 mg without a prescription. About 55% o cancers within the paranasal sinuses originate in the maxillary sinus heart attack trey songz 40 mg lasix purchase mastercard, 35% in the nasal passage blood pressure in the morning cheap 100 mg lasix mastercard, 10% in the ethmoids blood pressure goal diabetes lasix 40 mg with mastercard, and rare tumors (< 1%) in the rontal and sphenoid sinuses. These tumors are a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge as a end result of they o en current with signs that mimic widespread in ammatory sinonasal diseases. This mixed with the delicate surrounding constructions (eyes, brain, cranial nerves, carotid artery, etc) makes surgical procedure and comprehensive treatment advanced with high dangers. This permits or rozen section con rmation o neoplastic tissue and allows the surgeon to control bleeding. Imaging Computed tomography (C) Advantages: Evaluating tumor involvement o the paranasal sinuses, the boney cranium base and the retro-orbital and orbital apex region. Limitations: De ning so tissue illness in areas o high contrast in tissue density (ie, dental llings); evaluating orbital oor because o "partial volume averaging" o thin bone, demonstrating intracranial tumor extension; figuring out invasion o periorbita; and separating tumor rom submit obstructive sinus illness. On C most malignant lesions cause bony destruction; however, benign tumors, minor salivary gland carcinomas, extramedullary plasmacytomas, large cell lymphomas, hemangiopericytomas, and low-grade sinonasal sarcomas trigger tissue remodeling. O en on C imaging o inverted papillomas, hyperostotic bone could be ound at the web site o origin. Histopathologic Markers on Biopsy or Ol actory Groove Cancers Pathologic sub categorization or skull base malignancies is crucial or management and prognostication o these aggressive tumors. Endoscopic, mid acial degloving and trans acial (rom least invasive to most) approaches can be per ormed. Nasal Cavity and Ethmoid Sinus T Staging 1: umor restricted to one subsite with or without boney invasion. Distant metastasis Pa rt three: Rhinology reatment reatment o benign tumors ranges rom observation, to partial resection or obstructive sinonasal illness, to full resection with margins (inverted papillomas). Radiation is reserved or symptomatic tumors in nonsurgical candidates or or radiation delicate tumors such as plasmacytomas. Surgery or benign tumors have to be match with the biology o the tumor and the speci c affected person. For sinonasal cancers, the suitable dangers o surgical procedure are signi cant o en placing the eyes and brain in danger. This balanced with the difficulty o local tumor resection and the necessity to obtain adverse margins. However, the oncologic outcomes and therapy morbidity o patients with sinonasal cancer has been bettering over the last a number of a long time. This likely attributable to improved diagnostic imaging, extra e ective surgical treatment, the use o vascularized aps or reconstruction, and extra e ective adjuvant therapy. For high-grade cancers, o en tri-modality therapy supplies the most effective most cancers outcomes. The similar surgical dangers to the vision, cranial nerves and the brain/brainstem are additionally dangers with radiation therapy. Proton radiation therapy has the theoretical benefit o being extra con ormable with much less dosage to nontumor concerned sites similar to the attention and brain. The limitation o proton radiation is its relative unavailability across the country, limited outcomes studies and overall larger value. Surgical reatment o Maxillary Sinus Cancer Determining surgical prognosis � Ohngren line (Anterior/in erior tumors have higher outcomes) � Nodal disease ought to be managed with neck dissections and retropharyngeal dissections i possible. Approach should permit sufficient publicity whereas preserving unctional tissue and beauty outcomes, i potential. Preoperative session with neurosurgery, maxillo acial prosthodontist (i obdurator required), plastic and reconstructive surgical procedure and radiation oncology i needed. Cha pter 28: Tumors of the Parana sa l Sinuses 517 Extirpative options Maxillectomies must be individualized to the anatomy o the tumor and the want to acquire unfavorable margins. Skull base tumor surgery, especially o the anterior cranial ossa, started with a combination o approaches via acial incisions and rontal craniotomies. These two approaches then collided with the usual anterior cranio acial resection, which offers wonderful entry to the whole anterior cranial ossa, orbits and sinonasal cavities. The cranio