
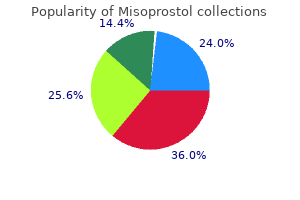
Misoprostol
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Misoprostol 100 mcg buy cheap on-line, gastritis symptoms light headed".
S. Grompel, M.A., Ph.D.
Deputy Director, University of Illinois College of Medicine
With rotation of the abdomen gastritis diet ��������� misoprostol 100 mcg generic without a prescription, the duodenum turns into C-shaped and rotates to the best; the fourth portion becomes fixed within the left higher stomach cavity gastritis inflammation buy discount misoprostol 200 mcg line. The mesoduodenum fuses with the adjacent peritoneum; each layers disappear gastritis diet kits 100 mcg misoprostol purchase amex, and the duodenum becomes fastened in its retroperitoneal location gastritis diet ������� generic 200 mcg misoprostol otc. The lumen of the duodenum is obliterated through the second month of growth by proliferation of its cells; this phenomenon is shortly adopted by recanalization. Small intestinal villus and crypt formation occurs in a proximalto-distal development. After the ascending and descending parts of the colon attain their ultimate destinations, their mesenteries fuse with the peritoneum of the posterior stomach wall, and they become retroperitoneal organs. Thus, the distal portion of the anal canal originates from ectoderm and is provided by the inferior rectal artery, which arises from the inner pudendal artery off the inner iliac artery; the proximal portion of the anal canal originates from endoderm and is supplied by the inferior mesenteric artery by means of the superior rectal artery. The inferior mesenteric ganglia and the pelvic splanchnic nerves innervate the superior portion of the anal canal. Angiopoietins and their receptors, Tie1 and Tie2, play a role in reworking and maturation of the growing vasculature. Arteries of the dorsal mesentery, originating from fusion of the vitelline arteries, give rise to the celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric arteries. Hindgut the distal third of the transverse colon, the descending colon and sigmoid, the rectum, and the higher part of the anal canal originate from the hindgut. Primitive stratified epithelium much like that within the small gut seems between eight and 10 weeks. Conversion to villus structure with developing crypts happens at 12 to 14 weeks. Remodeling to the adult-type crypt epithelium with lack of the villi occurs at 30 weeks. Initially the urinary, genital, and rectal tracts empty into a typical channel, the cloaca. They become separated by the caudal descent of the urorectal septum into an anterior urogenital sinus and a posterior intestinal canal. The lateral fold of the cloaca moves to the midline, and the caudal extension of the urorectal septum develops into the perineal physique. In a man, the lateral genital ridges coalesce to type the urethra and scrotum; in a woman, no fusion occurs, and the labia minora and majora evolve. The most distal portion of the hindgut enters into the posterior region of the cloaca, the primitive anorectal canal. This membrane ruptures by week 7 of embryonic improvement, creating the anal opening for the hindgut. The anal membrane separates the endoderm and ectodermal portions of the anorectal canal. The pectinate line marks separation of vascular provide of the upper and lower parts of the anal canal. Venous System Vitelline veins give rise to a periduodenal plexus that develops right into a single vessel, the portal vein. The umbilical veins join with the hepatic sinusoids, after which the right umbilical vein disappears and the left umbilical vein joins the inferior vena cava; finally the umbilical vein is obliterated and forms the ligamentum teres. The cardinal veins and the proximal portion of the right vitelline vein are involved with forming the inferior vena cava. Lymphatic System Lymphatic vessels originate from endothelial budding of veins, after which the peripheral lymphatic system spreads by endothelial sprouting into the surrounding tissues and organs. The proteins encoded by homeobox-containing genes act as regulatory molecules that management the expression of different genes. Several households of homeobox-containing genes are recognized, including the murine Hox family, which has been implicated in sample formation throughout embryogenesis. Abnormalities in lymphatic system growth can result in lymphangiectasia (see Chapter 31). The truncal neural crest offers rise to ganglia of the proximal abdomen, whereas the vagal neural crest provides ganglia to the entire intestine, together with the rectum; this colonization is complete by 13 weeks of embryonic growth. These cells kind extraintestinal pelvic ganglia that colonize the hindgut mesenchyma earlier than arrival of the vagal-derived neural crest cells. The prevertebral sympathetic ganglia develop subsequent to the main branches of the descending aorta and innervate tissue