
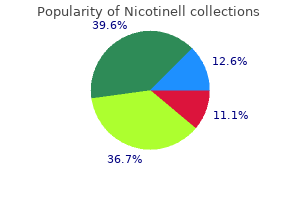
Nicotinell
| Contato
Página Inicial

"35 mg nicotinell purchase otc, quit smoking jitters".
E. Jarock, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Professor, William Carey University College of Osteopathic Medicine
A second consequence of T�B interdependence is that particular inefficiencies of central tolerance in a single limb may be compensated for in the other quit smoking 26 months ago buy nicotinell 52.5 mg cheap. For example quit smoking essential oil blend nicotinell 17.5 mg online, T cells are most likely very efficiently purged of cells that react with thymus-specific antigens quit smoking know discount 35 mg nicotinell amex, but B cells are in all probability not quit smoking brochures 17.5 mg nicotinell discount with amex. By analogy, only sure effector capabilities may trigger autoimmune illness, depending on the circumstances. The propensity to make these various types of responses depends on a number of factors together with the cytokine milieu, costimulation, genetics, route of antigen exposure, and dose of antigen. This is also related to B-cell autoimmunity per se as a outcome of, via using totally different isotypes of Ig, totally different effector capabilities can happen. The cytokines secreted by Th1 and Th2 cells have profound results on the isotypes of immunoglobulins that are produced throughout a response. Thus, not solely is the T-cell component of the response channeled in this way, but the humoral response can be influenced. Th17 cells, which are necessary for responses to extracellular micro organism as properly, have been recognized as essential pathogenic cells in several autoimmune diseases. These embrace mouse fashions of a quantity of sclerosis, collageninduced arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Thus genetic predisposition or environmental components that drive Th-cell differentiation to a specific Th subset might improve the possibilities of creating sure autoimmune illnesses which might be associated with that kind of response. Thus regulatory T cells symbolize a major peripheral tolerance mechanism to forestall aberrant autoreactive T-cell activation. The mechanisms of failure are probably different for the assorted autoimmune diseases and possibly even for different patients with related syndromes. Moreover, it appears likely both from phenomenologic and genetic research that failures at several levels are required to generate clinically vital autoimmunity. Grossly, autoimmune ailments have usually been divided into organ-specific and systemic autoimmune syndromes. This classification is helpful, however as these illnesses are becoming higher understood, the dividing traces are blurring; pathogeneses of all these ailments are likely to have much in frequent. In explicit, systemic autoimmune diseases are actually much more specific of their antigenic targets than is commonly realized. Both the selective nature of disease and its late onset argue towards gross defects in the primary central tolerance mechanisms as being the trigger. The absence of functional regulatory T cells in these sufferers results in a deadly systemic autoimmune syndrome inside 1 yr of age, unless bone marrow transplantation is carried out. Similar observations have been made in Scurfy mice and in mice genetically engineered to lack Foxp3. In instances that are less excessive than Foxp3 or Aire deficiency, perturbance in the homeostasis, growth, or expansion of regulatory T cells could still predispose individuals to develop autoimmune illnesses. Increasing regulatory T cells in sufferers with autoimmune illnesses could be therapeutically beneficial, as enlargement of regulatory T cells have been shown to stop autoimmune syndromes such as inflammatory bowel illness, sort I diabetes, and autoimmune encephalomyelitis in murine models. However, it does appear clear that a gross defect in central tolerance would lead to a severe syndrome of congenital autoimmunity. Many different autoimmune ailments are roughly associated with specific genotypes at this polymorphic locus. Interestingly, most of them seem to have direct results on B-cell operate or exercise. Note that these include genes concerned in the processes of antigen sequestration, T�B collaboration, and immune response downregulation that had been discussed earlier as key options of the self-tolerance mechanisms that usually forestall autoimmune disease. In ongoing work, the exact nature of defects in these genes may be defined; these embrace noncoding polymorphisms that have an result on expression ranges in addition to structural alleles. This will in flip permit screening for defects in human autoimmune disease sufferers with the ultimate goals of aiding analysis, offering insights into pathogenic mechanisms, and guiding patient-specific therapies. Although human genetic research and animal models recommend multigenic inheritance, there are particular instructive instances in