
Norfloxacin
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Norfloxacin 400 mg cheap with amex, fast acting antibiotics for acne".
H. Gonzales, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of Missouri–Kansas City School of Medicine
Renal lesion within the type of focal and segmental necrotizing antimicrobial test laboratories cheap norfloxacin 400 mg without a prescription, usually crescentic antibiotics for sinus infections best ones norfloxacin 400 mg cheap line, glomerulonephritis antibiotic 127 generic 400 mg norfloxacin amex. Probably represents a type of T cellediated hypersensitivity reaction to an exogenous (inhaled infectious or other environmental agent) or endogenous antigen bacteria 2013 400 mg norfloxacin proven. Morphology Mainly entails three organs but could also be widespread involving any organ similar to eyes, skin, kidney, and other organs. Upper respiratory tract lesions: They vary from inflammatory sinusitis to ulcerative lesions in the nose, palate, or pharynx. Lower respiratory tract: Lung exhibits multiple, bilateral, nodular cavitary infiltrates. Necrotizing granulomas: It consists of geographic patterns of central necrosis surrounded by a zone of fibroblastic proliferation with giant cells, paying homage to mycobacterial or fungal infections. Most of these lesions are current from delivery and Willebrand factor enhance in measurement because the baby grows. Hemangioma:Consists of large, dilated vascular channels; compared with small vascular spaces in Unencapsulated benign tumor. Morphology: Gross:Red-blue, delicate, spongy masses and measure 1 to 2 cm in diameter. They are found within the skin, on the mucosal surfaces and visceral organs such because the spleen, liver, and pancreas. Decreased/Impaired Coronary Blood Flow Coronary arterial occlusion is the main cause of myocardial ischemia. Coronary Atherosclerosis It narrows a quantity of of the epicardial coronary arteries decreases the coronary blood move in about 90% of cases. Extent and severity of pre-existing (fixed) atherosclerotic occlusionNumber of coronaries affected/involved: Atherosclerosis could have an result on one, two or all three coronaries. Sudden cardiac demise as a outcome of fatal ventricular arrhythmia Effects of myocardial ischemia: 1. Vulnerable plaque Vulnerable plaque:Central necrotic core with many foam cells and abundant extracellular lipidFibrous cap is thin with few smooth muscle cells or teams of inflammatory cellsLess likely to endure rupture. Vulnerable plaque: They have core with many foam cells and plentiful extracellular lipid. The fibrous cap is thin with few smooth muscle cells or groups of inflammatory cells and increased irritation. Fixed obstruction of 75% or more: It ends in critical stenosis precipitates ischemia by exerciseproduces symptom as chest pain-stable angina. Fixed obstruction of 90% and above: It results in inadequate coronary blood move even at rest-unstable angina. Sudden morphological changes in atheromatous plaque: It is called acute plaque change (refer web page 280-281) and is followed by thrombosis, produces unstable angina, myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac demise in a lot of the patients. Other Causes of Coronary Artery Occlusion (Other Nonatheromatous Causes-refer page 280) Coronary emboli from thrombi in left facet of the center Coronary vasospasm Diminished availability of blood or oxygen:Lowered systemic blood pressure. Variants of Angina Pectoris Stable Angina It is the most typical and is also called typical angina pectoris. Cause: Coronary atherosclerosis and it develops when myocardial oxygen demand will increase with increased bodily exercise or emotional pleasure. Pain:Site: Chest pain within the substernal region, which can radiate to the left arm, jaw, and epigastrium. Stable angina: Most frequent sort of angina pectoris, substernal chest pain induced by train. Unstable or Crescendo Angina Unstable angina: Cause: It is brought on by the disruption/rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque complicated by 1. Multivessel illness Characteristics: It is of extended period and happens with minimal physical activity or three. Consequence: May progress to myocardial infarction and is also referred to as preinfarction angina. Myocardial infarction: Commonly often identified as Definition: Myocardial infarction is a coagulative kind of necrosis of cardiac muscle and is "coronary heart assault" and is crucial type of due to prolonged extreme ischemia. It can develop at youthful age in sufferers