supplied by the respective arteries. The vagus nerve and the pelvic splanchnic nerves present preganglionic parasympathetic innervation to ganglia embedded in walls of visceral organs. Microenvironmental, genetic, or molecular mechanisms might intervene in these processes. Mutations of this gene have been reported in extrahepatic biliary atresia, the polysplenia syndrome (inferior vena cava abnormalities, preduodenal portal vein, intestinal malrotation, and situs inversus), and right-sided abdomen and congenital coronary heart disease. A examine evaluating information from the National Birth Defects Prevention Network demonstrated a prevalence of 1. The umbilical cord is usually inserted into the apex of the sac, and the blood vessels radiate within the sac wall. Although a central defect is present within the pores and skin and the linea alba, the remainder of the abdominal wall, together with surrounding musculature, is unbroken. Because a small occult omphalocele may not be observed at start, it is recommended that the umbilical wire be tied no much less than 5 cm from the abdominal wall on the time of supply. Close inspection of the umbilical cord earlier than clamping will avoid clamping an occult omphalocele. With a large omphalocele, the liver and spleen are regularly outside the belly cavity. Associated anomalies occur in about 75% of youngsters with omphalocele and include chromosomal abnormalities. If being pregnant is continued, mode of supply and provision for care of a kid with probably coexisting anomalies ought to be considered before labor and supply. The dimension of the omphalocele determines whether or not a primary repair or delayed primary closure is chosen. Negative stress wound therapy has a low complication and could additionally be an effective remedy for large omphalocele. The cause of gastroschisis is unknown, though a quantity of theories have been proposed, including irregular body wall folding, disruption of the best vitelline artery, and failure of mesoderm formation. Some affected infants may have an inflammatory peel, or serositis, of the bowel that will make particular person bowel loops tough to distinguish. Morbidity and mortality in sufferers with gastroschisis are largely associated to intestinal atresia. Gastroschisis could additionally be sophisticated by necrotizing enterocolitis, with all its attendant short- and long-term complications. It is necessary to look at the entire bowel in circumstances of gastroschisis, owing to the intestinal atresias associated with this defect. For the kid with significant intestinal atresia as an associated complication of gastroschisis, bowel exteriorization and secondary closure are sometimes most well-liked. Most infants require particular management and cautious serial inspection of the bowel quickly after delivery. Use of a spring-loaded silo to cowl the bowel might assist with bowel decompression, in addition to continuous inspection of blood move. Blood within the stool is usually maroon, even in patients with huge bleeding and hypovolemic shock. The explanation for bleeding is peptic ulceration secondary to acid production by the ectopic gastric mucosa throughout the Md; a "marginal" ulcer typically develops on the junction of the gastric and ileal mucosae. Although Helicobacter pylori has been observed in the gastric mucosa within a Md, a relationship between bleeding from a Md and presence of this organism is unlikely. Despite large bleeding, dying seldom occurs in kids because hypovolemia leads to contraction of the splanchnic blood vessels, inflicting the bleeding to diminish or stop. Also, youngsters rarely have comorbid conditions that compromise their capacity to compensate. Intestinal obstruction is the subsequent most typical manifestation of Md and is caused both by intussusception with the diverticulum as the lead point or by herniation through or volvulus round a persistent fibrous wire remnant of the vestigial vitelline duct. In youngsters older than age 4, intussusception is almost always secondary to a Md, though Md�related intestinal obstruction might occur at nearly any age; volvulus around a vitelline twine has been described in the neonatal period; as with other causes of obstruction, bilious vomiting and stomach distention are normally the preliminary signs.
Syndromes
- Secondary -- menstruation begins at the appropriate age, but later stops for more than 3 cycles or 6 months
- Tube through the mouth into the stomach to wash out the stomach (gastric lavage)
- Bleeding
- Prolonged lack of oxygen from shock, heart failure, or severe anemia
- Inability to pull the retracted foreskin over the head of the penis
- Soak the wound in as hot of water as the patient can tolerate for 30 - 90 minutes, if told to do so by trained personnel.
- What other symptoms are there, such as blue skin color, wheezing, high-pitched sound when breathing, coughing or sore throat?
