
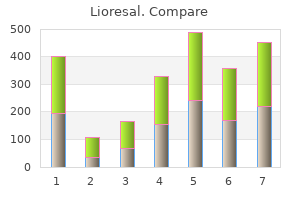
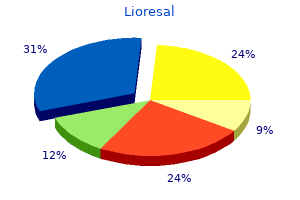
Lioresal
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Lioresal 10 mg order mastercard, spasms shoulder".
R. Varek, M.S., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Block the lesser occipital nerve with a fanlike injection of a local anesthetic answer spasms upper right abdomen discount 10 mg lioresal mastercard, 2 muscle relaxant recreational use 25 mg lioresal purchase mastercard. Ophthalmic (V1) Nerve Block the lateral and medial branches of the supraorbital spasms right abdomen generic 25 mg lioresal overnight delivery, supratrochlear back spasms 4 weeks pregnant discount 10 mg lioresal with visa, and infratrochlear nerves can be blocked by percutaneous native injection at the level the place they emerge from the superior aspect of the orbit. Anesthesia of the brow and scalp is achieved as far posteriorly because the lambdoid suture. This block can be utilized for d�bridement or topical remedy of burns or abrasions and for delicate lacerations of the upper eyelid. Additionally, an infraorbital (V2) block might be used to present anesthesia for restore of the maxillary laceration. The supraorbital notch is according to the pupil when the patient appears straight ahead Supraorbital nerve Supraorbital notch thought of when anesthesia of the forehead or the anterior facet of the scalp is desired. This nerve innervates the midline and should be blocked bilaterally for wounds or procedures that require midline anesthesia. Approach With the patient in the supine place, hold a finger or a roll of gauze firmly under the orbital rim to avoid ballooning of anesthetic into the higher eyelid and raise a skin wheal over the lateral border of the upper orbital ridge. Place another 1 to 2 ml of anesthetic within the area of the supraorbital notch as nicely. This successfully places a line of anesthetic resolution along the orbital rim laterally to medially to guarantee a block of all the branches of the ophthalmic nerve. Paresthesia within the type of an electrical shock sensation over the forehead indicates a profitable block. Complications hematoma formation or swelling of the eyelid may happen but requires solely local stress to restrict growth. Occasionally, ecchymosis of the periorbital region will seem the following day, and the patient must be warned of this chance. Insert the needle laterally and advance medially to include the supratrochlear nerve. Placing a finger inferiorly to the orbital rim can prevent eyelid swelling, and help in landmark identification. They can alleviate patient apprehension, reduce wound margin misalignment, and contribute to higher affected person outcomes. The blocks must be considered in all cooperative patients who require regional anesthesia within the head and neck. Rodella l, Buffoli B, labanca M, et al: A evaluate of the mandibular and maxillary nerve supplies and their clinical relevance. Singla h, Alexander M: Posterior superior alveolar nerve blocks: a randomised controlled, double blind trial. Chisci g, Chisci C, Chisci V, et al: Ocular issues after posterior superior alveolar nerve block: a case of trochlear nerve palsy. In Clinical anesthesia and pain drugs, ed four, Philadelphia, 2008, lippincott Williams & Wilkins. In Eriksson E, editor: Illustrated handbook in native anesthesia, ed 2, Philadelphia, 1980, Saunders. Peripheral vascular, coronary heart, and liver illness may increase the risk for extreme issues. Therefore information about the existence of those illnesses also needs to be sought. Instructions Explain the procedure to the patient, together with the ache of needle insertion, paresthesias, and potential complications which will happen. Discuss the potential want for extra anesthetic or various procedures if the nerve block fails. Be certain that the affected person understands that the additional administration of an anesthetic is part of the normal procedure quite than an try to appropriate an improperly carried out nerve block. Other widespread purposes embrace femoral blocks for fractures of the femur, ankle blocks for foot accidents and infections, intercostal blocks for rib fractures, and wrist blocks for accidents to the palm. The preparation, approach, selection of anesthetic, precautions, and problems are similar for all nerve blocks and are described