acial resection is the gold standard or this method with the sinonasal portion o the tumor dissected by way of a trans acial approach and the dural/skull base portion o the tumor dissected through a rontal craniotomy, allowing or en-bloc removing o the skull base/sinuses and dura. The cranio acial resection also permits or direct entry or reconstruction o the skull base and dural de ect with a pericranial ap. Several modi cations o the open anterior cranio acial method have been modi ed to scale back brain retraction, acial scarring and minimize (but not eliminate) this morbidity. Over the last decade, there have been signi cant advances within the area o endoscopic cranial base surgical procedure. These embrace an improved understanding o endoscopic anatomy, the development o new instrumentation, and the description o new endonasal surgical approaches and surgical techniques. Endoscopic approaches o er potential benefits similar to no acial incisions, no need or craniotomy, no brain retraction, and wonderful visualization and magni cation using the endoscope. Also all sufferers undergoing endoscopic transcribri orm cranio acial resections ought to have been recommended and in ormed consent obtained to convert to a normal open strategy i needed to clear margins. Endoscopic transnasal transcribri orm cranio acial resection Indications: Initially thought to be solely or those sufferers with low stage disease with no intracranial involvement; however, latest results with endoscopic dural and intradural resections have proven promise or extremely experienced skull base surgical procedure packages. There ore, the overall permanent morbidity (14 patients) and mortality (7 patients) was 2. The underlying principle o multilayered reconstruction to reestablish natural tissue limitations ought to be preserved. The use o vascularized reconstruction optimizes therapeutic and minimizes postoperative issues (especially within the setting o radiotherapy). Cranio acial resection or malignant paranasal sinus tumors: report o a world collaborative examine. What website o involvement throughout the paranasal sinuses pretends the worst prognosis What would be an absolute contraindication or a solely endoscopic strategy or sinonasal most cancers resection Which small spherical blue cell tumor is most correlated with the immunohistochemical staining sample o cytokeratin constructive, neuron speci ic immunomarker adverse This increase has led to an interest in surgical resection o tumors by way of an endonasal strategy. Advantages corresponding to improved surgical publicity, decreased period o hospitalization, elimination o external incisions, and decreased general morbidity have led to the insertion o endoscopic cranium base surgical procedure into mainstream follow. It articulates with the roo the ethmoid sinus anteriorly and the sella posteriorly. An onodi cell is a posterior ethmoid cell with superolateral pneumatization into the sphenoid sinus, creating a horizontal septation. Identi cation o an onodi cell is essential in cranium base surgical procedure as this can be disorienting to the conventional anatomy o the sphenoid sinus. Technique (a) o entry the sella the in erior, middle, and superior turbinates have to be lateralized. Anterior Cranial Fossa/Cribri orm Plate � Represents the roo o the nasal cavity Boundaries � Anterior: rontal sinus recess � Posterior: planum sphenoidale � Medial: perpendicular plate o the ethmoid in unilateral illness � Lateral: lamina papyracea (a) The cribri orm plate transmits ol actory bers rom the superior turbinate, the higher portion o the center turbinate and nasal septum. Technique (a) Begin with an anterior and posterior ethmoidectomy creating complete publicity o the skull base. This dissection ought to embody the ethmoid bulla, suprabullar cells, and posterior ethmoid cells posterior to the basal lamella. A modi ed Lothrop process may be required i the lesion extends into the rontoethmoid region or an obstructing mucocele has ormed. During this process the naso rontal beak is drilled out and the intersinus septum is removed. Cha pter 29: Endoscopic Skull Base Surgery 525 Osteotomies are then per ormed with a diamond burr and Kerrison rongeur guaranteeing an appropriate margin around the tumor. Suprasellar Region Boundaries � Anterior: ethmoid roo � Posterior: third ventricle, basilar tip, mammary body � Superior: rontal lobe gyri � In erior: sella � Lateral: optic nerve (a) The parameters or dissection within the suprasellar region are the optic nerves laterally and 1. Cavernous Sinus Region � Lateral to the sella are multiple bony protuberances, which characterize essential anatomic structures. Technique (a) For lesions restricted to the medial cavernous sinus, a sellar method per ormed as previously described.