- Exercise regularly.
- Bleeding
Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: up to date standards and genotype assignment internet resource gastritis mercola purchase 100 mcg misoprostol with amex. Identification of a naturally occurring recombinant genotype 2/6 hepatitis C virus gastritis diet ������ misoprostol 200 mcg buy line. Hepatitis C virus genotypes and viral concentrations in individuals of a general inhabitants survey in the United States chronic gastritis foods to eat discount misoprostol 100 mcg mastercard. Management of hepatitis C virus genotype four: recommendations of a world skilled panel gastritis en ingles 100 mcg misoprostol trusted. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus an infection in Egypt 2015: implications for future coverage on prevention and treatment. Role of hepatitis C virus genotype three in liver fibrosis progression in a scientific evaluate and metaanalysis. The consequence of acute hepatitis C predicted by the evolution of the viral quasispecies. Hepatitis C virus evasion of adaptive immune responses: a mannequin for viral persistence. High-resolution phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis C virus adaptation and its relationship to illness development. Recommendations for the identification of continual hepatitis C virus infection among individuals born throughout 1945-1965. The natural history and end result of liver transplantation in hepatitis C virus-infected recipients. Cholestatic hepatitis leading to hepatic failure in a patient with organ-transmitted hepatitis C virus infection. Natural killer cells are polarized toward cytotoxicity in continual hepatitis C in an interferon-alfadependent manner. Hepatitis C virus versus innate and adaptive immune responses: a tale of coevolution and coexistence. The German Hep-Net acute hepatitis C cohort: influence of viral and host elements on the preliminary presentation of acute hepatitis C virus infection. Treatment of acute hepatitis C: the success of monotherapy with (pegylated) interferon alpha. Evidence-based recommendations on the administration of extrahepatic manifestations of continual hepatitis C virus an infection. Safety and efficacy of rituximab in sufferers with hepatitis C virus-related mixed cryoglobulinemia and severe liver illness. Effect of sustained virological response to remedy on the incidence of irregular glucose values in persistent hepatitis C. Serum autoantibodies in chronic hepatitis C: comparability with autoimmune hepatitis and influence on the disease profile. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection increases mortality from hepatic and extrahepatic ailments: a community-based long-term prospective study. Cellular immune responses persist and humoral responses lower 20 years after recovery from a single-source outbreak of hepatitis C. Importance of specimen size in correct needle liver biopsy evaluation of patients with persistent hepatitis C. Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Coffee consumption is associated with lower rates of liver illness progression in persistent hepatitis C. Systematic review with meta-analysis: espresso consumption and the chance of cirrhosis. Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival tendencies in the United States from 1975 to 2005. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and associated threat components in hepatitis C-related advanced liver illness. The pure historical past of compensated cirrhosis because of hepatitis C virus: a 17-year cohort research of 214 patients. Morbidity and mortality in compensated cirrhosis kind C: a retrospective follow-up examine of 384 sufferers. Natural history of compensated viral cirrhosis: a prospective study on the incidence and hierarchy of major issues. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in diabetic patients and risk discount associated with anti-diabetic therapy: a population-based cohort research. Increased threat of hepatocellular carcinoma amongst sufferers with hepatitis C cirrhosis and diabetes mellitus. Magnitude and kinetics of decrease in liver stiffness after antiviral remedy in sufferers with persistent hepatitis C: a scientific review and meta-analysis. Outcome in a hepatitis C (genotype 1b) single supply outbreak in Germany-a 25-year multicenter research. Estimation of stage-specific fibrosis progression charges in persistent hepatitis C virus infection: a metaanalysis and meta-regression. Prevalence and clinical outcome of hepatitis C infection in youngsters who underwent cardiac surgical procedure earlier than the implementation of blood-donor screening. Progression of hepatic fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C: a potential paired liver biopsy examine. Older age at the time of liver biopsy is the essential threat issue for advanced fibrosis in sufferers with persistent hepatitis C. Progression of liver fibrosis in ladies contaminated with hepatitis C: long-term advantage of estrogen publicity. Hepatitis C an infection in African Americans: its pure history and histological progression. Identification of two gene