generally within the following sections. The clinician is inspired to use the same basic strategies and precautions for all nerve blocks. Specific precautions distinctive to a particular nerve block are included with the description of that block. Note that the needle sizes given in text are basic recommendations, but for nearly all of blocks, a 25-gauge needle is good. In addition, maintain commonplace resuscitation equipment for superior cardiac life help readily available any time that local anesthetic agents are given. Patients who require intensive repair and anesthesia of the entire extremity are often referred to a specialist, who may choose to examine an unanesthetized limb. Scenarios in which this requirement is met include the following: � When distortion from local infiltration hampers closure. In general, most nerve blocks are accomplished for the restore of painful traumatic accidents that are more probably to cause ache lengthy after the restore is accomplished. Buffering the anesthetic is strongly inspired to reduce the ache of infiltration (see Chapter 29). Literature from 2010 describes the use and confirms the security of lidocaine with epinephrine (1: a hundred,000 concentration) for digital blocks. Ropivacaine is one other anesthetic with a fast onset and a protracted period of motion (several hours). It has been reported to have fewer cardiotoxic and central nervous system effects than bupivacaine. When drawing up the anesthetic from the vial, cover this anxiety- and fearinducing portion of the procedure from the patient. Preparation of the Area to Be Blocked To restrict the incidence of infection, put together the sector in aseptic trend before needle puncture. Allow the antiseptic solution to dry absolutely to obtain its maximal antibacterial impact. Choosing the Nerves to Block Successful anesthesia requires appropriate data of the relevant anatomy. Most areas to be anesthetized have overlapping sensory innervation and due to this fact require two or extra nerves to be blocked. In addition, the cutaneous distribution of the varied peripheral nerves differs slightly from affected person to patient. Use a liberal margin of error when determining which nerves provide the desired space of anesthesia. The use of ultrasound is associated with superior success rates with fewer attempts, much less time to carry out the block, and fewer complications in comparability with anatomic nerve blocks or use of nerve stimulators. Using the in-plane technique, the needle is inserted at the side of the probe and advanced towards the goal. With this method, the complete needle is visualized because it traverses the aircraft of ultrasound. With the out-of-plane technique, the needle enters the skin away from the probe and is aimed on the plane of sound. Detailed descriptions of ultrasound-guided nerve blocks may be found later in this chapter (see Ultrasound Box 31. Paresthesia A frequent method to ensure that the tip of the needle is in shut proximity to the nerve is to elicit a paresthesia. In apply, the jolt of a true paresthesia is often difficult to distinguish from the "ouch" of a pain-sensitive structure. When blocking proximal nerves at the elbow or axilla, the paresthesia travels far enough away from the injection site that it can be reliably distinguished from locally induced pain. Paresthesias at the level of the hand and wrist are harder to distinguish from ache. Before the process, a simple explanation of what the patient should or may feel will facilitate cooperation. Although eliciting paresthesias is usually dependable in demonstrating that the needle is near its goal, some authors believe that it may theoretically enhance the speed of complications as a outcome of mechanical trauma or intraneural injection. Locating the Nerve When locating a nerve to be blocked, approach it from a site with easily identifiable anatomic landmarks. Nerves that course adjoining to simply palpable arteries, similar to in the axilla and groin, are also straightforward to find and are good sites for performing nerve blocks. Blocking nerves with good structural or vascular landmarks is easy: palpate the landmarks and observe the course of the nerve in relation to these landmarks. Blocking nerves with poor landmarks, such as the radial nerve at the elbow, requires talent, practice, and a point of luck.