Syndromes related to progressive hearing loss (ie blood pressure medication diltiazem lasix 40 mg online, Alport pre hypertension and diabetes discount 100 mg lasix with visa, Jervell heart attack mortality rate 100 mg lasix sale, and Lange-Nielsen pulse pressure waveform purchase lasix 100 mg without a prescription, Neuro bromatosis, Osteopetrosis, Pendred, Usher, Waardenburg). Postnatal in ections related to hearing loss corresponding to bacterial and viral (herpes, varicella) meningitis. May even have sensorineural hearing loss (mild to pro ound, audiogram at or downsloping high- requency loss), conductive hearing loss (low requency), could additionally be isolated or related to Mondini mal ormation. Presents as 20-30-year-old wholesome person with sudden onset syncope and sudden dying. Mutation in neural crest cells results in de ective intermediate layer o stria vascularis. Conductive hearing loss, ankylosis o malleus and incus to lateral wall and de ormed xed stapes ootplate, extensive cochlear aqueduct, absent inner auditory canal (prohibits cochlear implantation). High penetrance, variable expressivity, successive anticipation (worse with every generation). O en mild and goes undiagnosed there ore audiogram really helpful in all sufferers with amily historical past o branchial anomalies. Stands or Coloboma o the eye, Heart de ects, Atresia choanae, Retardation o growth/development, Genitourinary abnormalities, Ear anomalies and dea ness. Clinical diagnosis based mostly on main and minor criteria: � Major criteria (a) Coloboma o the attention (cle o iris, retina, macula or disc, not eyelid), microphthalmos, anophthalmos. Mutation in tumor suppressor gene schwannomin on chromosome 22 results in abnormal production o protein merlin. Diagnostic standards: � Microtia (also have aural atresia, conductive listening to loss, sensorineural hearing loss and vestibular dys unction) Cha pter forty seven: Pediatric Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery 863 � Mid ace hypoplasia (underdevelopment o zygomatic arch) � Downsloping palpebral ssures � Coloboma o outer third o decrease eyelid with absence o lashes � Micrognathia (may have cle palate, velopharyngeal insu ciency) i. C demonstrates narrow down-sloping external auditory canals, de ormed head o the malleus, rudimentary head o the incus, quick or absent long process o the incus or absent incus, lacking components o stapes or full absence, xed stapes ootplate (risk o gusher at surgery), dehiscence o acial nerve, absence o one or all semicircular canals, cochlear mal ormation or absence. A ected males have stable hearing at birth, then progressive combined hearing loss or sensorineural loss which is o en bilateral (75%). Entry into cochleovestibular apparatus results in gush o perilymphatic uid which can result in a lifeless ear. Retinal ecks, anterior lenticonus (protrusion o the lens), spherophakia (spherical lens), congenital cataracts. Superior helix olded over, stenotic external auditory canal, center ear and mastoid illness, sensorineural listening to loss, hypoplastic lateral semicircular canal bony island, superior semicircular canal dehiscence, narrow inside auditory canal, cochlear nerve stenosis, giant vestibular aqueduct. Cha pter forty seven: Pediatric Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery 865 Nose, Nasopharynx, and Paranasal Sinuses Developmental Anatomy A. Entrapped tissue becomes extranasal encephalocele (meninges with or without mind tissue). Entrapped tissue turns into intranasal glioma (no meningeal connection) or intranasal encephalocele (retains meningeal connection). Frontal prominence: joins medial nasal/maxillary processes to orm rontonasal process which develops into rontal/nasal bones, ethmoids, cartilaginous nose. Secondary pneumatization at 6 months to 2 years, but not radiologically visible until 6 years o age. Maxillary sinus oor is superior to nasal oor at start, same stage as nasal oor at 8 years o age, and 5 mm beneath nasal oor by adulthood. External nasal dimensions mature by 13 years o age in emales and 15 years o age in males. In ants are obligate nasal breathers or several weeks so nasal obstruction leads to respiratory misery. A er they start to breathe orally, obstruction mani ests as sleep apnea and eeding di culties. May be associated with single central incisor, holoprosencephaly or pituitary de ciency. Bilateral atresia presents in new child as "cyclical cyanosis" with