which single-gene defects play a significant function. A well-studied example of mutations in these genes is the lpr/lpr mouse, which carries an inactivated murine Fas. Exactly how defects in the apoptotic Fas pathway lead to autoimmunity has but to be elucidated. They show the critical nature of the late downregulatory controls in stopping autoimmune illness. They additionally level out pathways during which much less extreme mutations might be found that account for human illness. These findings highlight a genetic foundation for recognizing self-molecules in autoimmune ailments and recommend new therapeutic targets that are presently being explored. This is illustrated by the truth that concordance rates amongst equivalent twins, even raised in the identical family, are surprisingly low. There are many examples of environmental factors causing both chronic or transient autoimmune diseases. There are postinfectious syndromes similar to postmycoplasmal cold agglutinin disease. The pattern of incidence of multiple sclerosis suggests a viral etiology, although no causative virus has ever been convincingly demonstrated. Another category of infectious associations consists of postviral myocarditis, which follows certain coxsackievirus infections. It is sometimes conceptually difficult to draw a line between viral injury and consequent immune system injury; however, if sensitization to self-antigens happens as a consequence of viral infection and these later are pathogenic targets impartial of viral antigens, it seems affordable to think about the syndrome as autoimmune. Drugs corresponding to procainamide that cause lupus-like syndromes are particularly outstanding examples. Note that the sensitization concerned in steps 1 and a pair of might take place in a primary response during the first transfusion or exposure and that step 3 may happen in a clinically noticeable way solely after a secondary exposure to homologous platelets. ExamplesinHematology:EpitopeSpreadingin PosttransfusionPurpura One potential way to break self-tolerance may be notably relevant to syndromes found in hematology and is worthy of elaboration. Although how such destruction of self-platelets occurs secondary to destruction of allogeneic platelets is controversial, one of the best rationalization is the development of an autoimmune response. The possible pathway bears important parallels to one demonstrated in mice a number of years ago by Janeway and colleagues. The mice made each an antibody response and a T-cell response to the human cytochrome c; nevertheless, because the human and mouse cytochromes are so similar, the antibody response (but not the T-cell response) cross-reacted with murine cytochrome c. Presumably this reflected activation of ignorant B cells with specificity for self-cytochrome c (and also human). However, a number of weeks later, if the mice were given a dose of self-cytochrome c, now each a vigorous B-cell and T-cell antiself response ensued. These authors advised that priming with the cross-reactive antigen first induced self-reactive B cells, which in flip may then break tolerance in anergic or ignorant self-reactive T cells. Moreover, these activated B cells can then present self-platelet antigens along with costimulatory signals to self-reactive T cells. When this occurs, the immune response can perpetuate even in the absence of the overseas platelets. Thus a international platelet is analogous to foreign cytochrome c in having a couple of completely different antigens together with many shared antigens. The key events are the activation of ignorant B cells that cross-react with both self and overseas molecules after which the activation of T cells which might be particular for self by these B cells. It is affordable to query how such antiself responses are ever stopped as soon as started. In the absence of an autoimmune-prone host who has mutations affecting the downregulation of immune responses, these autoimmune reactions will stay transient. A fundamental understanding of the mechanisms of self-tolerance and their breakdown in autoimmune illness raises the potential of many forms of specific therapeutic interventions. One of the clearest would be to identify initiating components, such as infections, and to stop or treat them. A second strategy could be to reset Chapter25 ToleranceandAutoimmunity 293 tolerance. If the system can be set again to the state earlier than that occasion, the disease might be cured. Another promising space is in channeling the immune response, notably because the steering mechanisms have gotten better understood at the molecular level. A third area is to design extra specific modulators of inflammation, including interfering with costimulatory alerts. Current remedy is rather more crude and usually includes general nonspecific immunosuppression either with steroids or cytotoxic medication. Additionally, the injection of cytokines themselves is also efficient at treating autoimmunity.
Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood in nearby capillaries quit smoking symptom timeline purchase 17.5 mg nicotinell, and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli (fig quit smoking timeline day by day nicotinell 52.5 mg free shipping. Predict the path of diffusion of gases between alveoli and alveolar capillaries quit smoking online support buy discount nicotinell 17.5 mg on-line. Lungs the lungs are gentle quit smoking vietnam nicotinell 17.5 mg buy generic, spongy, cone-shaped organs in the thoracic cavity (see fig. The mediastinum separates the right and left lungs medially, and the diaphragm and thoracic cage enclose them. The parietal pleura, in turn, borders part of the mediastinum and features the internal wall of the thoracic cavity and the superior floor of the diaphragm (see figs. The potential (possible) space between them known as the pleural cavity (plooral kav-te). It has a skinny film of serous fluid that lubricates adjacent pleural surfaces, reducing friction as they transfer against one another during respiratory. This fluid additionally helps maintain the pleural membranes collectively, as defined in part sixteen. A lobe additionally has connections to blood and lymphatic vessels and lies within connective tissues. Thus, a lung contains air passages, alveoli, blood vessels, connective tissues, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. Breathing, or ventilation, is the movement of air from outside the physique into and then out of the bronchial tree and alveoli. The actions offering these air movements are termed inspiration (insp-rashun), or inhalation, and expiration (eksp-rashun), or exhalation. Inspiration Just as blood flows from high pressure to low pressure, so does a combination of gases, similar to strange air. Atmospheric stress, the pressure of the air round us, offers the force that strikes air into the lungs. At sea stage, this pressure is enough to help a column of mercury about 760 millimeters (mm) excessive in a tube. Because the airways are open to the surface, the airways and alveoli are subjected to exterior air strain. This is easiest to envision at the end of a normal, resting expiration, when no air is transferring in or out. At this level the pressures on the within of the airways and alveoli and on the outside of the thoracic wall are about the same. For instance, pulling back on the plunger of a syringe increases the amount inside the barrel, which decreases the air pressure inside. In distinction, pushing on the plunger reduces the volume contained in the syringe, increasing the stress inside and forcing air out into the atmosphere. If the stress contained in the lungs decreases, atmospheric strain will push outside air into the airways and alveoli. The diaphragm moves downward, the thoracic cavity enlarges, and the strain in the alveoli (intra-alveolar pressure) falls to about 2 mm Hg under that of atmospheric strain. In response, atmospheric strain forces air via the airways into the alveoli (fig. If an individual needs to take a deeper than regular breath, whereas the diaphragm is contracting and transferring downward, the external (inspiratory) intercostal muscular tissues between the ribs could also be stimulated to contract. Additional muscles, such because the pectoralis minors, the sternocleidomastoids, and the scalenes, can also pull the thoracic cage farther upward and outward. As a end result, the intra-alveolar stress is lowered additional, and atmospheric pressure forces even more air into the alveoli (fig. Lung growth is dependent upon movements of the pleural membranes in response to actions of the diaphragm and chest wall. When the external intercostal muscle tissue transfer the thoracic wall upward and outward, and the diaphragm strikes downward, the parietal pleura moves too, and the visceral pleura follows it. First, any tendency for the pleural membranes to draw back from one another decreases pressure in the pleural cavity, holding them collectively. Second, solely a thin movie of serous fluid separates the parietal pleura on the internal wall of the thoracic cavity from the visceral pleura hooked up to the surface of the lungs. The water molecules in this fluid are drawn to the pleural membranes and to each other, helping to adhere the moist surfaces of the pleural membranes, a lot as a moist coverslip sticks to a microscope slide. The moist pleural membranes play a task in expanding the lungs, but the moist inner surfaces of the alveoli have the alternative impact. In the alveoli, the attraction of water molecules to each other creates a pressure referred to as surface pressure that makes it difficult to inflate the alveoli and may very well collapse them. Certain alveolar cells, nevertheless, synthesize a mix of lipids and proteins called surfactant (serfaktant). To assist many of those newborns survive, physicians introduce synthetic surfactant into the tiny lungs by way of an endotracheal tube. A newborn should use twenty instances the vitality to take the first breath as for subsequent breaths. Expiration the forces for resting expiration come from the elastic recoil of tissues and from floor pressure. The lungs include considerable