
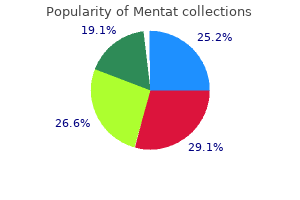
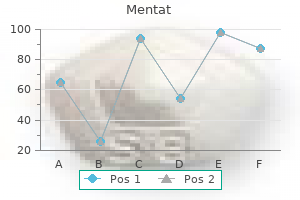
Mentat
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Purchase mentat 60 caps with visa, treatment resistant anxiety".
E. Ugrasal, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences College of Osteopathic Medicine
Zheng W treatment uterine fibroids order 60 caps mentat, Xie Y medicine quetiapine mentat 60 caps discount free shipping, Li G treatment 4 burns buy mentat 60 caps with mastercard, et al: Critical function of calbindin-D28k in calcium homeostasis revealed by mice lacking both vitamin D receptor and calbindin-D28k medicine 4 times a day mentat 60 caps proven. Sooy K, Kohut J, Christakos S: the position of calbindin and 1,25dihydroxyvitamin D3 within the kidney. Benign tumors can come up from any cell kind inside the kidney, and most are of epithelial or mesenchymal origin. Other benign tumors are cystic masses or are composed of both epithelial and mesenchymal parts. Nephrectomy is normally the remedy of selection for large renal plenty no matter kind, but the potential for oncocytoma should be thought-about with incidentally discovered small renal lots or tumors in a solitary kidney. The peak incidence of this tumor is within the fifth and sixth decades of life8 with a female predominance of two. Reported symptoms embody stomach or flank pain, palpable mass, fever, and hematuria. Renal adenomas are often discovered by the way during surgery or at post-mortem, with an incidence of 7. The cytoplasm of those cells is full of mitochondria, resulting in their histologic look. Immunohistochemical studies counsel that oncocytomas in all probability additionally arise from the intercalated cells of the distal amassing tubules. Larger oncocytomas can have a stellate central fibrous scar, which is visible on preoperative radiologic research in 6. The traditional kind accommodates variable quantities of vascular, easy muscle, and adipose elements, whereas in the epithelioid variant, epithelioid cells predominate and vascular and adipose elements are usually absent. Treatment options embrace angioembolization, partial nephrectomy, and radical nephrectomy. The peak incidence of this tumor is within the second or third decade, with a 2: 1 female-to-male predominance. Most typically, affected patients present with poorly controlled hypertension, polyuria, polydipsia, muscle aches, and complications. Surgical resection provides definitive remedy and leads to reversal of hypertension and hypokalemia. Hemangiomas are small, normally lower than 2 cm,26 and located in the tip of the papilla and the renal pelvis. Hemangiopericytomas of the kidney are uncommon, with lower than forty instances reported within the literature. Most sufferers with this tumor current within the fourth decade of life and might have hematuria or hypoglycemia because of glucose hypermetabolism inside the mass. If intervention is required, therapeutic options embody percutaneous32 or laparoscopic aspiration,33 cyst marsupialization,34 and nephrectomy. Ninety % of those tumors happen in girls and may be related to estrogen therapy. Transitional carcinomas arising from the renal pelvis are the subsequent most typical, accounting for 7% to 8% of major renal neoplasms. Other parenchymal epithelial tumors, corresponding to oncocytomas, accumulating duct tumors, and renal sarcomas, are unusual however are becoming extra incessantly recognized pathologically. Metastatic lesions to the kidney (secondary neoplasms) happen in 7% to 20% of sufferers with cancer at autopsy. A brief description of the biology and administration of the much less common tumors as well as evaluation of suspected metastatic illness is also offered. The incidence in Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders is half that of their white and African American counterparts. Between 1975 and 1995 within the United States the incidence charges per 100,000 person-years elevated by 2. Since 1950, there has been a 126% increase within the incidence, accompanied by a 37% improve in annual mortality. The carcinomas are a number of and bilateral in approximately half the instances, a