
Linezolid
| Contato
Página Inicial
"Generic 600 mg linezolid free shipping, bacteria 4".
P. Milten, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Weill Cornell Medical College
Male intercourse drinking on antibiotics for sinus infection linezolid 600 mg discount with visa, neck circumference necro hack infection linezolid 600 mg purchase with amex, and Mallampati rating have been shown to predict difficult intubation in overweight sufferers antibiotics for acne permanent cheap linezolid 600 mg otc, though these outcomes are inconsistent throughout multiple studies and the constructive predictive worth for such factors is low bacteria kingdom 600 mg linezolid purchase mastercard. Laryngoscopic view is improved in morbidly overweight sufferers with using a video laryngoscope. Higher initial doses may be essential to obtain adequate sedation, resulting in extended sedation. Increased volume of distribution and elimination half-life due to excessive lipophilicity. Lower doses will lead to poor intubating circumstances due to increased extracellular quantity and elevated exercise of pseudocholinesterase exercise in obese sufferers. Airway and respiratory derangements in overweight sufferers make this long-acting neuromuscular blocker undesirable. Obese patients have a better risk of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism perioperatively than nonobese patients. Remarks Increased cardiac output in overweight sufferers results in decrease peak arterial focus, leading to more fast awakening. Preoperative medical administration of the comorbidities, when attainable, could assist scale back the perioperative threat. Intraoperative Considerations Equipment and Positioning Whenever possible, patients should position themselves on the operating desk. In excessive circumstances, a mechanical lifting device may be required to transfer the affected person. Although most working room tables are capable of dealing with moderately obese patients, specifically designed tables are required for surgery in the extremely obese. For surgical procedures that require tilting or turning of the desk, strapping or taping the patient to the table along with stiffened "bean baggage" can forestall accidental falls. Gel and foam pads ought to be used to help pressure factors and forestall peripheral neuropathy and skin breakdown. The supine position is related to discount in lung volumes and hypoxemia, and venous return may be impeded through caval compression. In the inclined position, emphasis must be placed on free abdominal wall motion, with help for the chest wall and the pelvis. Lateral positioning and the sitting position allow the burden of the stomach fats to fall away from the chest and diaphragm. Also, recording occasions may be prolonged, resulting in delayed recognition of a change in blood strain. Although the utilization of the forearm for blood stress measurement could additionally be sufficient, use of invasive monitoring ought to be considered, especially in the presence of comorbid situations. Peripheral venous entry may additionally be difficult and should require ultrasound guidance. Airway Management In order to cut back the incidence and impact of aspiration, antacids, prokinetics, H2 receptor antagonists or proton-pump inhibitors should be administered prior to induction in patients with an identifiable danger of aspiration (discussed later). Although cricoid pressure is reasonable, the risk of aspiration must be weighed in opposition to the risk of worsened view during laryngoscopy. Placing the overweight affected person in a ramped place could be beneficial for laryngoscopy and intubation. The head, shoulders, and higher body are elevated above the chest, with the aim of elevating the external auditory meatus to the extent of the anterior chest wall. The goal of such positioning is to deliver a line drawn between the external auditory meatus and the sternal notch (yellow line) into a position parallel to the horizontal plane (red line). Standard supine positioning (left) demonstrates a 30� distinction between these two strains, whereas correct ramp positioning (right) has reduced this angle to solely 10�. Reduced ventilatory compliance could cause excessive airway pressures, making it tough to maintain plateau pressures <30, particularly with pneumoperitoneum during laparoscopic surgeries. However, hypercapnia can lead to a further enhance of pulmonary vascular resistance in patients with pre-existing pulmonary hypertension. Fluid Management Obese sufferers may suffer increased perioperative blood loss due to technical difficulties with surgical publicity. It can be tough to estimate fluid steadiness, adequacy of peripheral perfusion, and blood loss. Measurement of urine output, venous pressures, and acid�base balance could also be indicated. Monitored Anesthesia Care and Sedation Procedural sedation of the obese affected person is to not be taken lightly. There