elastic tissue, which stretches with lung expansion during inspiration. As the diaphragm and external intercostal muscular tissues chill out following inspiration, the elastic tissues trigger the lungs to recoil and return to their authentic shapes. This pulls the visceral pleural membrane inward, and the parietal pleura and chest wall comply with. Also, throughout inspiration the diaphragm compresses the belly organs beneath it. When the diaphragm relaxes, the abdominal organs spring again into their earlier shapes, pushing the diaphragm upward (fig. At the same time, the floor rigidity that develops on the moist surfaces of the alveolar linings decreases the diameters of the alveoli. Together these elements increase intra-alveolar pressure about 1 mm Hg above atmospheric strain, in order that the air contained in the lungs is compelled out via respiratory passages with no muscle motion. If a person must exhale extra air than normal, the internal (expiratory) intercostal muscles can contract (fig. These muscular tissues pull the ribs and sternum downward and inward, increasing the air pressure in the lungs to pressure more air out. Also, the stomach wall muscle tissue, including the external and internal obliques, transversus abdominis, and rectus abdominis, can squeeze the stomach organs inward (see fig. In this fashion, the stomach wall muscle tissue can enhance stress in the stomach cavity and force the diaphragm nonetheless larger against the lungs. Low pressure and wet surfaces maintain the visceral and parietal pleural membranes collectively, so no actual house usually exists in the pleural cavity between them. However, a puncture in the thoracic wall admits atmospheric air into the pleural cavity and creates a real area between the membranes. Diaphragm Diaphragm (cut) Lung (cut) Abdominal organs recoil and press diaphragm upward Internal intercostal muscles pull ribs down and inward (External intercostals have been eliminated to reveal underlying inner intercostals) Abdominal wall muscles contract and compress belly organs, forcing the diaphragm greater (a) (b) Air actions aside from respiration are called nonrespiratory movements. They are used to clear air passages, as in coughing and sneezing, or to categorical emotion, as in laughing and crying. A cough, for example, can be produced via aware effort or could additionally be triggered by a overseas object in an air passage. Coughing entails taking a deep breath, closing the glottis, and forcing air upward from the lungs towards the closure. Then the glottis is all of a sudden opened, and a blast of air is compelled upward from the lower respiratory tract. A sneeze is very like a cough, however it clears the upper respiratory passages somewhat than the decrease ones. This reflex is often initiated by a mild irritation in the lining of the nasal cavity, and in response, a blast of air is pressured up through the glottis. The air is directed into the nasal passages by miserable the uvula, closing the opening between the pharynx and the oral cavity.
During S and G2 phases quit smoking 45 days nicotinell 52.5 mg purchase otc, procentrioles elongate until they reach the length of the older centrioles quit smoking free patches purchase nicotinell 52.5 mg fast delivery. After chromosome condensation quit smoking coupons order 35 mg nicotinell with visa, centrosome separation quit smoking 800 quit now generic 17.5 mg nicotinell visa, and nuclear envelope breakdown during prophase, chromosomes become hooked up to microtubules of the mitotic spindle equipment in prometaphase. They are shaped by centromere proteins throughout G2 phase and prophase and link chromosomes to the mitotic spindle equipment, in order that sister chromatids become connected to reverse poles. As the ring closes, the spindle midzone is transformed to form the densely packed telophase midbody, which organizes the intracellular bridge. At this time in telophase, nuclear membranes type to envelop each of the 2 separated sets of chromosomes, which also start to decondense. This is quickly followed by the abscission event near the midbody, which completes mitosis. G1 has been subdivided into segments and regulatory factors based mostly largely on the research of the proliferative response of cells to sequential software of various growth factors, vitamins, and metabolic inhibitors. From the standpoint of cell cycle regulation, a particularly important level in G1 is the restriction level, or R, which happens near the G1�S boundary. Notably, nearly the entire variability within the size of G1 could be accounted for by the G1ps interval. Experiments have shown that, to depart quiescence and to enter the cell cycle, cells require development signals either continuous for a quantity of hours throughout G1 or, alternatively, as two discrete pulses of approximately 1 hour in length and with a pause of a quantity of hours in between. In contrast, terminally differentiated cells have irreversibly exited the cell cycle in the course of the means of differentiation. When cells sense that situations are suitable for proliferation, they go away quiescence into G1 part and turn into competent to enter the cell cycle. G1 has been subdivided