discovering in keeping with the diffuse nature of the underlying illness. Patients with this prognosis are at increased threat for renal pelvic tumors and probably kidney most cancers, though the latter association stays controversial. The issues embrace von Hippel�Lindau syndrome, hereditary papillary renal most cancers, hereditary leiomyoma renal most cancers syndrome, and Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome. These cancers had been all staged as T1 illness, and not certainly one of the tumors had been seen on preoperative imaging. An elevated incidence of sarcomatoid features was not seen in this group, probably due to the benign indications for extirpation. Renal cell tumors occur with equal frequency in proper and left kidneys and are distributed equally all through the kidney. Previously, renal lesions smaller than 2 to 3 cm had been incorrectly thought of to be benign adenomas. Such distinctions between benign and malignant tumors are made no longer on the basis of size but somewhat based on fundamental histologic standards. Therefore, from a sensible standpoint, all stable renal plenty require resection or biopsy for accurate histologic analysis. Improved percutaneous biopsy techniques have a task within the administration of renal masses however are definitively much less correct than extirpation in offering pathologic and histologic data. Renal cell carcinomas have historically been categorized based on cell sort (clear, granular, spindle, or oncocytic) and development sample (acinar, papillary, or sarcomatoid). Each of these tumors has a unique progress sample, cell of origin, and cytogenetic traits. In hereditary illness papillary carcinomas are multifocal and bilateral, and so they commonly manifest as small tumors. This classification is predicated on the work of Storkel S, van den Berg E: Morphological classification of renal cancer. These tumors usually have a low stage at presentation and are thus attributed a more favorable prognosis,89,ninety but in advanced phases, they are often as aggressive as clear cell lesions. In distinction to clear cell carcinomas, accumulating duct tumors produce mucin and react with antibodies to each high-molecular-weight and lowmolecular-weight keratins. Neither oncocytomas nor amassing duct tumors have been associated with a constant sample of genetic abnormalities. The architecture is predominantly strong, tubular, acinar, or alveolar, with areas with a pseudopapillary look. Tumor improvement on this setting is linked to somatic inactivation of the remaining wild-type allele. Their protein products play critical roles in mobile and systemic physiologic responses to hypoxia, together with glycolysis, erythropoiesis, angiogenesis, and vascular remodeling. These knowledge might underestimate the importance of alterations in c-Met, as a outcome of different mutations, chromosomal duplications. This condition is associated with progressive encephalopathy, cerebral atrophy, seizures, hypotonia, and renal developmental delay. Many tumors are clinically occult, leading to delayed diagnosis, when a more superior and symptomatic stage is common. Indeed, 25% of individuals have distant metastases or domestically advanced disease at the time of presentation. In a research of 3912 sufferers who had been surgically treated for by the way found renal masses, 3650 patients (90%) had been diagnosed with a primary renal malignancy, of whom 28. Cancer-specific mortality in this group of patients with by the way found kidney cancers was 14. Varicoceles typically result from obstruction by tumor thrombus of the gonadal vein at its entry level into the left renal vein. Varicocele development in an adult should all the time raise the risk of an related neoplasm within the kidney. In addition, inferior vena cava involvement by tumor thrombus can produce quite a lot of clinical manifestations, including ascites, hepatic dysfunction probably related to Budd-Chiari syndrome, pulmonary emboli, and bilateral lower extremity edema. Other common websites, from most to least widespread, are lymph nodes, bone, liver, adrenal gland, contralateral kidney, and brain.