ought to be close monitoring of respiratory operate due to pre-existing respiratory compromise, elevated danger of respiratory melancholy with sedation, and the potential for tough masks ventilation and intubation. Dexmedetomidine is a selective 2-adrenergic agonist that provides sedation with out respiratory depression. However, extreme sedation used to perform or handle the regional anesthetic could negate the advantages. Neuraxial Techniques Spinal or epidural placement in the sitting position allows for simpler identification of the vertebral midline. Ultrasound can be used to establish the spinous processes and to reduce the number of needle passes. When longer needles are used, a cautious assessment of the midline will keep away from injury. Epidural placement may be challenging due to the loss of resistance felt in fats planes and difficulties in predicting the depth of the epidural house. There is the next initial failure price for epidural catheters in overweight laboring patients than in lean patients. During spinal anesthesia, local anesthetics and opioids can have an exaggerated cephalad spread because of (a) decreased cerebrospinal fluid quantity as a outcome of fatty tissue spread into the intervertebral foramina and engorged epidural veins (due to elevated venous pressures) and (b) head-down positioning of the vertebral column as a outcome of giant buttocks. A ramp under the chest elevates the cervical and thoracic spine, limiting cephalad spread of hyperbaric local anesthetic. Obese patients undergo the next price of block failure than nonobese sufferers, significantly with epidural, paravertebral, steady supraclavicular, and superficial cervical blocks. Although the use of ultrasound might enhance the success rate and reduce process time, ultrasound imaging in overweight patients may be suboptimal as a end result of an increased variety of reflective surfaces and higher depth to the buildings. Retraction and taping of the excessive soft tissue away from the procedural site allow for sterile preparation and easier access to insertion websites. In addition to antiemetics, adequate fluid substitute reduces postoperative nausea and vomiting in bariatric surgery sufferers. An opioid-sparing postoperative analgesia strategy consists of native anesthetic wound infiltration, intravenous acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, and thoracic epidural infusion of native anesthetics. Implementation of bariatric clinical care pathways improves affected person care and reduces price. Postoperative Management, Critical Care, and Resuscitation In addition to challenges with airway, vascular entry, and positioning and pharmacologic variations just like those in the intraoperative period, postoperative care in overweight patients presents a novel set of issues. Special beds and lifts are often required to move obese patients, and radiologic imaging can be problematic. Frequent repositioning of the patient, use of pressure-relief mattresses, and early mobilization will forestall decubitus ulcers. Appropriate antibiotic dosing and redosing, prevention of hyperglycemia, and upkeep of arterial and tissue oxygenation are required to stop surgical site infections in obese sufferers. Should cardiopulmonary resuscitation be required, chest compressions may be ineffective in morbidly obese patients. Repeat defibrillation shocks could additionally be necessary due to the higher transthoracic impedance. Although airway administration by conventional means could be challenging, surgical entry Did You Know Tracheal intubation of the overweight patient in the intensive care unit is to be averted unless needed. The affected person will typically be better off if different modalities of treatment are used. Hepatic Disease Patients with hepatic disease present for hepatic and nonhepatic surgical procedure. The anesthesiologist must be familiar with the unique pathophysiology of cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
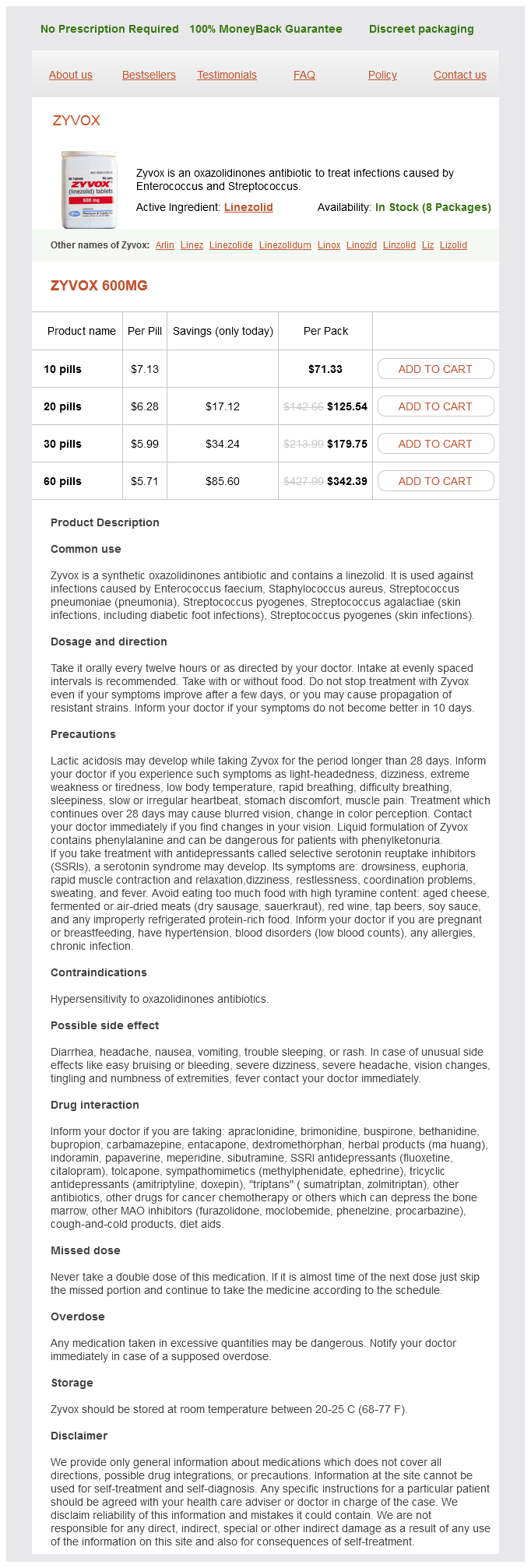
First kinds of antibiotics for acne cheap 600 mg linezolid with amex, these rules require the Two-Compartment assumption of the body as a single compartment infection 8 weeks after surgery linezolid 600 mg discount online. A pharmacokinetic compartKinetics ment is a mathematical assemble during which the general shape or conduct of the drug focus versus the time curve may be described by a specific and definable exponential algorithm antibiotics for sinus infection contagious linezolid 600 mg buy without a prescription. Following oral dosing antibiotic 4 times daily purchase linezolid 600 mg free shipping, for instance, the kinetics of absorption tends to mask the early drug distribution to tissues, and a single compartment is sufficient to well describe the pharmacokinetic occasions of a single or multiple doses. Thus, monoexponential kinetics applies in these cases and permits full use of the half-life guidelines