However spasms with stretching 25 mg lioresal buy free shipping, incision and drainage is contraindicated as a end result of it may result in spasms calf muscles lioresal 25 mg generic on-line bacterial superinfection muscle relaxant histamine release purchase lioresal 10 mg with amex. Many causes of this irritating condition have been described muscle relaxant easy on stomach cheap lioresal 25 mg overnight delivery, together with fungal, bacterial, viral, and psoriatic situations. Herpes infection of the hand predominantly presents in a bimodal age distribution: youngsters youthful than 10 years of age and younger adults between 20 and 30 years of age. In youngsters, herpetic whitlow tends to be associated with gingivostomatitis attributable to herpes simplex 1, whereas adults most commonly harbor herpes simplex 2. In the affected finger the infection is characterized by tenderness, adopted by throbbing or burning ache (out of proportion to the findings on bodily examination), edema, and erythema. Vesicles containing clear, bloody, or cloudy fluid type and mark probably the most infectious stage of the process. Viral vesicles typically involve the digits however can even involve other areas of the hand. Drainage of herpetic whitlow is contraindicated as it might induce a secondary bacterial an infection and delay healing. Oral antiviral agents effective in opposition to herpes infections (acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir) can shorten the course of the illness if given early. Infection recurs in 30% to 50% of cases, but the initial an infection is often essentially the most extreme. Acyclovir, 200 mg taken orally three to 4 instances a day, can decrease recurrence rates. An occlusive dressing decreases the prospect of viral transmission, however health care providers with herpetic whitlow should limit and possibly even chorus from patient contact, especially till all lesions have crusted over and viral shedding has stopped. An essential anatomic characteristic of this area is that many fibrous septa lengthen from the volar pores and skin of the fat pad to the periosteum of the phalanx; these septa subdivide and compartmentalize the pulp space. When an infection occurs within the pulp, these buildings make it a closed-space infection. The septa restrict swelling, delay pointing of the abscess, and inhibit drainage after incomplete surgical decompression. The distal phalanx was virtually fully resorbed due to pressure, inflammation, and chronic osteomyelitis. The infection can progress to osteomyelitis of the distal phalanx, septic arthritis, and flexor tenosynovitis. Although the septa may facilitate an infection within the pulp, in addition they present a barrier that protects the joint house and tendon sheath by limiting proximal spread of the infection. A affected person in whom a felon is creating will describe a gradual onset of pain and tenderness of the fingertip. In a few days, the pain turns into fixed and throbbing and gradually becomes severe. In the preliminary phases, physical examination may be fairly unimpressive as a result of the fibrous septa limit swelling within the closed pulp space. Occasionally, one may elicit level tenderness, but frequently, the complete pulp house is extraordinarily tender. The affected person characteristically arrives with the hand elevated over the head because the pain is so intense within the dependent position. During the early levels of cellulitis, a felon may be controlled by remedy consisting of elevation, oral antibiotics (see Box 37. A minor felon can normally be drained on an outpatient basis after the applying of a digital nerve block. Surgical drainage should be carried out rigorously to keep away from injury to nerves, vessels, and flexor tendons. Most felons could be managed with a limited process, but many surgical choices have been advocated, none of which has been proved to be superior for all circumstances. The preferred preliminary remedy is a straightforward longitudinal incision over the area of biggest fluctuance,194,195 3 to 5 mm distal to the distal interphalangeal joint. Frank pus may be encountered during incision, but usually only a few drops are expressed. A potential downside to an incision in the center of the fats pad is the production of a scar in a very sensitive and commonly traumatized area. The incision should not extend to the distal interphalangeal crease due to the hazard of injuring the flexor tendon. The subcutaneous tissue is bluntly dissected with a hemostat to present adequate drainage. A gauze pack may be placed within the wound for twenty-four to forty eight hours to guarantee continued drainage. Recurrent or extra extreme infections might require a extra aggressive method by a hand specialist. Follow-up suggestions for patients with a diagnosis of felon ought to embrace referral to a hand surgeon. No matter which incision is made, it must not be carried proximal to the closed pulp space due to the danger of entrance into the tendon sheath or the joint capsule. A cosy dressing, splinting, elevation, and enough opioid analgesics are conditions for a successful end result. On the primary postoperative go to, perform a digital block and take away the packing if present. Irrigate the incision copiously with saline and take away any extra necrotic tissue. At the first revisit, verify the sensitivities of the bacterial cultures and decide to continue or change antibiotics. Some clinicians advocate radiographic analysis for retained