The so-called coffin lid crystals of struvite are additionally very characteristic and point out that an infection-related stone is likely medicine in ukraine mentat 60 caps cheap with amex. Although uric acid and calcium oxalate crystals generally occur and are comparatively nonspecific medicine images 60 caps mentat free shipping, when a kidney stone exists these crystals may be very helpful etiologic clues medicine to stop diarrhea cheap 60 caps mentat with amex. The saturation-supersaturation state of the urine for various stone-forming crystals can additionally be routinely calculated medicine 018 60 caps mentat cheap free shipping. In general, a minimal of two 24-hour samples must be collected because of vital every day variation in excretion rates. Urine metabolic stone risk testing ought to be accomplished every time recurrent stones develop or when a primary stone is documented in a affected person with a higher than ordinary danger for recurrence. Some experts imagine that 24-hour urine studies should be performed after the first kidney stone in all patients, however this method may not be sensible. Calcium stones are radiopaque, cysteine stones are slightly radiopaque, and pure uric acid stones are radiolucent. Therefore, sonography is usually used to follow the progress of identified stone disease, but not as an preliminary study. However, sonography is indicated because the initial procedure in pregnant girls or whenever radiation publicity have to be minimized. Any form of renal bleeding associated with blood clots may cause ureteral obstruction and produce signs similar to those of a kidney stone. Other clinical mimics of kidney stones are an stomach aortic aneurysm, pyelonephritis, renal cancer, renal tuberculosis, papillary necrosis, renal infarction, and renal vein thrombosis. Papillary necrosis, which is extra likely in patients with diabetes or sickle cell illness, may cause true renal colic when sloughed papillae obstruct the ureter. However, admission and pressing urologic session is required if the patient is septic, has an an infection proximal to an obstruction, or has obstruction of a solitary kidney (including a renal transplant). Bilateral kidney obstruction, high-grade obstruction with a large (>7 mm) stone, acute kidney damage, urine extravasation, or unrelenting ache despite analgesics also requires urologic session. The most important determinant of the likelihood that a stone will cross is its size. Consequently, conservative outpatient therapy becomes less more likely to be successful as the stone dimension increases past four to 5 mm. This could be achieved by urinating through a filter or fantastic screen-an aquarium web is a good choice. If none is available, the affected person can urinate by way of a fine gauze pad or simply void right into a glass jar in order that the calculus might be seen. Older age, feminine gender, respiratory failure, liver failure, sepsis, and impaired consciousness all correlate with greater in-hospital mortality charges. Prerenal azotemia (a dysfunction characterized by renal hypoperfusion, by which renal parenchymal tissue integrity is preserved) 2. In this regard, a careful evaluate of medical, pharmacy, nursing, laboratory and radiologic information is important. A comparatively latest serum creatinine determination is invaluable but not all the time available. It can also be important to establish another potential nephrotoxic agents such as phosphate loads given as cathartics. A historical past of voiding signs similar to urinary frequency, hesitancy, or incontinence suggests the chance of obstructive uropathy. Patients with renal artery emboli and a few with renal vein thrombosis could current with flank ache and a history of hematuria. A history of fever, skin rash, arthralgias, sinusitis, and/or hemoptysis raises the potential for glomerulonephritis associated to an infection, collagen vascular disease, or vasculitis. Signs of the previous condition embrace distended neck veins, pulmonary rales, an S3 gallop, and pitting peripheral edema. Stigmata of chronic liver illness, including jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, ascites, gynecomastia, nail clubbing, palmar erythema, vascular spiders, and testicular atrophy ought to be sought. This usually ignored condition usually happens following an invasive procedure that requires intraarterial catheterization. Skin findings embody livedo reticularis, ulcers, purpura, petechiae, painful erythematous nodules, cyanosis, and gangrene. If lower tract obstruction is a severe consideration, a diagnostic postvoiding bladder scan or catheterization should be