into segments, and a particularly necessary level is the restriction point, or R, which occurs near the G1�S boundary. Restriction Point In 1974, Arthur Pardee revealed the primary report on the restriction point, and defined it as a degree at which cells turn out to be committed to coming into S phase, regardless of subsequent availability of development components or important vitamins. In the 4 decades which have handed for the rationale that initial description of the restriction point, many essential insights have been gained that revealed the signaling events that contribute to proliferation and progress. During senescence, cells have committed to proliferation and presumably have handed the restriction level. In contrast to quiescence, senescent cells are unable to reenter the cell cycle in response to external stimuli, such as progress signals. Zetterberg A, Larsson O: Kinetic analysis of regulatory events in G1 resulting in proliferation or quiescence of Swiss 3T3 cells. In the physiologic contexts of embryonic growth and tissue renewal, or as a pathologic response to cell harm and infectious pathogens, cell deaths are orchestrated for multiple functions that profit the organism. These embrace maintenance of epithelial barrier function, destruction of microbes, adaptive immune responses, recycling of biologic macromolecules, intracellular signaling, and preservation of genomic integrity. Necrosis, an alternative mechanism of cell demise, occurs within the aftermath of utmost cellular insults and could be considered as a failure of cellular homeostasis. Recently, a programmed pathway of necrosis, referred to as necroptosis, has been identified. Although cells comprise their very own dying apparatus, cell demise in multicellular organisms is exquisitely sensitive to the consent of neighboring cells. As could be expected, the internal cell death equipment is tightly interwoven with other essential cell pathways. Investigations of cell dying have additionally informed our understanding of residing cells; for example, the popularity that cellular reworking shares some pathways with apoptotic cell death. This scheme offers a quickly accessible reserve under situations of upper demand. A ultimate physiologic utility for apoptosis is as a mechanism for choice of specific cell phenotypes. Affinity maturation of immunoglobulin-bearing B cells takes place in germinal centers of lymphoid organs. In each case, cells run through a gauntlet of near-death experiences, with dying and survival alerts immediately linked to the binding properties of the antigen receptor on individual cells. A serine protease that additionally recognizes aspartic acid motifs, granzyme B, is equally involved in cytolytic T-cell killing. Often only one or two caspase cleavage sites are present in a selection of cellular proteins, in lots of instances members of the same complicated or biochemical pathway, leading to restricted digestion of substrate proteins. Proteins truncated by caspase cleavage frequently exhibit altered features, demonstrating that caspases can act as signaling proteases. In the intracellular battle between survival and proapoptotic components, caspases can also swing the advantage toward death by altering the balance of forces. Not solely does N-terminal truncation eliminate a survival operate, but the cleaved variations additionally behave as proapoptotic components. Apoptotic cell demise in the grownup happens most clearly within the context of cyclically renewing (endometrium, breast, hair follicle) tissues. Homeostatic mechanisms in skin and intestine stability technology of latest cells with loss of terminally differentiated cells, principally by nonapoptotic mechanisms. In the intestinal epithelium, terminally differentiated enterocytes migrate onto the epithelium floor and are extruded as viable cells, triggered by mobile crowding. Keratinocytes within the exterior layer of skin undergo a means of cornification to type an epithelial barrier before being shed. Neutrophils recruited to websites of irritation bear apoptosis upon removal of the inflammatory stimulus. Apoptotic neutrophils are unable to degranulate, and reprogram macrophages to an antiinflammatory phenotype when phagocytosed (termed efferocytosis). This clearance mechanism is specialized to apoptotic neutrophils, as necrotic neutrophils and opsonized cells trigger macrophages to secrete inflammatory cytokines. Reversible physiologic cell deaths also provide a reserve production capacity for functionally mature cells. Downstream or executioner caspases (caspase-3, -6, and -7) exist as preformed dimers. Processing of procaspases occurs instantly after aspartate residues within caspase recognition motifs. Subsite specificities are distributed amongst caspases in order that many caspase zymogens have to be processed in trans by a special caspase, creating a hierarchy of proteolytic activation. Subject specificity of caspases is set by the geometry of specificity binding pockets S4�S1, recognizing peptide aspect chains numbered P1�P4 on the acyl facet of a scissile peptide bond. Caspase substrate motifs at cleavage websites allow sequential caspase activation, or in the case of initiator