with main danger elements of atherosclerosis (hyperlipidemia, hypertension, diabetes and cigarette smoking). Sex: Males have considerably higher risk than females primarily through the reproductive interval. Other danger factors: Refer under danger factors for atherosclerosis (refer pages 255-257). Coronary Atherosclerosis Coronary artery occlusion in 90% of cases, myocardial infarction is as a end result of of atherosclerotic narrowing of one or more coronary arteries. It may be due to: Vasospasm with out coronary atherosclerosis Emboli: the source of which can be:Left atrium in affiliation with atrial fibrillationLeft-sided mural thrombusVegetations of infective endocarditisIntracardiac prosthetic materialParadoxical emboli: the emboli from the right facet of the center or the peripheral veins, which journey via a patent foramen ovale to the coronary arteries. Ischemia due to other causes:VasculitisHematologic disorders like sickle cell diseaseAmyloid deposition in vascular wallsVascular dissectionLowered systemic blood pressure. Acute plaque change: It is the sudden change/event occurring in an atheromatous plaque. The initial event in pathogenesis of myocardial infarction is sudden change within the atheromatous plaques. These as acute plaque modifications convert partially occlusive atherosclerotic plaque to produce sudden ischemia. Rupture, fissuring of plaqueexposes highly thrombogenic plaque constituents sudden thrombus formationsudden occlusion of lumen. Erosion/ulceration of plaqueExposes extremely thrombogenic subendothelial basement membraneSudden thrombus formationSudden occlusion of lumen. Acute plaque change: Sudden morphological adjustments occurring in an atheromatous plaque. Hemorrhage into the central core of plaqueincreases the plaque sizesudden occlusion of lumen. Factors that set off acute plaque change:Intrinsic: Plaque composition and construction (namely susceptible plaque). Formation of microthrombi: Acute plaque changes exposes thrombogenic subendothelial collagenplatelets adhere to the siteplatelet activation and aggregationformation of microthrombi on the atheromatous plaque partial or complete occlusion of the affected coronary artery. Vasospasm: Activated platelets, endothelial cell and inflammatory cells release mediatorscause vasospasm at the sites of atheromafurther narrowing of the lumen. Activation of the coagulation pathway: Tissue issue released at the site of acute plaque changeactivates coagulation systemincrease the dimensions of the thrombus. Complete occlusion of vessel: Within minutes, the thrombus might utterly occlude the lumen of the vessel. Myocardial necrosis: Complete occlusionresults in ischemic coagulative necrosis of the realm provided by the actual coronary artery. Consequence of Myocardial Ischemia these include functional, biochemical and morphological adjustments. Morphological adjustments may be divided into reversible and irreversible damage/injury. Functional disturbances: Loss of contractility inside 60 secondscan precipitate acute heart failure. Morphological modifications: They are seen at ultrastructural level corresponding to mitochondrial swelling, glycogen depletion and myofibrillar relaxation. Irreversible damage: A develops solely after extended, severe myocardial ischemia of more than 20 to 40 minutes Biochemical changes: They cause leakage of cytoplasmic proteins into the blood. Morphological modifications: Coagulative necrosis of cardiac muscle fibers often complete inside 6 hours of the onset of myocardial ischemia. Zones broken: First necrosis within the subendocardial zonelater transmural infarct Q. Usually associated with persistent coronary atherosclerosis, acute plaque change, and superimposed thrombosis. Occurs as a end result of plaque disruption adopted by a coronary thrombus, which undergoes lysis or extended, extreme reduction in systemic blood stress. Depending on the anatomic region concerned: Anterior, posterior, lateral, septal and their mixture like posterolateral. Left circumflex coronary artery occlusion (150%): Infarcts contain the lateral wall of left ventricle except at the apex. Triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (a histochemical stain) can grossly determine infarct inside 2 to three hours after onset. Appears pale reddish-blue space (due to stagnated, trapped blood)progressively becomes sharply defined, yellow-tan, and gentle. After 3 to 5 days: Mottled with a central pale, yellowish, necrotic area with well-demarcated border of hyperemic zone (due to granulation tissue).