carried out. This will increase the urine particular gravity and should generate positive dipstick protein outcomes. Microscopy usually reveals hyaline casts, however in general there should be few cells and no cellular casts. Less severe quantity depletion is usually recommended by an orthostatic pulse increase of more than 30 beats/min (measured 1 minute after standing). Orthostatic hypotension, defined as a drop in systolic blood strain of greater than 20 mm Hg after standing, is much less useful as a end result of it occurs in 10% of regular subjects. The fractional excretion of Na and fractional excretion of urea are often also very low with contrast nephropathy, rhabdomyolysis, acute myeloma kidney, and acute urate nephropathy. However, a rising creatinine concentration signifies that the renal damage is stable or worsening, whereas a falling creatinine concentration is usually indicative of enchancment. Potentially lifethreatening hyperkalemia and severe metabolic acidosis must be identified and handled. Although a measurement of the urine sodium focus can be helpful in distinguishing these problems, the fractional excretion of sodium and/or urea are better indicators. Renal damage could have been present for hours to days before a noticeable rise in plasma creatinine concentration is detected. Early measurement of those biomarkers may enable the detection of renal injury within hours of the insult. Doppler ultrasonography may also be used to assess renal arterial and venous patency when vascular obstruction is suspected. The plasma concentrations of urea nitrogen and creatinine, two such substances which are routinely measured, enhance. Although overt signs may be absent, cautious analysis typically reveals a large spectrum of abnormalities in these sufferers. Uremic syndrome is the outcome of severely reduced excretory operate, with retention of metabolic merchandise, fluid and acid-base derangements, hormonal abnormalities, and different consequences of the loss of renal operate. In late 2011, the prevalence had risen to 1901 per million population (this number consists of dialysis patients and those with a functioning renal transplant). The focus of the history, bodily examination, and laboratory research in these patients is to set up the particular prognosis, determine the severity of kidney dysfunction, identify any reversible part, identify and quantitate any comorbid circumstances and issues, assess the danger for continued loss of kidney function, and assess the danger for cardiovascular disease. In some, the kidney disease is an isolated abnormality; in others, an underlying disease known to be related to kidney involvement such as diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, hepatitis B or C, scleroderma, or vasculitis could exist. The period of the kidney disease and price of progression must be established every time possible. The affected person may learn about a particular diagnosis, severity or stage of the kidney disease, and its tempo. Any prior laboratory knowledge, biopsy reports, imaging results, and urologic interventions ought to be reviewed. Polygenic familial issues embrace diabetes mellitus, hypertension, weight problems, hyperlipidemia, and untimely vascular disease. Sometimes, family members can present a extra correct evaluation of these parameters than the patient. Urinary voiding symptomatology ought to be identified, including voiding symptoms such as polyuria, nocturia, hesitancy, frequency, and any history of urinary tract infections, back, flank, abdominal, or pelvic pain, renal calculi, or urologic manipulation. A cardiovascular, peripheral vascular, and cerebrovascular disease history must be elicited. A historical past of coronary artery interventions, important arrhythmias, or insertion of a pacemaker or defibrillator should be identified. It is imperative that any history of resting or exertional chest ache and/or shortness of breath be acknowledged. A historical past of claudication, peripheral ulcers, revascularization, gangrenous extremities, or extremity amputation must be documented. The interpretation of weight change is sophisticated, nonetheless, as a result of loss of physique mass may be masked by fluid accumulation. Medications should be reviewed for potential nephrotoxic effects and for acceptable dosing for renal function. When diabetes exists, its period, particular drugs, adequacy of control, hemoglobin A1C levels, and results of microalbuminuria studies should be ascertained. In general, the onset of type 2 diabetes is difficult to decide as a outcome of this disease could also be clinically silent for years.