airway obstruction and cyanosis at rest that resolves with crying and agitation (due to openmouth posture). Unilateral atresia presents later in li e as unilateral nasal obstruction and thick, stringy, unilateral nasal discharge. Oral airway or McGovern nipple (eeding nipple with end minimize o) while in ant is obligate nasal breather. Unilateral atresia may be repaired when problematic, often prior to beginning college. Encephalocele is so and compressible, transilluminates, and has constructive Furstenberg take a look at (expands with crying, Valsalva maneuver, or compression o jugular vein). De ective dynein arms lead to poor mucociliary clearance, otitis media, sinusitis and bronchiectasis. Most widespread bacteria cultured are S aureus (47%) and P aeruginosa (26%) (P aeruginosa more frequent in patients older than eight years o age). Both o these micro organism ound in same sinus in solely 7% o patients, suggesting separate specimens should be obtained rom a quantity of sinuses. Sinus bacteria highly predictive o pulmonary micro organism in kids over 8 years o age. Pancreatic insu ciency, at malabsorption, coagulopathy (due to vitamin K de ciency), meconium ileus. Evidence o dys unctional cystic brosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein evidenced by any o the ollowing: 1. Elevated sweat chloride stage (rst line, diagnostic i larger or equal to 60 mmol/L). Drainage and nasal packing to minimize threat o abscess, per oration and saddle nostril de ormity. Drainage, packing and antibiotics (to cowl S pneumoniae and group A betahemolytic streptococci). Reduce immediately be ore swelling occurs or 5 to 7 days a er trauma when swelling subsides. Button/disk batteries should be removed immediately because of risk o necrosis and septal per oration. Bruising beneath eyes "allergic shiners" and "supratip crease" (rom rubbing nose upwards) frequent. Examination reveals pale, boggy edematous mucosa, in erior turbinate hypertrophy, thin clear rhinorrhea, +/- polyps. Pharmacotherapy (nasal saline, decongestants, steroid sprays, antihistamines, leukotriene inhibitors, mast cell stabilizers, anticholinergics) c. Pathogens embrace rhinovirus, coronavirus, adenovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. First stage-presents in rst 3 months o li e with watery rhinorrhea which progresses to mucopurulent drainage. Second stage-presents later in childhood with "snuf es" and gumma ormation in nasal cavity. Open mouth posture leads to unopposed compressive motion o masseter muscular tissues on maxilla and overgrowth o molars due to lack o contact. X-ray (bene t: no scope or uncooperative kids; dangers: radiation, crying kids elevate so palate which makes nasal aperture look smaller thus overestimating adenoid dimension. Recurrent obstruction ollowing surgery responds better to nasal steroids than previous to surgery. Uncomplicated in ections as a outcome of: � S pneumoniae (30%) � H inf uenzae (20%) � M catarrhalis (20%) � S pyogenes (5%) 3. Risks o spread � Frontal bone (Pott pu y tumor) � Meningitis � Abscess (subdural, epidural, brain) b. Cultures rom center meatus/ethmoid/maxillary sinus assist ul i � Immunocompromised � Systemic sickness � Progression despite appropriate remedy � Suppurative issues c. Related to allergy, continual sinusitis or cystic brosis (see above) Neoplasms Most sinonasal tumors in kids are benign. Extend laterally to pterygomaxillary area and superiorly to cavernous sinus and center cranial ossa. Approaches embody: 874 � � � � � Pa rt 6: Pediatrics Endoscopic (most common) LeFort I osteotomy and mid ace degloving Lateral rhinotomy ranspalatal Lateral in ratemporal ossa three.
Bisphosphonate therapy of osteoporosis is completed with daily oral dosing (alendronate hypertensive disorder lasix 100 mg order, risedronate blood pressure yahoo answers 40 mg lasix discount amex, ibandronate); weekly oral dosing (alendronate hypertension 130100 lasix 40 mg order without a prescription, risedronate); month-to-month oral dosing (ibandronate); quarterly injection dosing (ibandronate); or annual infusions (zoledronate) blood pressure chart guide order lasix 40 mg without a prescription. The main toxicity of the low oral bisphosphonate doses used for osteoporosis is gastric and esophageal irritation. Which of the following medication is routinely added to calcium dietary supplements and milk for the purpose of preventing rickets in youngsters and osteomalacia in adults The active metabolites of vitamin D act via a nuclear receptor to produce which of the following results Since menopause at fifty two years of age, she had been treated with