overseas our bodies at the preliminary visit, as properly as a baseline evaluation of the bone for subsequent analysis of osteomyelitis. Other clinicians reserve radiographs for wounds not displaying significant improvement in 5 to 7 days. Evidence of osteomyelitis, nonetheless, will not be found radiographically for a number of weeks after the looks of the lesion. After adequate drainage, osteomyelitis might reply surprisingly nicely to outpatient antibiotic remedy, with nearly full regeneration of bone being achieved if the I&D process has been enough. A fat pad incision is generally avoided but can be acceptable for localized infections. The transverse fats pad incision ought to avoid the digital nerves (2), and the longitudinal fats pad incision should keep away from the flexor tendon (3). The eponychium is lifted, which resulted in instant drainage of large portions of pus. A hemostat is used to break up loculations in the fats pad after which to seize gauze for a pull-through pack. The gauze pack is pulled via the incision and left in place for twenty-four to forty eight hours to guarantee continued drainage. For a felon the authors choose the through-and-through drainage process shown in B. Culture can aid in the number of long-term antibiotics, but most initially cowl for community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. In this instance, blood accumulated solely underneath the nail, not in any paronychial areas. B, Subungual hematoma of the nice toe after dropping a heavy object on the foot (a widespread injury). Patients present with horrible throbbing pain that will increase with the strain under the nail. There is an related blue-black discoloration under the affected nail, indicative of the hematoma. The source of the pain is strain in a contained house, urgent against nerve fibers and never from the gentle tissue injury or bony injury alone. The nail matrix is the tissue under the bottom of the nail that permits nail growth and migration. Its longitudinal fibers anchor the dermis to the periosteum of the distal phalanx. Scarring of the matrix, as occurs with nail trauma, can disrupt nail growth and result in nail deformity or permanent loss of the nail. The examination should include tests of the extensor and flexor tendons, of circulation by capillary refill, and of the sensitivity of the area. Crush accidents are related with three types of distal phalanx fractures: longitudinal, transverse, and comminuted. If the fracture is angulated, displaced, unstable, or intraarticular or includes a third or more of the articular surface, refer the patient to a hand surgeon.
10 mg lioresal with visa. What is erectile dysfunction (ED)? Causes symptoms and treatment for erectile dysfunction.
This is extraordinarily important in athletes as a outcome of coaches usually reduce these injuries spasms with spinal cord injury buy 25 mg lioresal mastercard. The mechanism is usually a blow to the top of the finger muscle relaxants quizlet cheap 10 mg lioresal with mastercard, similar to from a thrown ball spasms 1st trimester generic lioresal 10 mg amex, that creates an axial load and hyperextends the finger spasms while pregnant lioresal 25 mg order without a prescription. If a large fragment of bone is avulsed from the bottom of the phalanx, the dislocation is unstable after discount. The collateral ligaments will tear in varying degrees and should be assessed with stress testing after discount. If this fracture affects greater than 33% of the joint surface, closed discount shall be unstable as a end result of the collateral ligament is connected to the bony fragment. Apply strain to the base of the middle phalanx as the finger is brought into flexion. These accidents often reduce fairly easily, and failure of routine makes an attempt should raise suspicion of interposed gentle tissue, for which orthopedic session ought to be sought. After discount is completed, place the joint by way of a range of motion to guarantee stability of the discount. However, with disruption of the central slip of the extensor tendons, immobilization in flexion will lead to the event of a boutonni�re deformity. It is mostly finest to seek early orthopedic consultation for these accidents as a result of some require operative repair. If the emergency clinician accomplishes a closed reduction, postreduction films should demonstrate regular congruity of the joint surfaces, and a central slip attachment fracture should be excluded. These accidents are fairly frequent and will have dramatic and obvious scientific findings. The dislocation is often lowered in the area, earlier than emergency division analysis. If nonetheless dislocated, re-create the injury and then apply longitudinal traction to scale back the dislocation. Treat partial tears of the collateral ligaments by buddy taping the finger for 3 to 6 weeks. Hyperextend the finger and apply traction to distract the joint, after which apply strain on the bottom of the distal phalanx throughout flexion. Following reduction, verify the joint for stability and place the finger in a dorsal splint for 10 to 12 days. The affected person is unable to prolong the fingertip, but the joint seems regular on passive extension by the examiner. The harm is a rupture of the extensor tendon, with or without avulsion of a small piece of bone. Unless the damage is correctly splinted or surgically immobilized, permanent deformity will occur (see Chapter 48). The same classification of simple and complicated applies; the complex kind requires operative restore. For dorsal dislocations, flex the wrist to relax the tendons and hyperextend the joint so far as potential. If no fracture is seen on radiographs, contemplate carpal bone fracture or dissociation as the culprit. Scaphoid fracture, scapholunate disassociation or lunate or perilunate dislocation must be considered. Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging may be required to define the exact pathology. Note that patients with such injuries hold the wrist in flexion, worsening the edema by compression of dorsal hand veins. It can happen with or with out (demonstrated here) an avulsion fracture after seemingly minor trauma. B, this mallet deformity was caused by a baseball putting the fingertip end on and producing acute flexion of the joint. C, A stack splint, with the proximal interphalangeal joint left free to allow leisure of the distal interphalangeal joint, is saved in place for 6 to eight weeks. Caution the affected person to keep away from flexing the joint to "check it out" during splint changes. The diagnosis may be fairly difficult to make because the appearance may be subtle even on a lateral radiograph. Associated fractures and different accidents are regularly present, and percutaneous fixation is usually required. Nonetheless, these injuries often produce vital long-term disability, similar to persistent pain and weakness, untimely arthritis, and avascular necrosis. Definitive therapy is past the scope of this chapter and is carried out by a marketing consultant, usually a hand surgeon. The commonest carpal injuries are scapholunate dissociation and lunate and perilunate dislocation, although a selection of variations exist. Carpal dislocations and dissociations produce ache, weak spot, decreased range of motion, and often significant soft tissue swelling, with many signs seemingly out of proportion to the radiographic findings. Even although the symptoms and swelling may be spectacular, the radiographic findings are refined and sometimes overlooked, with preliminary and subsequent complaints being attributed to a extreme bruise or sprain. A, A posteroanterior view of the wrist demonstrates a widened space between the scaphoid (S) and the lunate (l) (arrow) due to ligamentous disruption from an impaction injury. B, A regular wrist reveals that the standard distance between the scaphoid and lunate ought to be roughly the same as that between the scaphoid and the radius. B, A lateral view shows that the lunate remains in alignment with the end of the radius (R) however the remainder of the carpal bones have been dislocated. The head of the femur is deeply located in the acetabulum, and liga- mentous and muscular assist could be very sturdy. Therefore hip dislocations are normally the result of vital pressure, and a careful search for different limb- or life-threatening injuries have to be undertaken. Common mechanisms of hip dislocation include bike or automobile accidents, automobiles striking pedestrians, and falls. A, On a posteroanterior view of the wrist, vital overlap is seen of the capitate (C) and scaphoid (S), as properly as the hamate (H) and lunate (l). B, On the lateral view, the carpal bones remain in alignment with the distal finish of the radius (R), however the lunate has rotated and dislocated in the palmar direction (arrow). However, the emergency clinician should have the ability to scale back easy hip dislocations, which are dislocations with out an related fracture or with a really minor fracture. A missed prognosis also can happen when a fracture of the femur obscures the medical image of hip dislocation. Yang and colleagues122 found that reduction past 24 hours was associated with a worse prognosis, but they might not find a significant time factor for those reduced in lower than 24 hours. If evidence of nerve damage exists, the dislocation should be treated as an emergency and lowered as early as possible. Posterior dislocation occurs 90% of the time and is seen here on the left, with the femoral head displaced superior and lateral to the acetabulum. On the best is an anterior dislocation with the femoral head displaced inferiorly and medially. This patient additionally has a fracture of the pelvis and possibly the left acetabulum and will require a computed tomography scan to unravel the extent of all injuries. A lateral or oblique view of the hip may assist make clear the kind of dislocation and allow detection of related fractures. Howard127 suggested modifying this system by making use of lateral traction on the flexed higher a half of the femur to disengage the pinnacle of the femur from the outer lip of the acetabulum. The left leg is shortened, kidnapped, flexed at the knee, and externally rotated, similar to the looks of a hip fracture. Posterior Hip Dislocation Posterior dislocation is the most common type of hip dislocation. Posterior dislocations generally occur secondary to a blow to the flexed knee with the hip in various levels of flexion. The larger the quantity of flexion of the hip on the time of the injury, the much less the chance of an associated fracture. The sciatic nerve is situated just behind the hip joint and could also be injured with a posterior hip dislocation. The supine position may be preferable in multiply injured sufferers because of the issue concerned in closely monitoring a critically sick affected person within the prone position. With the other hand, anchor the ankle of the affected leg firmly in opposition to the stretcher.