Schnermann J medicine xalatan mentat 60 caps cheap line, Traynor T symptoms job disease skin infections order mentat 60 caps, Pohl H medicine quinidine mentat 60 caps purchase without a prescription, et al: Vasoconstrictor responses in thromboxane receptor knockout mice: tubuloglomerular suggestions and ureteral obstruction treatment plan for anxiety discount 60 caps mentat visa. Rocca B, Secchiero P, Ciabattoni G, et al: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is induced during human megakaryopoiesis and characterizes newly shaped platelets. Taniura S, Kamitani H, Watanabe T, et al: Transcriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase-1 by histone deacetylase inhibitors in regular human astrocyte cells. Rossat J, Maillard M, Nussberger J, et al: Renal effects of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition in normotensive salt-depleted topics. Whelton A, Schulman G, Wallemark C, et al: Effects of celecoxib and naproxen on renal perform in the aged. Segasothy M, Samad S, Zulfigar A, et al: Chronic renal disease and papillary necrosis related to the long-term use of nonstroidal anti-inflammatory medication as the solely real or predominant analgesic. Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S, Ichikawa A: Distribution and performance of prostanoid receptors: studies from knockout mice. Sato T, Sawada S, Tsuda Y, et al: the mechanism of thrombininduced prostacyclin synthesis in human endothelial cells as regards to the gene transcription of prostacyclin-related enzymes and Ca2+ kinetics. Okahara K, Sun B, Kambayashi J: Upregulation of prostacyclin synthesis-related gene expression by shear stress in vascular endothelial cells. Soler M, Camacho M, Sola R, et al: Mesangial cells release untransformed prostaglandin H2 as a serious prostanoid. Guan Y, Zhang Y, Schneider A, et al: Urogenital distribution of a mouse membrane-associated prostaglandin E(2) synthase. Yokoyama C, Yabuki T, Shimonishi M, et al: Prostacyclin-deficient mice develop ischemic renal problems, including nephrosclerosis and renal infarction. Urade Y, Eguchi N: Lipocalin-type and hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthases as a novel example of functional convergence. Narumiya S, Sugimoto Y, Ushikubi F: Prostanoid receptors: structures, properties, and functions. Abramovitz M, Adam M, Boie Y, et al: the utilization of recombinant prostanoid receptors to decide the affinities and selectivities of prostaglandins and associated analogs. Abe T, Takeuchi K, Takahashi N, et al: Rat kidney thromaboxane A2 receptor: molecular cloning signal transduction and intrarenal expression localization. Hirata T, Kakizuka A, Ushikubi F, et al: Arg60 to Leu mutation of the human thromboxane A2 receptor in a dominantly inherited bleeding disorder. Kiriyama M, Ushikubi F, Kobayashi T, et al: Ligand binding specificities of the eight varieties and subtypes of the mouse prostanoid receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Eguchi N, Minami T, Shirafuji N, et al: Lack of tactile ache (allodynia) in lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase-deficient mice. Vitzthum H, Abt I, Einhellig S, et al: Gene expression of prostanoid forming enzymes along the rat nephron. Tanikawa N, Ohmiya Y, Ohkubo H, et al: Identification and characterization of a novel kind of membrane-associated prostaglandin E synthase. Zhang Y, Schneider A, Rao R, et al: Genomic construction and genitourinary expression of mouse cytosolic prostaglandin E(2) synthase gene. Francois H, Athirakul K, Howell D, et al: Prostacyclin protects in opposition to elevated blood strain and cardiac fibrosis. H�bert R, Regnier L, Peterson L: Rabbit cortical accumulating ducts categorical a novel prostacyclin receptor. Hirata M, Kakizuka A, Aizawa M, et al: Molecular characterization of a mouse prostaglandin D receptor and functional expression of the cloned gene. Sri Kantha S, Matsumura H, Kubo E, et al: Effects of prostaglandin D2, lipoxins and leukotrienes on sleep and brain temperature of rats. Matsuoka T, Hirata M, Tanaka H, et al: Prostaglandin D2 as a mediator of allergic bronchial asthma. Sugimoto Y, Yamasaki A, Segi E, et al: Failure of parturition in mice missing the prostaglandin F receptor. Hasumoto K, Sugimoto Y, Gotoh M, et al: Characterization of the mouse prostaglandin F receptor gene: a transgenic mouse examine of a regulatory region that controls its expression in the abdomen and kidney but not within