raloxifene for osteoporosis prevention. Which of the next medicine can be utilized to cut back the fracture threat by further stimulating bone formation in this affected person A 58-year-old postmenopausal lady was despatched for dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry to evaluate the bone mineral density of her lumbar spine, femoral neck, and total hip. If this patient started oral therapy with alendronate, she would be advised to drink giant quantities of water with the tablets and remain in an upright place for no less than 30 min and until eating the first meal of the day. In the therapy of sufferers like this with secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic kidney disease, cinacalcet is a substitute for vitamin D-based drugs. The 2 forms of vitamin D-cholecalciferol and ergocalciferol- are generally added to calcium supplements and dairy products. Calcitriol, the lively 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 metabolite, would forestall vitamin D deficiency and is out there as an oral formulation. Pamidronate is a robust bisphosphonate used parenterally to deal with hypercalcemia. The energetic metabolites of vitamin D enhance serum calcium and phosphate by selling calcium and phosphate uptake from the gastrointestinal tract, rising bone resorption, and reducing renal excretion of both electrolytes. Teriparatide will increase bone formation and bone resorption; through the first 6 months, it causes a internet achieve in bone. Long-term remedy with glucocorticoids similar to prednisone is associated with a discount in bone mineral density and an increased threat of fractures. The threat of this toxicity is lowered by consuming water and by remaining in an upright place for 30 min after taking the treatment. Salmon calcitonin is available as a nasal spray or a parenteral kind for injection. In sufferers with continual kidney illness that requires dialysis, the impaired manufacturing of active vitamin D metabolites compounded with elevated serum phosphate as a result of renal impairment leads to secondary hyperparathyroidism. The molecular foundation of this selective action is poorly understood however is of value within the management of hyperparathyroidism and psoriasis. Cinacalcet is a member of a novel class of drugs that activate the calcium-sensing receptor in parathyroid cells. Loop diuretics (eg, furosemide) and thiazide diuretics have opposite effects on urine calcium concentrations; loop diuretics enhance urine concentrations of calcium, whereas the thiazides decrease urine calcium. By disrupting the lumenpositive potential that usually serves as the driving drive for resorption of Mg2+ and Ca2+, loop diuretics inhibit Mg2+ and Ca2+ resorption, leaving extra Mg2+ and Ca2+ within the urine and less in the blood. When thiazides inhibit the Na+/Cl� transporter in cells that line the distal convoluted tubule, they decrease the intracellular concentration of sodium and thereby enhance the Na+/Ca2+ change that occurs on the basolateral floor. This, in flip, creates a greater driving force for passage of Ca2+ via the apical membrane calcium channels. In sufferers with hypercalcemia, treatment with a loop diuretic plus saline promotes calcium excretion and lowers serum calcium. In sufferers with intact regulatory function, increases in calcium resorption promoted by thiazides have minor influence on serum calcium due to buffering in bone and intestine. However, thiazides can unmask hypercalcemia in sufferers with ailments that disrupt regular calcium regulation (eg, hyperparathyroidism, sarcoidosis, carcinoma). Compare and distinction the medical uses and results of the major types of vitamin D and its lively metabolites. Recall the results of adrenal and gonadal steroids on bone construction and the actions of diuretics on serum calcium ranges. Strategies designed to combat microbial resistance include using adjunctive agents that may defend against antibiotic inactivation, using antibiotic mixtures, the introduction of recent (and usually expensive) chemical derivatives of established antibiotics, and efforts to keep away from the indiscriminate use or misuse of antibiotics. The beta-lactams embody some of the most effective, broadly used, and well-tolerated brokers obtainable for the treatment of microbial infections. More than 50 antibiotics that act as cell wall synthesis inhibitors are presently available, with particular person spectra of exercise that afford a broad range of scientific applications. Penicillin subclasses have further chemical substituents that confer differences in antimicrobial activity, susceptibility