introduced above. A pharmacokinetic compartment is a mathematical assemble that assumes instantaneous and repeatedly uniform mixing of drug (or solute) within it. Clearance is calculated as the amount of distribution instances the exiting switch fee fixed. A monoexponential drug concentration versus time curve is equivalently described by a one-compartment mannequin. Likewise, a multiexponential concentration versus time curve (usually with two or three exponential terms) is equivalently described by a multicompartment mannequin with two or three compartments. It is conceptually simpler to envision a central compartment related by switch price constants to rapid and gradual equilibrating compartments (in the case of a three-compartment model) than a multiexponential equation. Additionally, computing energy has removed the use of the multiexponential equation, which may be solved with a easy hand-held calculator. Now, functions running on phones can simply clear up the differential equations of multicompartmental fashions, merging each conceptual and computational ease. Context-sensitive Decrement Times To one extent or one other, all tissues in the physique act as drug depots. The charges that they accumulate drug as tissues equilibrate their drug concentrations with blood�drug concentrations varies with the blood flow to the tissue in relation to the tissue mass and its propensity to sequester the drug. For giant depots with comparatively low blood circulate, a day or more is required to reach steady state. Thus, for drug administration times that are less than those required to bring all tissues to steady-state blood�tissue drug focus ratios, the degree to which every tissue depot is "full" will differ as will the rates at which the assorted tissues will release drug back into the blood as the online switch reverses after administration ceases. Clinicians have to predict when drug concentrations in blood (or effect site) will fall (or decrement) from that wanted to preserve the desired anesthetic drug effect to a drug focus associated with another state, say, wakefulness. However, when there has been steady or repeated drug administration, the length of action is dependent upon the length of drug administration (or context sensitivity). While a 25% lower within the plasma focus after a 360 minute infusion takes less than 20 minutes (green dashed line), it takes over 240 minutes for a 50% decrease in plasma focus after the same 360-minute infusion (solid black line). In addition, a 75% lower in plasma focus takes roughly 500 minutes for infusions of one hundred eighty minutes or longer (red dashed line). These are plotted as time for a percentage drug concentration decrement, say, 50% (or half-time), on the y-axis versus the length of time the drug was repeatedly infused on the x-axis. Typically, the size of decrement time will rise because the infusion period increases, however the shape of the curve is unique to each drug. Covariates that Effect Pharmacokinetics There are a number of physiologic components that can alter the pharmacokinetics of a drug. Most of the focus within the clinical pharmacology literature is on the effects of hepatic or renal disease on pharmacokinetic parameters. Fortunately, restoration from a single bolus, repeated boluses, and even brief infusions depends as much, if not more, on drug distribution to and redistribution from tissue than elimination clearance. Therefore, until severe end-organ disease is present, a small decrease within the frequency or repeated boluses or the infusion rate could be made and adjusted based mostly on clinically observed drug impact. Increasing weight alters pharmacokinetic parameters as a end result of growing tissue volumes and blood volume increase the tissue available for drug uptake. Increases in the blood move to these tissues improve the volume of distribution for each of the tissues and the total physique. Although most hypnotics and opioids are relatively lipophilic, dosing these medication to the precise body weight overshoots the target focus. Yet dosing these medication to the best physique weight undershoots the target focus. This is as a outcome of the relative poor perfusion of the fat ends in little or no contribution of this compartment 128 Clinical Anesthesia Fundamentals Did You Know Weight and age have extra vital scientific results on pharmacokinetic parameters than all but essentially the most extreme derangements of the hepatic or renal perform. However, the elevated muscle mass required to carry the increased body weight does contribute substantially to the increased dose necessities. The physiologic bases for agerelated changes in drug distribution and clearances are unclear. They most likely characterize a mix of a decrease within the distribution of lean tissue versus muscle with age and the distribution of blood circulate to these tissues, an age-related decrease in cardiac output, and