the ovary. Bek M, Nusing R, Kowark P, et al: Characterization of prostanoid receptors in podocytes. Ishibashi R, Tanaka I, Kotani M, et al: Roles of prostaglandin E receptors in mesangial cells under high-glucose situations. Inscho E, Carmines P, Navar L: Prostaglandin influences on afferent arteriolar responses to vasoconstrictor agonists. Silldorf E, Yang S, Pallone T: Prostaglandin E2 abrogates endothelin-induced vasoconstriction in renal outer medullary descending vasa recta of the rat. Francisco L, Osborn J, Dibona G: Prostaglandins in renin release during sodium deprivation. Zhang Y, Guan Y, Scheider A, et al: Characterization of murine vasopressor and vasodepressor prostaglandin E2 receptors. International Union of Pharmacology classification of prostanoid receptors: properties, distribution, and construction of the receptors and their subtypes. Boie Y, Stocco R, Sawyer N, et al: Molecular cloning and characterization of the four rat prostaglandin E2 prostanoid receptor subtypes. Imanishi M, Tsuji T, Nakamura S, et al: Prostaglandin i(2)/e(2) ratios in unilateral renovascular hypertension of various severities. Carmines P, Bell P, Roman R, et al: Prostaglandins in the sodium excretory response to altered renal arterial stress in canines. Roman R, Lianos E: Influence of prostaglandins on papillary blood circulate and pressure-natriuretic response. Baum M, Loleh S, Saini N, et al: Correction of proximal tubule phosphate transport defect in Hyp mice in vivo and in vitro with indomethacin. Sakuma S, Fujimoto Y, Hikita E, et al: Effects of metal ions on 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase activity in rabbit kidney cortex. Oliw E: Oxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by cytochrome P450 monooxygenases. Kliewer S, Lenhard J, Wilson T, et al: A prostaglandin J2 metabolite binds peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Rossl A, Kapahl P, Natoli G, et al: Anti-inflammatory cyclopentenone prostaglandins are direct inhibitors of IkB kinase. Takahashi S, Fukamizu A, Hatae T, et al: Species-specific kinetics of mouse renin contribute to upkeep of normal blood pressure in transgenic mice with overexpressed human angiotensinogen. Kimura H, Takeda M, Narikawa S, et al: Human natural anion transporters and human natural cation transporters mediate renal transport of prostaglandins. Singhal P, Sagar S, Garg P, et al: Vasoactive agents modulate matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity by mesangial cells. Ruschitzka F, Shaw S, Noll G, et al: Endothelial vasoconstrictor prostanoids, vascular reactivity, and acute renal failure. Jedlitschky G, Keppler D: Transport of leukotriene C4 and structurally related conjugates. Chanmugam P, Feng L, Liou S, et al: Radicicol, a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppresses the expression of mitogen-inducible cyclooxygenase in macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and in experimental glomerulonephritis. Hirose S, Yamamoto T, Feng L, et al: Expression and localization of cyclooxygenase isoforms and cytosolic phospholipase A2 in anti-Thy-1 glomerulonephritis. Tomasoni S, Noris M, Zappella S, et al: Upregulation of renal and systemic cyclooxygenase-2 in sufferers with energetic lupus nephritis. Zoja C, Benigni A, Noris M, et al: Mycophenolate mofetil mixed with a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor ameliorates murine lupus nephritis. Kitahara M, Eitner F, Ostendorf T, et al: Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition impairs glomerular capillary healing in experimental glomerulonephritis. Schneider A, Harendza S, Zahner G, et al: Cyclooxygenase metabolites mediate glomerular monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 formation and monocyte recruitment in experimental glomerulonephritis. Miyajima A, Ito K, Asano T, et al: Does cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor forestall renal tissue harm in unilateral ureteral obstruction Ozturk H, Ozdemir E, Otcu S, et al: Renal results on a solitary kidney of specific inhibition of cyclooxygenease-2 after 24 h of complete ureteric obstruction in rats. Tonshoff B, Busch C, Schweer H, et al: In vivo prostanoid formation throughout acute renal allograft rejection. Hocherl K, Dreher F, Vitzthum H, et al: Cyclosporine A suppresses cyclooxygenase-2 expression in the rat kidney. Laffi G, La Villa G, Pinzani M, et al: Arachidonic acid derivatives and renal operate in liver cirrhosis.