variants associated with danger of superior fibrosis in patients with persistent hepatitis C. Role of a cirrhosis threat rating for the early prediction of fibrosis progression in hepatitis C sufferers with minimal liver disease. A comparison in the progression of liver fibrosis in continual hepatitis C between persistently normal and elevated transaminase. Role of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 in liver fibrosis progression-a systematic evaluate and metaanalysis. A sustained virologic response reduces danger of all-cause mortality in sufferers with hepatitis C. Hepatitis C reactivation in sufferers with continual an infection with genotypes 1b and 2c: a retrospective cohort research of 206 untreated sufferers. Impact of peginterferon and ribavirin remedy on hepatocellular carcinoma: incidence and survival in hepatitis C sufferers with advanced fibrosis. Impact of sustained virologic response with direct-acting antiviral remedy on mortality and hepatocellular carcinoma. Survival advantage of directacting antiviral remedy in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Reduction within the incidence of hepatitis C-related decompensated cirrhosis associated with national scale-up of direct-acting antiviral therapies targeting patients with advanced liver fibrosis. Association between antiviral treatment and extrahepatic outcomes in sufferers with hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatitis C virus infection is related to increased cardiovascular mortality: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Short article: viral dynamics among hepatitis C virus persistent infected patients throughout direct-acting antiviral brokers therapy: impact for monitoring and optimizing therapy length. Future treatment of persistent hepatitis C with direct performing antivirals: is resistance essential Effectiveness of ledipasvir-sofosbuvir mixture in sufferers with hepatitis C virus infection and components related to sustained virologic response. Delayed versus immediate treatment for sufferers with acute hepatitis C: a randomised controlled non-inferiority trial. Influence of alcohol on the progression of hepatitis C virus infection: a meta-analysis. Peginterferon alfa-2b or alfa-2a with ribavirin for therapy of hepatitis C infection. Efficacy of elbasvir and grazoprevir in participants with hepatitis C virus genotype 4 infection: a pooled evaluation. Direct-acting antiviral therapy in adults contaminated with hepatitis C virus: reactivation of hepatitis B virus coinfection as a further challenge.
Syndromes
- Antihistamines (such as meclizine or dimenhydrinate)
- Paralysis of the eye muscles, causing double vision (ophthalmoplegia)
- Relieving chronic pain and spasticity
- Blurred vision of close objects
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Problems with lung development and growth (bronchopulmonary dysplasia)
Prospective gastritis symptoms foods avoid 200 mcg misoprostol generic visa, controlled examine of vinyl glove use to interrupt Clostridium difficile nosocomial transmission chronic gastritis malabsorption misoprostol 100 mcg purchase line. The impact of ultraviolet light on clostridium difficile spore restoration versus bleach alone gastritis fundus order 200 mcg misoprostol fast delivery. Multicenter examine of the impression of community-onset Clostridium difficile an infection on surveillance for C gastritis gaps diet 100 mcg misoprostol order with amex. The epidemiology of community-acquired Clostridium difficile infection: a population-based examine. Suppression of Clostridium difficile by normal hamster cecal flora and prevention of antibiotic-associated cecitis. Targeted restoration of the intestinal microbiota with a simple, defined bacteriotherapy resolves relapsing Clostridium difficile illness in mice. Systemic and mucosal antibody responses to toxin A in patients contaminated with Clostridium difficile. Human colonic aspirates containing immunoglobulin A antibody to Clostridium difficile toxin A inhibit toxin A�receptor binding. Human antibody response to Clostridium difficile toxin A in relation to medical course of infection. Immunization of adult hamsters in opposition to Clostridium difficile�associated ileocecitis and switch of safety to infant hamsters. Active and passive immunization in opposition to Clostridium difficile diarrhea and colitis. Immunoglobulin G directed against toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile within the common population and sufferers with antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Treatment with intravenously administered gamma globulin of persistent relapsing colitis induced by Clostridium difficile toxin. Association between antibody response to toxin A and protection towards recurrent Clostridium difficile diarrhoea. Risk of Clostridium difficile diarrhea among hospital inpatients prescribed proton pump inhibitors: cohort and case-control studies. Iatrogenic gastric acid suppression and the danger of nosocomial Clostridium difficile an infection. Association between proton pump inhibitor remedy and Clostridium difficile an infection: a up to date systematic evaluate and meta-analysis. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea and proton pump inhibitor therapy: a metaanalysis. Proton pump inhibitors and threat of Clostridium difficile an infection: affiliation or causation. Underlying disease severity as a major danger factor for nosocomial Clostridium difficile diarrhea. Outbreak of Clostridium difficile�related diarrhoea in an adult oncology unit: threat factors and microbiological characteristics. Epidemiology and outcomes of Clostridium difficile infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Diminished Clostridium difficile toxin A sensitivity in new child rabbit ileum is associated with decreased toxin A receptor. Clostridium difficile an infection associated with antineoplastic chemotherapy: a evaluation. Evidence for holin function of tcdE gene within the pathogenicity of Clostridium difficile. Secretion of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B requires the holin-like protein TcdE 2012;8(6):e1002727. Cloning of Clostridium difficile toxin B gene and demonstration of excessive N-terminal homology between toxin A and B. The enterotoxin from Clostridium difficile (ToxA) monoglucosylates the Rho proteins. Clostridium difficile toxin B is stronger than toxin A in damaging human colonic epithelium in vitro. Serum antibody response to Clostridium difficile toxins in patients with Clostridium difficilediarrhoea. Therapeutic implications of Clostridium difficile toxin during relapse of chronic inflammatory bowel illness. The diagnostic yield of stool pathogen studies throughout relapses of inflammatory bowel illness. Enteric infection in relapse of inflammatory bowel disease: significance of microbiological examination of stool. A nationwide survey of the prevalence and impact of Clostridium difficile an infection amongst hospitalized inflammatory bowel illness patients. Glucocorticoids are associated with elevated danger of short-term mortality in hospitalized sufferers with Clostridium difficile-associated disease. Bacteremia due to Clostridium difficile: case report and evaluate of extraintestinal C. Chronic septic arthritis and osteomyelitis in a prosthetic knee joint because of Clostridium difficile. Factors related to prolonged symptoms and severe illness as a outcome of Clostridium difficile. Treatment of asymptomatic Clostridium difficile carriers (fecal excretors) with vancomycin or metronidazole: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection by toxin detection kits: a systematic review. Effective detection of toxigenic Clostridium difficile by a two-step algorithm together with checks for antigen and cytotoxin. Diagnostic accuracy of real-time polymerase chain reaction in detection of Clostridium difficile within the stool samples of sufferers with suspected Clostridium difficile infection: a meta-analysis. Molecular techniques for analysis of Clostridium difficile an infection: systematic evaluation and metaanalysis. Impact of medical signs on interpretation of diagnostic assays for Clostridium difficile infections. Rectal sparing in antibioticassociated pseudomembranous colitis: a prospective study. Clostridium difficile� related diarrhea in a region of Quebec from 1991 to 2003: a changing pattern of illness severity. Efficacy of fidaxomicin versus vancomycin as remedy for Clostridium difficile an infection in individuals taking concomitant antibiotics for other concurrent infections. Prospective derivation and validation of a clinical prediction rule for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Prospective randomised trial of metronidazole versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile�associated diarrhoea and colitis. Unfavorable impact of atropine-diphenoxylate (Lomotil) remedy in lincomycin-caused diarrhea. Diarrhoea caused by Clostridium difficile: response time for remedy with metronidazole and vancomycin. Changes in sensitivity patterns to chosen antibiotics in Clostridium difficile in geriatric in-patients over an 18-month period. Epidemics of diarrhea attributable to a clindamycin-resistant strain of Clostridium difficile in 4 hospitals. Reassessment of Clostridium difficile susceptibility to metronidazole and vancomycin. Prospective research of oral teicoplanin versus oral vancomycin for remedy of pseudomembranous colitis and Clostridium difficile�associated diarrhea. Comparison of vancomycin, teicoplanin, metronidazole, and fusidic acid for the treatment of Clostridium difficile�associated diarrhea. Nitazoxanide versus vancomycin in Clostridium difficile an infection: a randomized, doubleblind examine. Rifaximin Is Effective for the therapy of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: results of an open-label pilot examine. Bacitracin remedy of antibiotic-associated colitis and diarrhea attributable to Clostridium difficile toxin. Oral bacitracin versus vancomycin therapy for Clostridium difficile�induced diarrhea: a randomized double-blind trial. Fusidic acid for the therapy of antibiotic-associated colitis induced by Clostridium difficile.