Diseases
- Fistulous vegetative verrucous hydradenoma
- Knuckle pads, leuconychia and sensorineural deafness
- Acitretine antenatal infection
- Dysmorphism cleft palate loose skin
- Keratosis palmoplantaris with corneal dystrophy
- Desmoid disease
- Oliver McFarlane syndrome
- Delirium tremens
- Dysostosis acral with facial and genital abnormalities
- Chromosome 14, trisomy mosaic
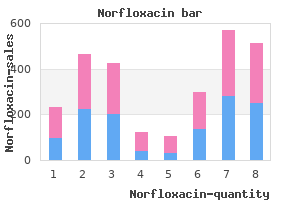
These embody correction of obesity virus vaccine norfloxacin 400 mg generic overnight delivery, avoidance of ethanol consumption antibiotics for strep throat cheap norfloxacin 400 mg without a prescription, and avoidance of high-purine meals antibiotics for dogs and cats norfloxacin 400 mg generic line. These abnormalities embody mental retardation antibiotic infusion buy discount norfloxacin 400 mg, spasticity (increased muscle rigidity leading to continuous improve of resistance to stretching), choreoathetosis (characterized by irregular, jerky, or explosive involuntary actions, and writhing or squirming, which may involve any extremity or the trunk), and a compulsive type of self-mutilation. The most important abnormality recognized in neurotransmitter methods is within the dopaminergic pathway (Chapter 30). Hershfield, Immunodeficiency illnesses caused by adenosine deaminase and purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. This autosomal recessive trait ends in incapability to salvage adenine, which accumulates and is oxidized to 2,8-dihydroxyadenine by xanthine oxidase. The major clinical abnormality is the excretion of 2,8-dihydroxyadenine as insoluble materials (gravel) within the urine. Both enzymes operate in the conversion of adenosine and deoxyadenosine to hypoxanthine. This cycle performs an important position in vitality manufacturing in skeletal muscle during exercise. In contrast, in de novo purine nucleotide biosynthesis, ribose 5-phosphate is an integral a half of the earliest precursor molecule. In the biosynthesis of each pyrimidine and urea (or arginine) (Chapter 15), carbamoyl phosphate is the supply of carbon and nitrogen atoms. In pyrimidine biosynthesis, carbamoyl phosphate serves as donor of the carbamoyl group to aspartate with the formation of carbamoyl aspartate. In urea synthesis, the carbamoyl moiety of carbamoyl phosphate is transferred to ornithine, giving rise to citrulline. In eukaryotic cells, two separate pools of carbamoyl phosphate are synthesized by totally different enzymes positioned at different websites. It provides carbamoyl phosphate for pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis and makes use of the amido group of glutamine as nitrogen donor. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain how the rise in flux is responsible for the maintenance of acceptable power ranges throughout train. For instance, pyrimidine nucleotides are involved in the biosynthesis of glycogen (Chapter 14) and of phospholipids (Chapter 17). Biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides can happen by a de novo pathway or by the reutilization of preformed pyrimidine bases or ribonucleosides (salvage pathway). The second gene codes for dihydro-orotate dehydrogenase, which is located on the outer aspect of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Dihydro-orotate, the product of Pyr 1, passes freely via the outer mitochondrial membrane and converts to orotate. Use of multifunctional polypeptides may be very efficient, because the intermediates neither accumulate nor turn out to be consumed in aspect reactions. Other pathways in eukaryotic cells, corresponding to fatty acid synthesis, occur on multifunctional polypeptides. Pyr 5,6 5 5, orotate phosphoribosyltransferase; 6, orotidine-50 -monophosphate decarboxylase. Biosynthesis of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides requires carbon dioxide and the amide nitrogen of glutamine. Both use an amino acid "nucleus"-glycine in purine biosynthesis and aspartate in pyrimidine biosynthesis. Thymidine nucleotide deficiency can additionally be induced by aggressive inhibitors of dihydrofolate reductase. A related toxic manifestation because of deficiency of thiopurine metabolizing enzyme was mentioned earlier. The study of the position of genetic inheritance that results in variations