age-related changes within the distribution of cardiac output (1,2,5,6). Dose�Response and Concentration�Effect Relations Anyone who has ever taken an analgesic understands that as the dose of a drug is increased, the analgesic response can be increased. In addition, the likelihood that he or she has a satisfactory analgesic response is increased with the next dose. Furthermore, extra painful injuries require greater doses of drug to achieve a passable response. The interindividual variability in the relation of the dose needed to produce a given pharmacologic effect varies considerably, even in normal patients. The interindividual variability in the dose�response relation is caused by interindividual variability within the relation between the drug focus and pharmacologic impact (pharmacodynamic variability) superimposed on interindividual variability in the concentration of drug produced by a given dose of drug (pharmacokinetic variability). This highlights the most important disadvantage of the dose�response relation versus the concentration�response relation. The dose�response relation is unable to accurately establish whether or not the interindividual variability is brought on by variations in pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, or each. Most drugs produce their physiologic results (both therapeutic and toxic effects) by binding to a drug-specific receptor on the cell membrane, within the cytoplasm, or in nucleoplasm of the cell. Drug binding to the receptor is a reversible course of that follows the legislation of mass action-higher concentrations of drug lead to larger numbers of drug-receptor complexes and a bigger drug effect. The relation between drug concentration and the intensity of the response is most often characterised by a curvilinear relation. Once a pharmacologic impact is produced, small will increase in drug focus normally produce relatively massive increases in drug impact. As the drug effect reaches close to most, will increase in focus produce minimal modifications in effect. Therapeutic Thresholds and Therapeutic Windows the previous discussion alluded to the reality that in a given individual, there could not solely be interindividual variability but in addition vital intraindividual variability in the focus that produces the specified scientific impact without unwanted effects. Did You Know Increasing the dose of drug above the dose that provides maximal impact often results in undesirable unwanted effects. Between a 25% to 75% effect, the curve is approximately linear, and small adjustments within the concentration of fentanyl lead to a big change in impact. In distinction, under 25% and above 75% effect, the curve is relatively flat, and huge changes in fentanyl concentration are required to produce a small change in clinical effect. First, the minimum efficient concentration that produces a clinically significant impact (therapeutic threshold) can vary relying on the magnitude of the stimulation requiring treatment. Therefore, the dose of fentanyl that produces analgesia in the melanoma patient might not produce discernable analgesia in the backbone fusion patient. Although the therapeutic window (toxic threshold � therapeutic threshold) may be the similar magnitude, the spine fusion affected person will have the entire window "shifted greater. Furthermore, the duration of sufficient analgesia (time above the therapeutic threshold M) shall be longer for the melanoma patient if given the bigger dose of fentanyl. Therefore, most pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic research involve repeated measurement of blood concentrations of drugs and repeated measurements of a drug one hundred thirty Clinical Anesthesia Fundamentals 2. Representative therapeutic thresholds (the minimum focus required to produce analgesia) and toxic threshold (the concentration above which ventilatory depression occurs) are demonstrated for a patient after superficial melanoma surgical procedure (green dashed traces, M) and for a affected person after lumbar backbone fusion surgical procedure (dotted pink lines, S). A given bolus of fentanyl only produces analgesia from the time it produces an effect website concentration above the therapeutic threshold concentration for a affected person until the time when the impact site focus decreases below the therapeutic threshold focus. For instance, in a affected person after superficial melanoma resection, a 1 g/kg bolus of fentanyl (solid black line) will initially produce detectable analgesia roughly 2 minutes after administration (when it crosses the therapeutic threshold M, lower dashed green line), which is ready to last roughly 10 minutes after administration (when the focus decreases below the therapeutic threshold, lower green dashed line). So, though the larger bolus produces a faster onset of analgesia and an extended period of motion, it produces toxicity for a portion of this time.