caspases, autoactivation. Interactions at a dimer interface (induced proximity or induced conformation model) reorient and stabilize the binding pocket conformation of those caspases. Normally monomeric, these zymogens are distinguished by the presence of an extended prodomain that serves as a docking site for recruitment into a self-activating complex. The prodomain of caspase8/10 is severed throughout processing, dispersing energetic caspases to mobile substrates. Analysis of unprocessed caspase-8 dimers demonstrated that energetic sites may be fashioned within the absence of processing, stabilized by hydrophobic interactions on the dimer interface. Formation of the cytoplasmic apoptosome is initiated by launch of the soluble electron service, cytochrome c, from mitochondria. Eventual dissociation from the apoptosome as a end result of cleavage of the prodomain ends in lack of proteolytic exercise. Both pathways converge with proteolytic activation of caspase-3 by caspase-8, -9, or -10. The inflammasome scaffold is postulated to set off caspase-1 activity according to the induced proximity mannequin. An inflammatory cell death termed pyroptosis is initiated by inflammasome activation. Several dramatic structural alterations related to cell differentiation additionally appear to require transient caspase activation. Cleavage of a restricted number of caspase substrates precede nuclear and chromatin changes during terminal erythroid differentiation, and caspase inhibitors block proplatelet formation from megakaryocyte and macrophage differentiation. Caspase-8, in some contexts, has a prosurvival perform, inhibiting necroptosis or apoptosis. The extra limited caspase activation in these situations might contain some degree of compartmentalization in space or time.
The strategy of Ig gene rearrangement happens in a step-wise manner as murine and human B cells mature via the cellular phases of development simply described quit smoking zyban treatment buy nicotinell 17.5 mg on-line. An increasingly accepted quit smoking banner discount 17.5 mg nicotinell otc, second mannequin of allelic exclusion is that the expression of heavy chain protein from a efficiently rearranged allele inhibits rearrangements at the other heavy chain allele quit smoking using hypnosis 52.5 mg nicotinell generic overnight delivery. LightChainGeneRearrangement Ig gentle chain protein can be encoded by the kappa or lambda genes quit smoking aids that really work 17.5 mg nicotinell discount with visa. However, the proportions of human and proteins are extra equal, with roughly 60% of human B cells expressing mild chain protein. The human gene is situated on chromosome 2 and contains round forty V area genes, clustered in as a lot as seven households, five functional J area genes, and one C region gene. There are seven human C genes, four of which are useful and three of that are pseudogenes. If rearrangements on the first allele are unsuccessful, attempts are made to rearrange the second gene. HeavyChainGeneRearrangement the preliminary Ig rearrangement events during B-cell growth occur on the heavy chain locus. The Ig heavy chain locus contains a number of variable (V), diversity (D), joining (J), and constant (C) area gene segments which are separated from each other by introns. The V area genes are located at the 5 end of the Ig heavy chain locus, and each consists of approximately 300 base pairs. These genes, that are separated by quick intron sequences, are organized into seven households based mostly on sequence homology. Finally, 10 C region genes representing alternative Ig isotypes are organized in tandem. The transcription of the unrearranged heavy chain locus happens prior to actual Ig gene recombination. This leads to the production of developmentally regulated transcripts of unrearranged Ig genes, referred to as germline or sterile transcripts. Multiple species of sterile transcripts have been described, and a few may conceivably encode proteins. A mechanistic hyperlink between transcription and Ig gene rearrangement has been hypothesized. Although in theory any D area gene can be a part of with equal frequency to any J region gene, there may be preferential utilization of selected D and J area genes at various occasions throughout fetal and grownup B-cell development. Evidence means that biased usage of J proximal V genes happens within the newly generated repertoire of neonatal mice and people. Before Ig gene rearrangement, E12 and E47 proteins may be in an inactive state owing to their heterodimeric association with another protein known as Id. Thus, profitable transition from the pro-B- to pre-B-cell stage relies on cessation of Id expression. This conclusion is consistent with the truth that mice expressing an Id transgene have a complete block in B-cell differentiation. Each pro-B cell has two Ig heavy chain genes, but solely one of these encodes heavy chain protein in any given cell. The enzymes that mediate these functions act by way of recognition of recombination sign sequences which would possibly be situated three of every heavy chain V area exon, 5 of each heavy chain J section, and 5 and 3 of every heavy chain D area gene. First, heavy and light-weight