The bladder is an stomach organ in infants muscle relaxers to treat addiction 10 mg lioresal purchase amex, and inserting the needle too close to muscle relaxant baclofen lioresal 25 mg generic with visa the pubic bone or angling towards the ft might trigger the needle to miss the bladder back spasms 35 weeks pregnant purchase lioresal 10 mg with visa. Adult In adults spasms face lioresal 10 mg generic without prescription, the peritoneum is pushed cephalad by the crammed bladder during suprapubic aspiration. Description Background In conditions the place emergency bladder entry is necessary, the Seldinger (guidewire) method allows for suprapubic placement of a Foley balloon catheter for definitive bladder drainage. They are probably at greater threat for bowel damage throughout percutaneous suprapubic cystostomy tube placement than those with out earlier stomach surgical procedure. Patients with bleeding diatheses are at larger risk for postinsertion bleeding, either into the bladder, into the retropubic area, or at the web site of skin entry. Procedure the next comments concern the placement of the Cook peel-away sheath, as described by Chiou and colleagues. Raise a pores and skin wheal within the proposed web site (~2�3 cm above the pubic symphysis), and infiltrate the subcutaneous tissue and rectus abdominis muscle fascia at a 10- to 20-degree angle toward the pelvis. Locate the bladder by advancing the needle within the prescribed course while aspirating the syringe. Withdraw the needle, leaving solely the guidewire traversing the anterior stomach wall and positioned inside the bladder. Aftercare Connect the catheter to a drainage bag, after which costume the wound with four � four gauze pads to complete the procedure. Those with retention balloons, such as the usual Foley urethral catheter, are the most safe and need solely tape to attach them to the anterior stomach wall. A, Any catheter that can be utilized as a central venous catheter can be inserted suprapubically via the Seldinger technique. Pathophysiology In emergency conditions, nearly all of patients requiring suprapubic cystostomy are trauma sufferers with urethral disruption, or males with severe urethral stricture or complex prostatic disease. Even in the case of main trauma, many affected sufferers would require laparotomy for associated injuries, so the suprapubic catheter may be positioned intraoperatively. Contraindications as a result of placement of a suprapubic tube involves some risk, correct affected person selection is essential. Although no absolute reported minimum bladder quantity has ever been established, there must be enough urine within the bladder to permit the needle to totally penetrate the bladder dome without immediately exiting via the base. A small stab wound in the anterior abdominal fascia could additionally be required to accommodate the dilator and sheath. A 5-mL balloon will accommodate 10 mL simply and make unintentional catheter distraction less probably. The most severe complications contain perforation of the peritoneum or the intraperitoneal contents. Although discovering the bladder using a small-gauge "scout" needle may help reduce bowel damage, even in probably the most apparently profitable of bladder punctures, a complication may still result. Allowing the bladder to refill over time may be an necessary consideration, especially if preliminary attempts to locate the bladder had been unsuccessful. Ultrasound steering may also be useful for determining bladder measurement and placement. Conclusions Suprapubic cystostomy could be readily performed when emergency bladder access is required. As such, when time affords, dialogue with a urologist is prudent to discover alternative strategies of bladder entry and urine drainage. The timing of any radiologic analysis may be challenging within the emergency setting, particularly when confronted with a critically ill, multiply injured affected person. The trauma team of clinicians concerned in each resuscitation should determine the priority and extent of such an evaluation on a case-by-case basis. In sufferers with urologic trauma, the decrease urinary tract should be studied earlier than the