Cheap linezolid 600 mg mastercard. CDC Vital Signs: Stop the Spread of Antibiotic Resistance (Short).
With the exception of remifentanil antibiotic 294 linezolid 600 mg order visa, limited work has characterised the conduct of opioids in overweight sufferers treatment for dogs ear mites 600 mg linezolid cheap with visa. The key to administering opioids to overweight sufferers is the selection of a dosing scalar: dosing an obese patient based on total physique weight will reliably end in extreme plasma concentrations bacteria shape purchase linezolid 600 mg free shipping, while dosing based on lean body mass or fats free mass could additionally be insufficient antibiotics zoloft generic linezolid 600 mg online. Dosing remifentanil to fats free mass in obese sufferers most intently mimics whole physique weight dosing in lean patients. Indications, Doses, and Special Considerations Morphine Morphine is the prototypic opioid and a very effective analgesic. Although this extended onset time permits partial pressure of carbon dioxide levels to climb progressively, lowering the danger of acute respiratory melancholy, it could also lead to clinicians inappropriately redosing morphine before the peak effect is achieved. Morphine undergoes intensive first-pass metabolism after oral administration, leading to excessive morphine-6-glucuronide ranges. This excessive hepatic extraction ratio implies that orally administered morphine has decrease bioavailability than parenteral morphine (13). It has a protracted medical impact (2 hours) and is suitable for use in patientcontrolled analgesia. Fentanyl Fentanyl could be administered intravenously as properly as by the transdermal, transmucosal, intranasal, and transpulmonary routes. Fentanyl has a peak onset three to 5 minutes after intravenous administration, and its analgesic impact lasts 30 to 45 minutes. Peak respiratory melancholy occurs between 3 and 5 minutes after an intravenous dose. Sufentanil Sufentanil is probably the most potent opioid commercially out there for human use; 5 g of intravenous sufentanil is the analgesic equivalent to 50 g of fentanyl. Alfentanil Alfentanil reaches peak effect rapidly, 90 seconds after bolus intravenous dose, and plasma concentrations fall quickly, much like remifentanil. In distinction to remifentanil, nevertheless, termination of the impact of alfentanil after an infusion (context-sensitive half-time) is comparable to that of sufentanil. The combination of fast onset of impact after bolus dosing and relatively extended termination of impact after an infusion might make alfentanil an attractive anesthetic adjunct during a stimulating surgery during which important postoperative pain is anticipated. Remifentanil Remifentanil is a potent fentanyl congener characterized by speedy onset (within ninety seconds), brief period (3 minutes), and brief context-sensitive half-time (5 minutes). It is metabolized by ester hydrolysis in the blood and tissues and is thus unaffected by hepatic or renal failure. It is an eminently titratable drug and allows the anesthesiologist to respond successfully to changing levels of surgical stimulation. Its very short context-sensitive half-time will terminate the analgesic impact shortly after the infusion is stopped. Therefore, if postoperative analgesia is required, a longeracting analgesic must be administered as an alternative. Methadone Methadone is on the market in oral and intravenous types and is mostly used in the remedy of opioid dependancy as a outcome of its prolonged pharmacokinetics makes acute withdrawal symptoms unlikely. Reversal Agents and Associated Effects Naloxone is an opioid receptor competitive antagonist with the greatest affinity for the receptor. In the absence of opioid, naloxone administration has 10 Analgesics 183 no effect. In the presence of opioid, naloxone can reverse all medical effects of opioids when dosed appropriately and is most often used to reverse opioidinduced ventilatory melancholy. Patients should be fastidiously monitored after administration of naloxone for a recurrence of ventilatory despair. Naloxone can cause tachycardia and, not often, pulmonary edema and even sudden demise in beforehand wholesome individuals (14). The combined opioid agonist-antagonists embody nalbuphine, pentazocine, and butorphanol. These "partial agonists" have much less abuse potential than opioid agonists but are also much less efficient at treating ache. They are mostly used to attenuate unwanted facet effects of opioids (ventilatory depression, pruritus) while maintaining some analgesia (the partial agonism). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication and perioperative bleeding in paediatric tonsillectomy. Effect of perioperative systemic alpha2 agonists on postoperative morphine consumption and pain depth: Systematic evaluate and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium tips for cytochrome P450 2D6 genotype and codeine therapy: 2014 replace. Naloxone reversal of morphine- and morphine-6-glucuronide-induced respiratory depression in healthy volunteers: A mechanism-based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling study. The time it takes for the plasma concentration of a drug to lower by 50% after the infusion of the drug is stopped. The time it takes for the plasma concentration of a drug to reach 50% of its steady-state concentration throughout a continuing infusion. The time it takes to enhance the plasma focus of a drug by 50% when the drug infusion price is doubled. The time it takes to lower the plasma concentration of a drug by 50% when the drug infusion fee is halved. In a patient weighing one hundred forty kg with a fat free mass (lean physique mass) of 70 kg, what would be the modified fats free mass to use for the initial calculation of the infusion price of remifentanil The potassium ion (K+) channels in the nerve terminal space limit the extent of Ca+2 entry into the terminal and restrict the transmitter quantal launch, initiating nerve membrane repolarization. Did You Know the precision of the muscle contraction is determined by the variety of muscle fibers every neuron innervates. In large muscles that require coarse, powerful movement (thigh or back muscles), the innervation ratio approaches 1 to 2,000. The central channel permits sodium ion (Na+) inflow and K+ efflux, leading to muscle cell membrane depolarization. Voltage-gated Na+ channels on the muscle membrane propagate the action potential across the membrane, leading to growth of muscle rigidity (the excitation�contraction coupling). Pharmacologic Characteristics of Neuromuscular Blocking Agents Potency of a drug is decided by the dose required to produce a certain impact and is expressed as a dose versus response sigmoidal curve. Onset time is inversely associated to dose and may be affected by fee of supply to action website (blood flow, speed of injection, and so on. Nondepolarizing agents can be classified based on their chemical construction (benzylisoquinolinium or steroidal) or to their length of motion (short, intermediate, or lengthy duration). Depolarizing Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs: Succinylcholine Succinylcholine has the fastest onset, the shortest period, and best reliability. This desensitization then results in flaccid paralysis after the initial receptor activation (manifested clinically as muscle "fasciculations"). This is characterised by fade of responses to repetitive stimulation and amplification of muscle responses after high-frequency stimulation (posttetanic potentiation), similar to nondepolarizing block. Myalgias are also quite common 1 to 2 days postoperatively (in 50% to 60% of patients). However, this system might render some sufferers susceptible to regurgitation and pulmonary aspiration due to partial paralysis of pharyngeal muscular tissues. Furthermore, because of the large particular person variability, pretreatment may be ineffective in other patients. Inadequate ranges of anesthesia throughout laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation, nonetheless, are much more likely to enhance intracranial strain. Approximately 1 in 25 patients could also be heterozygous and 1 in 2,500 individuals may be homozygous for the "atypical" deficiency gene and may require prolonged (hours) postoperative mechanical air flow. The degree of fade could be decided by a sequence of 4 stimuli delivered at a 2 Hz frequency by calculating the ratio of the amplitude of the fourth response (T4) to the amplitude of the first response (T1). They additionally could be categorized primarily based on their chemical construction as benzylisoquinolinium (atracurium, cisatracurium, mivacurium) or aminosteroid (pancuronium, rocuronium, vecuronium) compounds. Other elements, corresponding to muscle temperature, mode of evoked response monitoring, sort or web site of muscle monitoring, will have an result on the information. This higher focus distinction between plasma and the biophase partly explains the more fast onset of rocuronium. Although it will velocity up the onset, the much bigger dose will also markedly prolong the whole length of motion. Did You Know the vecuronium metabolite (3-desacetyl) has 60% of the mother or father compound efficiency.