The simpler experimental accessibility to apical membranes has allowed a more thorough data of the transporters up to now symptoms 20 weeks pregnant 60 caps mentat generic fast delivery, and this is nonetheless relevant within the age of genomes medicine 223 mentat 60 caps cheap amex. Differences among species complicate the examine of amino acid transport within the kidney medications given for migraines 60 caps mentat proven. Currently treatment coordinator mentat 60 caps otc, we acknowledge that intestinal and renal epithelia have a remarkably related set of plasma membrane amino acid transporters, but there are also divergent isoforms. To our information, the molecular correlate of the renal system Gly has not been unequivocally identified. It is an H+ symporter with a excessive affinity (Km within the micromolar range) for imino acids and neutral amino acids (1: 1 stoichiometry). In basic, iminoglycinuria appears to be the recessive phenotype, whereas glycinuria is present in lots of, but not all, heterozygotes and thus can current as a dominant trait. TauT-/- mice present an impaired ability to decrease urine osmolality and improve urinary water excretion. This is the molecular correlate of the renal and intestinal cationic amino acid transport system b0,+ named by Van Winkle initially in the mouse blastocyst292 and that was detected in brush border membranes from the small intestine and kidney. Similarly, system b0,+ mediates the uptake of cystine from the lumen because, as soon as in the epithelial cell, the amino acid is reduced to cysteine. Final proof got here from the fact that mutations in system b0,+ trigger cystinuria,288,301 characterized by defective renal reabsorption and intestinal malabsorption of cationic amino acids (lysine, arginine, and ornithine) and cystine, however not other neutral amino acids (see Table 8. Cystinuria is recessive in inheritance; homozygotes hyperexcrete giant amounts of cationic amino acids (mainly lysine) and cystine. In contrast, clearance of cationic amino acids is simply partially affected (40 to 60 mL/min/1. Indeed, lysine transport has been reported in the human kidney, which was also present in sufferers with cystinuria. The native oligomeric state of system b0,+ is a heterotetramer (dimer of heterodimers), in which every dimer independently catalyzes transport. Cystinuria is assessed clinically primarily based on the urinary phenotype of the heterozygotes-type I are silent (without aminoaciduria) and those with reasonable aminoaciduria (mainly lysine and cystine) are referred to as kind non-I. This is considered one of the two molecular correlates of system y+L, initially described in erythrocytes and placenta,320,321 and is the mediator of cationic amino acid efflux in epithelial cells. In this mode, this electroneutral transporter mediates the efflux of cationic amino acids in opposition to the membrane potential (positive outside). Impairment of intestinal and renal reabsorption of cationic amino acids in homozygotes causes a metabolic derangement characterised by a low cationic amino acid plasma concentration, which causes dysfunction of the urea cycle and results in hyperammonemia and protein aversion (see Chapter 45). Two mutations (I395del and R445W) had been recognized in three patients from two households segregating with the phenotype and leading to the close to absence of floor expression in a heterologous system. Since the start of the twenty-first century, the atomic resolution buildings of prokaryotic models of several mammalian amino acid transporters have been reported and are summarized in Table 8. The motif consists of two interior pairs of symmetry-related helices, surrounded by an arch of outer helices. To translocate substrate, LeuT fold transporters transit by way of completely different outward-facing and inward-facing conformations of apo, substrate-bound open and substrate-bound occluded states. Interestingly, the LeuT fold is shared by 5 transporter households, with no obvious major amino acid homology between them (<10%). This construction has the substrate binding web site in a conformation that may be open to the cytosol had been it not for blockade by the C-terminus of the transporter. Thus, mutations E501K and G93R most probably affect the folding and position of this unwound area, compromising binding and ultimately substrate translocation. Grundemann D, Gorboulev V, Gambaryan S, et al: Drug excretion mediated by a model new prototype of polyspecific transporter. Motohashi