to acid and enzymatic hydrolysis, and biodisposition. Pharmacokinetics Penicillins differ of their resistance to gastric acid and due to this fact differ in their oral bioavailability. Parenteral formulations of ampicillin, piperacillin, and ticarcillin are available for injection. They are usually excreted unchanged in the urine through glomerular filtration and tubular secretion; the latter process is inhibited by probenecid. This ring must be intact for antimicrobial motion Bacterial enzymes (penicillinases, cephalosporinases) that hydrolyze the beta-lactam ring of sure penicillins and cephalosporins; confer resistance Potent inhibitors of some bacterial beta-lactamases utilized in mixtures to shield hydrolyzable penicillins from inactivation Lowest focus of antimicrobial drug able to inhibiting progress of an organism in an outlined growth medium Bacterial cytoplasmic membrane proteins that act because the initial receptors for penicillins and other beta-lactam antibiotics Chains of polysaccharides and polypeptides which are cross-linked to form the bacterial cell wall More toxic to the invader than to the host; a property of useful antimicrobial medicine Bacterial enzymes concerned in the cross-linking of linear peptidoglycan chains, the final step in cell wall synthesis undergoes enterohepatic cycling. Procaine and benzathine forms of penicillin G are administered intramuscularly and have long plasma half-lives as a result of the active drug is launched very slowly into the bloodstream. Most penicillins cross the blood-brain barrier only when the meninges are inflamed. Mechanisms of Action and Resistance Beta-lactam antibiotics are bactericidal medication. Enzymatic hydrolysis of the beta-lactam ring ends in lack of antibacterial exercise. The formation of beta-lactamases (penicillinases) by most staphylococci and tons of gram-negative organisms is a major mechanism of bacterial resistance. Inhibitors of these bacterial enzymes (eg, clavulanic acid, sulbactam, tazobactam) are often utilized in mixture with penicillins to prevent their inactivation. Narrow-spectrum penicillinase-susceptible agents- Penicillin G is the prototype of a subclass of penicillins which have a restricted spectrum of antibacterial activity and are prone to beta-lactamases. Clinical uses embrace remedy of infections brought on by widespread streptococci, meningococci, gram-positive bacilli, and spirochetes. Most strains of Staphylococcus aureus and a major variety of strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae are resistant via manufacturing of beta-lactamases. Although no longer appropriate for remedy of gonorrhea, penicillin G remains the drug of choice for syphilis. Very-narrow-spectrum penicillinase-resistant drugs- this subclass of penicillins consists of methicillin (the prototype, but not often used owing to its nephrotoxic potential), nafcillin, and oxacillin. Their primary use is in the therapy of known or suspected staphylococcal infections. Ampicillin and amoxicillin-These medication make up a penicillin subgroup that has a wider spectrum of antibacterial exercise than penicillin G but stays prone to penicillinases. The outer membrane shown in this simplified diagram is present solely in gram-negative organisms. It is penetrated by proteins (porins) which are permeable to hydrophilic substances similar to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactamases, which inactivate beta-lactam antibiotics, could additionally be present in the periplasmic house or on the outer floor of the cytoplasmic membrane. When utilized in mixture with inhibitors of penicillinases (eg, clavulanic acid), their antibacterial activity is often enhanced. In enterococcal and listerial infections, ampicillin is synergistic with aminoglycosides. Piperacillin and ticarcillin-These drugs have exercise against several gram-negative rods, including Pseudomonas, Enterobacter, and in some cases Klebsiella species. Most drugs in this subgroup have synergistic actions with aminoglycosides towards such organisms. Piperacillin and ticarcillin are susceptible to penicillinases and are often utilized in mixture with penicillinase inhibitors (eg, tazobactam and clavulanic acid) to improve their exercise. Allergy-Allergic reactions embrace urticaria, severe pruritus, fever, joint swelling, hemolytic anemia, nephritis, and anaphylaxis. About 5�10% of individuals with a history of penicillin response have an allergic response when given a penicillin once more.
Lasix 100 mg purchase free shipping. Miracle Acupressure Points to Lower High Blood Pressure Naturally Fast - Dr Alan Mandell DC.