Perioperative beta-blocker therapy should 246 Clinical Anesthesia Fundamentals Table 13-4 Recommendations for Perioperative Beta-Blocker Therapy 2009 Perioperative Focused Update Recommendations 1 antibiotics and mirena safe linezolid 600 mg. Beta blockers are most likely recommended for patients undergoing vascular surgery in whom preoperative evaluation identifies coronary coronary heart disease antibiotic 802 linezolid 600 mg without a prescription. Beta blockers titrated to coronary heart price and blood stress are cheap for sufferers in whom preoperative evaluation for vascular surgical procedure identifies excessive cardiac danger antibiotic xifaxan colitis linezolid 600 mg discount, as defined by the presence of more than 1 clinical danger issue antibiotics tired 600 mg linezolid cheap mastercard. Beta blockers are probably beneficial for patients in whom preoperative assessment for vascular surgery identifies excessive cardiac danger, as defined by the presence of more than 1 medical threat issue. New suggestion a Clinical risk elements embrace history of ischemic heart disease, history of compensated or prior coronary heart failure, historical past of cerebrovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and renal insufficiency (defined within the Revised Cardiac Risk Index as a preoperative serum creatinine of >2 mg/dL). Beta-blockers are effective for the treatment of important hypertension and also exert useful antiarrhythmic effects, particularly within the presence of elevated sympathetic nervous system tone related to surgical procedure or during situations characterised by elevated levels of circulating catecholamines. Beta-blockers reduce heart fee, myocardial contractility, and arterial stress by binding to 1 adrenoceptors and inhibiting the actions of circulating catecholamines and norepinephrine launched from postganglionic sympathetic nerves. These mixed results serve to scale back myocardial oxygen demand whereas simultaneously increasing provide. Betablockers range in their affinity for and relative selectivity at the 1 adrenoceptor, while a few of these medication exert "intrinsic sympathetic activity" by appearing as partial adrenoceptor agonists. The speedy onset and metabolism of esmolol makes the drug very useful for the remedy of acute tachycardia and hypertension during surgery. Esmolol is most frequently administered as an intravenous bolus, which causes nearly immediate dose-related decreases in heart rate and myocardial contractility. Arterial strain declines as a outcome of these direct adverse chronotropic and inotropic results. Esmolol is usually used to attenuate the sympathetic nervous system response to laryngoscopy, endotracheal intubation, or surgical stimulation, significantly in patients with identified or suspected coronary artery illness who may be susceptible to myocardial ischemia. Esmolol is also helpful for fast management of heart rate in sufferers with supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Finally, esmolol effectively blunts the sympathetically mediated tachycardia and hypertension that happen shortly after the onset of seizure activity throughout electroconvulsive therapy. Labetalol Labetalol consists of four stereoisomers that inhibit a and b adrenoceptors to various levels. The web effect of this mixture is a drug that selectively inhibits 1 adrenoceptors while concurrently blocking 1 and 2 adrenoceptors in a nonselective method. The intravenous formulation of labetalol accommodates a ratio of 1 to adrenoceptor blockade of approximately 1:7. Blockade of the 1 adrenoceptor causes arteriolar vasodilation and decreases arterial strain by way of a discount in systemic vascular resistance. Despite its nonselective beta-blocking properties, labetalol is also a partial 2 adrenoceptor agonist; this latter attribute additionally contributes to vasodilation. Labetalol-induced inhibition of 1 adrenoceptors decreases heart fee and myocardial contractility. Stroke quantity and cardiac output are primarily unchanged as a outcome of the mixed actions of labetalol on 1 and adrenoceptors. This action may be especially useful for the therapy of hypertension in the setting of acute myocardial ischemia. Labetalol can also be useful for controlling arterial strain with out producing tachycardia in sufferers with hypertensive emergencies and people with acute sort A aortic dissection. The internet impact of this shift in K+ stability is cellular hyperpolarization, which closes the voltage-gated Ca2+ channel and likewise facilitates rest. Vasodilation reduces venous return, contributing to declines in left and proper ventricular end-diastolic volume, stress, and wall stress, and likewise reduces systemic and pulmonary arterial pressures, which decreases left and proper ventricular end-systolic wall stress, respectively. Simultaneously, nitrovasodilators enhance myocardial oxygen provide by way of direct dilation of epicardial coronary arteries within the absence and presence of flow-limiting stenoses. A progressive attenuation of hemodynamic responses to nitrovasodilators could develop in different sufferers because of sympathetic nervous system and renin�angiotensin�aldosterone axis activation. This phenomenon (pseudo-tolerance) accounts for the rebound hypertension that might be observed after abrupt discontinuation of nitrovasodilator remedy. Inhibition of guanylate cyclase exercise is most likely responsible for true tolerance to natural nitrates. A "drug holiday" is a helpful technique for reversing this impact in sufferers requiring extended treatment in the intensive care unit. Administration of N-acetylcysteine, a sulfhydryl donor, may be