upper urinary tract. These research must be carried out in the proper sequence and in a retrograde fashion to keep away from lacking potential accidents. Retrograde refers to the technique of instilling contrast retrograde by way of the urethra or by gravity filling of the bladder. Complications: tissue irritation from contrast extravasation; progression of urethral damage from overly forceful injection of distinction materials. Equipment: tools and personnel for plain radiographs (or fluoroscopy), small Foley catheter (or Toomey syringe), distinction material for injection. The pendulous and bulbous urethral segments are anterior, and the membranous and prostatic segments are posterior. Pathophysiology the male posterior urethra, which incorporates the membranous and prostatic urethra, is injured extra regularly than the anterior urethra. The urogenital diaphragm encloses and fixes the membranous urethra; the prostate and prostatic urethra are firmly hooked up to the posterior surface of the symphysis pubis by the puboprostatic ligaments. The feminine urethra, in contrast, is short and comparatively mobile and usually escapes harm in blunt trauma. Occasionally, a big pelvic fracture will lead to a laceration or avulsion of the female urethra at the bladder neck. Direct accidents to the feminine urethra can also occur secondary to penetrating trauma to the vagina or perineum. These injuries often are disclosed by blood at the introitus or an irregular vaginal examination within the feminine pelvic fracture patient. This happens mostly because of straddle injuries in males however may result from any blunt perineal trauma. Penetrating accidents or urethral instrumentation can also cause accidents to the penile urethra. Gently lengthen and stretch the penis alongside the medial thigh to maximize urethral unfolding. In different instances, orient the hips in a slightly oblique position in relation to the stretcher. Remove the central plunger from a 60-mL catheter-tip syringe and fasten the tip to a Foley catheter. Hold the syringe above the extent of the bladder and pour distinction materials into the syringe. Allow the bladder to fill by gravity instillation, and fill to capability (~400 mL in an adult). Description Background In the resuscitation of any trauma patient, placement of a Foley catheter is a normal methodology of monitoring urinary output. In this case, a distended bladder and connected prostate gland are sheared from the mounted membranous urethra. Note the event of a perivesical hematoma and the presence of a high-riding prostate gland. However, the value of those findings to the emergency clinician has been known as into question, given their low sensitivity. It assumes that the urethra is regular before passing the Foley catheter required for retrograde cystography. Contraindications Uncertainty about urethral integrity is a contraindication to blind urethral catheterization. As such, urethral integrity must be ensured prior to Foley catheter placement, which is essential for retrograde cystography. History of a prior response to radiographic distinction materials is a relative contraindication to distinction use, depending on the route of administration chosen. Procedure Several different iodinated contrast agents are suitable for retrograde research (urethography, cystography). Retrograde Urethrogram A affected person with an related pelvic fracture ought to remain supine all through the whole radiographic examination. A, Disruption of the anterior urethra (bulbous urethra) happens with straddle-type accidents in a male. Extravasation of urine and blood may occur in the perineum or scrotum or alongside the anterior abdominal wall. In this case, extravasation is confirmed and leads to a swollen and ecchymotic penis. Second, hold the penis between the long and the ring fingers of the nondominant hand to permit a comfortable fit of the contrast-filled syringe or catheter contained in the urethral meatus. Stretch the penis laterally over the proximal thigh with average traction to stop urethral folding. Seat the balloon portion of the catheter in the fossa navicularis of the penile urethra, and delicately inflate it with 1.