H, Sakurai Y, Saito H, et al: Gene expression ranges and immunolocalization of organic ion transporters in the human kidney. Abramson J, Smirnova I, Kasho V, et al: Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. He X, Szewczyk P, Karyakin A, et al: Structure of a cation-bound multidrug and poisonous compound extrusion transporter. Sekine T, Watanabe N, Hosoyamada M, et al: Expression cloning and characterization of a novel multispecific natural anion transporter. This location can be consistent with the noticed altered substrate selectivity of T123M (defective binding for cystine however not for cationic amino acids) in isolated cystinuria. Broer S, Palacin M: the position of amino acid transporters in inherited and acquired illnesses. Kowalczyk L, Ratera M, Paladino A, et al: Molecular foundation of substrate-induced permeation by an amino acid antiporter. Biagi B, Kubota T, Sohtell M, et al: Intracellular potentials in rabbit proximal tubules perfused in vitro. Takata K, Kasahara T, Kasahara M, et al: Localization of Na(+)dependent lively kind and erythrocyte/HepG2-type glucose transporters in rat kidney: immunofluorescence and immunogold examine. Turk E, Zabel B, Mundlos S, et al: Glucose/galactose malabsorption attributable to a defect within the Na+/glucose cotransporter. De Paoli P, Battistin S, Jus A, et al: Immunological characterization of renal glycosuria patients. Fanconi G, Bickel H: [Die chronische aminoacidurie (aminosaeurediabetes oder nephrotischglukosurisscher zwergwuchs) ber der glykogenose und cystinkrankheit]. Asano T, Ogihara T, Katagiri H, et al: Glucose transporter and Na+/glucose cotransporter as molecular targets of anti-diabetic medicine. Somogyi A, McLean A, Heinzow B: Cimetidine-procainamide pharmacokinetic interplay in man: proof of competition for tubular secretion of fundamental medication. Acara M, Rennick B: Regulation of plasma choline by the renal tubule: bidirectional transport of choline. Saito H, Masuda S, Inui K: Cloning and useful characterization of a novel rat natural anion transporter mediating basolateral uptake of methotrexate in the kidney. Schomig E, Spitzenberger F, Engelhardt M, et al: Molecular cloning and characterization of two novel transport proteins from rat kidney. Merovci A, Solis-Herrera C, Daniele G, et al: Dapagliflozin improves muscle insulin sensitivity however enhances endogenous glucose manufacturing. Koepsell H: Substrate recognition and translocation by polyspecific natural cation transporters. Bello-Reuss E, Higashi Y, Kaneda Y: Dopamine decreases fluid reabsorption in straight parts of rabbit proximal tubule. Schali C, Schild L, Overney J, et al: Secretion of tetraethylammonium by proximal tubules of rabbit kidneys. Otsuka M, Matsumoto T, Morimoto R, et al: A human transporter protein that mediates the final excretion step for toxic organic cations. Hartmann G, Vassileva V, Piquette-Miller M: Impact of endotoxininduced changes in P-glycoprotein expression on disposition of doxorubicin in mice. Brast S, Grabner A, Sucic S, et al: the cysteines of the extracellular loop are crucial for trafficking of human natural cation transporter 2 to the plasma membrane and are concerned in oligomerization. Keller T, Egenberger B, Gorboulev V, et al: the massive extracellular loop of natural cation transporter 1 influences substrate affinity and is pivotal for oligomerization. Keller T, Schwarz D, Bernhard F, et al: Cell-free expression and practical reconstitution of eukaryotic drug transporters. Budiman T, Bamberg E, Koepsell H, et al: Mechanism of electrogenic cation transport by the cloned organic cation transporter 2 from rat. Chen Y, Li S, Brown C, et al: Effect of genetic variation within the natural cation transporter 2 on the renal elimination of metformin. Biermann J, Lang D, Gorboulev V, et al: Characterization of regulatory mechanisms and states of human organic cation transporter 2. Tsuda M, Terada T, Mizuno T, et al: Targeted disruption of the multidrug and toxin extrusion 1 (mate1) gene in mice reduces renal secretion of metformin. Tsuda M, Terada T, Ueba M, et al: Involvement of human multidrug and toxin extrusion 1 within the drug interplay between cimetidine and metformin in renal epithelial cells. Garrigues A, Loiseau N, Delaforge M, et al: Characterization of two pharmacophores on the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein. Shimada H, Moewes B, Burckhardt G: Indirect coupling to Na+ of p-aminohippuric acid uptake into rat renal basolateral membrane vesicles.