efficient 250 Clinical Anesthesia Fundamentals for reversing true tolerance. Notably, extended use of natural nitrates may cause methemoglobinemia, intrude with platelet aggregation, and produce heparin resistance. It can be essential to recognize that natural nitrates must also be used with caution in patients receiving phosphodiesterase sort V inhibitors. At lower doses, this organic nitrate produces venodilation with out causing a big decrease in systemic vascular resistance. Arterial strain and cardiac output fall in response to the discount in preload, despite a modest baroreceptor reflex�mediated improve in coronary heart price. Nitroglycerin also decreases pulmonary arterial pressures and vascular resistance. Overshoot hypotension and tachycardia is a very common setting of hypovolemia, corresponding to is often observed in sufferers with poorly controlled essential hypertension and parturients with pregnancy-induced hypertension. Nitroglycerin improves the stability of myocardial oxygen provide to demand through its actions as a direct coronary vasodilator (which increases supply) and its systemic hemodynamic results (which scale back demand). Nitroglycerin dilates each regular and poststenotic epicardial coronary arteries, enhances blood move by way of coronary collateral vessels, and preferentially improves subendocardial perfusion. These results are particularly important in sufferers with acutely decompensated coronary heart failure resulting from myocardial ischemia. Under these circumstances, administration of nitroglycerin could precipitate life-threatening hypotension by compromising coronary perfusion stress, decreasing coronary blood circulate despite epicardial vasodilation, and worsening ischemia. These traits make sodium nitroprusside a first-line drug for the treatment of hypertensive emergencies. Unlike nitroglycerin, sodium nitroprusside is comparatively contraindicated in patients with acute myocardial ischemia as a outcome of the drug causes abnormal redistribution of coronary blood flow away from ischemic myocardium (coronary steal) by producing higher coronary vasodilation in vessels that perfuse normal myocardium in contrast with those that provide the ischemic territory. Sodium nitroprusside is often combined with a 1 adrenoceptor antagonist similar to esmolol to lower arterial pressure, depress myocardial contractility, and reduce ascending aortic wall stress in sufferers with acute type A aortic dissection till direct surgical management of the harm can be achieved. Clinical use of sodium nitroprusside is restricted by its poisonous metabolites, which predictably accumulate when administration is extended or comparatively high doses are used. Metabolism of sodium nitroprusside produces cyanide, which binds with cytochrome C to inhibit aerobic metabolism and trigger lactic acidosis. The latter metabolite may accumulate in patients with renal insufficiency and produce neurologic complications including delirium and seizures. Hydralazine Hydralazine is a direct vasodilator that reduces intracellular Ca2+ focus in vascular clean muscle, a minimal of partly, by activating adenosine triphosphate� delicate potassium channels. This motion produces direct rest of small arteries and arterioles in coronary, cerebral, splanchnic, and renal vascular beds, declines in systemic vascular resistance, and decreases in arterial strain. The primary reduction in afterload stimulates baroreceptor reflex�mediated tachycardia and will increase cardiac output. The magnitude of tachycardia observed with administration of hydralazine is commonly higher than anticipated based solely on baroreceptor reflexes alone and may as an alternative reflect a direct effect of the drug on other centrally mediated cardiovascular regulatory mechanisms. The pronounced tachycardia related to administration of hydralazine might produce acute myocardial ischemia in sufferers with critical coronary stenoses based mostly on increases in myocardial oxygen demand and reductions in coronary perfusion strain. Hydralazineinduced tachycardia responds appropriately to 1 adrenoceptor antagonists, but caution must be exercised as a outcome of further declines in arterial strain can also occur. Calcium Channel Antagonists Calcium channels are asymmetric biochemical pores consisting of no less than 4 subunits (1, 2/, and with or without) that traverse many biologic membranes. Under quiescent situations, Ca2+ channels are closed, however they may open through a voltage-dependent (requiring cell depolarization) or receptoroperated (activation) mechanism to enable Ca2+ entry into the cell or an organelle. Myocardial and vascular clean muscle cell membranes contain two distinct forms of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels which might be denoted primarily based on the relative duration of pore opening: T (transient) and L (long). There are four main courses of chemically distinct Ca2+ channel antagonists: (a) 1,4-dihydropyridines. Did You Know All Ca2+ channel blockers produce higher relaxation of arterial than venous vascular smooth muscle. All Ca2+ channel antagonists trigger higher rest of arterial in contrast with venous vascular easy muscle. Calcium channel antagonists improve myocardial oxygen supply through coronary arterial vasodilation and inhibition of coronary artery vasospasm. However, it is very important observe that some dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel antagonists might inadvertently enhance myocardial oxygen demand as a result of baroreceptor reflex�induced tachycardia, and consequently, could not constantly produce anti-ischemic effects in patients with coronary artery disease.