chain proteins can be encoded by multiple germline V, J, and, within the case of the heavy chain, D area genes, and the combinatorial variety amongst them is gigantic. The determine reveals the Ig heavy chain gene and the signal sequences three of each V region locus, 5 and 3 of each D region locus, and 5 of each J area locus. These encompass heptamer and nonamer sequences separated by both 12 or 23 base pairs. During immunoglobulin (Ig) recombination, a signal sequence of 12 base pairs can only join to one other of 23 base pairs (the so-called 12�23 rule). As shown within the figure, preliminary heavy chain gene rearrangements kind coding joints between D and J regions, in addition to sign joints that are finally degraded. The quick (509-amino acid) variant catalyzes the addition of nontemplated nucleotides at coding joints and the long (529-amino acid) type is a 3�5 exonuclease that catalyzes the deletion of nucleotides at coding joints. Finally, somatic mutation of V region genes can occur, normally in secondary lymphoid tissues. This latter process, which outcomes in an elevated affinity of the antibody for antigen, is mentioned in additional detail in the part on secondary B-cell growth. Because the process of Ig gene recombination is random, some B cells which might be self-reactive may be produced. Several mechanisms have been proposed to account for the destiny of such self-reactive cells. In some instances, the presence of self-antigen may not activate self-reactive B cells. This situation may end result from weak B-cell affinity for the antigen or the autoantigen could also be current at a particularly low concentration. In different cases, interplay of antigen with the autoreactive B cell may end in anergy. In this course of, which represents the commonest mechanism for negative choice, rearranged mild chain alleles can be changed by secondary rearrangements of upstream V genes to downstream, unrearranged J segments. One role of the surrogate mild chains is to select heavy chains that can finally be able to pairing with standard light chains. These events result in calcium flux and activation of signaling cascades within the pre-B cell. As a outcome, affected males develop recurrent bacterial infections early in life because of a profound decrease in circulating Ig. The identification of such ligands has been troublesome, although galectin-1 may perform in this capability. Initially they endure a quantity of rounds of proliferation, which expands the size of the clone that expresses a specific �-heavy chain. Rag gene expression is also suppressed in these proliferating cells, which contributes to allelic exclusion. Once the recombinatorial equipment is reactivated, light chain gene rearrangement and expression happens. As with heavy chain ThePro-B-toPre-B-CellTransition the key event through the pro-B- to pre-B-cell transition is the rearrangement and expression of the Ig heavy chain genes. It is essential to acknowledge that not all pro-B cells efficiently navigate this transition. The principal reason for this is that not all Ig gene recombination events are profitable. For example, Ig heavy chain gene rearrangements are productive in solely round one-third of pro-B cells. However, if Ig heavy chain recombination is productive and � heavy chain protein is expressed, it appears on the surface of the pre-B cells in association with two extra molecules referred to because the surrogate light chains. The surrogate light chain proteins, Vpre-B and 5, are encoded by genes positioned on chromosome 16 in mice and on chromosome 22 in humans, and are noncovalently linked to one another. Cross-section of bone showing elements of the medullary circulation, the marrow sinusoids, and the placement of stromal cells (top). This signalosome mediates a cascade of intracellular alerts that features the initiation of calcium influx. The stage and period of receptor activation and hence transcriptional output are further modified by a sequence of cell surface coreceptors or "response modifiers" that bind to complement or to receptors on the surface of stromal cells, activated T cells, or different populations present in secondary lymphoid organs. These nonhematopoietic supporting cells, also referred to collectively as stromal cells, help blood cell improvement via direct cell-to-cell interactions and through the secretion of various soluble mediators. These intercellular interactions presumably would allow B cells to obtain proliferative or developmental indicators (or both) from stromal cells. The stromal cells will not be passive populations that constitutively provide these indicators. Instead, the binding of the B-lineage cell could stimulate the stromal cell in turn to produce such differentiation or growth-potentiating actions. However, the main focus could be narrowed significantly when solely these with obligate effects on B-cell development are considered. Whether or not these occasions additionally happen in human B lymphopoiesis has not been established. It additionally has been demonstrated that hormones can negatively affect B-cell development. In explicit, elevated ranges of estrogens occurring throughout being pregnant inhibit lymphopoiesis.