in drug response is named pharmacogenomics. They are transformed to nucleosides by nucleoside phosphorylases and then to nucleotides by appropriate kinases. All of these compounds require conversion to acceptable nucleotides before they become active. An antifungal agent, flucytosine (5fluorocytosine), acts through conversion to 5-fluorouracil by cytosine deaminase in the fungal cells. Idoxuridine (iododeoxyuridine), another halogenated pyrimidine by-product, is utilized in viral infections. The 20 -hydroxyl group of the arabinose moiety is in a trans place with respect to the 30 hydroxyl group (instead of in a cis place, as in the ribose) and causes steric hindrance to rotation of the base around the nucleoside bond. Phosphorylated derivatives of cytarabine inhibit nucleic acid synthesis in addition to being included into nucleic acids. During fast proliferation of cells, either as a normal physiological process or in pathological processes. These outcomes recommend that adenosine inhibits the conversion of orotic acid to orotidine-50 -monophosphate. Adenosine deaminase reduces the poisonous effect of adenosine by changing it to inosine. This inhibition of formation of pyrimidine nucleotides within the presence of excess purine nucleosides and nucleotides has been termed pyrimidine hunger. In contrast to purine catabolism, pyrimidine catabolism yields highly soluble end products. Orotic aciduria is characterized by failure of regular progress and by the presence of hypochromic erythrocytes and megaloblastic bone marrow, none of which is improved by the same old hematinic brokers. Treatment with uridine (2 g/d) results in marked enchancment in the hematological abnormalities, in progress and improvement, and in decreased excretion of orotic acid. These patients are pyrimidine auxotrophs and require an exogenous source of pyrimidine simply as all people want vitamins, important amino acids, and important fatty acids. Deficiency of folate or vitamin B12 can cause hematological adjustments similar to hereditary orotic aciduria. This interrelationship Nucleotide Metabolism Chapter 25 487 Folate is immediately involved in thymidylic acid synthesis and indirectly concerned in the metabolic capabilities of vitamin B12. Orotic aciduria with out the attribute hematological abnormalities happens in disorders of the urea cycle that result in the buildup of carbamoyl phosphate in mitochondria. The carbamoyl phosphate exits from the mitochondria and augments cytosolic pyrimidine biosynthesis. Treatment with allopurinol or 6-azauridine additionally produces orotic aciduria because of inhibition of orotidine-50 -phosphate decarboxylase by their metabolic products. Synopsis A 54-year-old man with four arthritic attacks in the course of the previous year was found to have serum urate levels of seven. His serum renal perform check was inside the reference interval, with creatinine of 1. The concern was what course of medical options to undertake to correct his hyperuricemia. In order to forestall acute attacks, every day colchicine administration was used as prophylaxis. The affected person was suggested to chorus from intake of alcohol and extreme consumption of meat and seafood. Acute inflammatory gout illness is caused by monosodium urate crystals present process phagocytosis within the synovial joint fluid. This process leads to activation of the inflammatory response, with manufacturing and release of several inflammatory mediators, resulting in severe pain. The acute attacks are handled with colchicine, glucocorticoids, and/or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication. Hyperuricemia can be handled with uricosuric drugs: probenecid, sulfinpyrazone, and benzbromarone. Synopsis An 8-year-old male with cervical lymphadenopathy, malaise, and repeated vomiting was brought to the emergency division. Laboratory research revealed he had hyperphosphatemia and acute renal failure, and later he was recognized with acute tumor lysis syndrome. Excessive cell destruction of tumor cells throughout chemotherapy causes mobile contents to be spilled into the bloodstream, inflicting hyperuricemia, hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, and acute kidney failure.
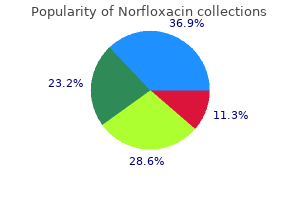
The renal threshold for fructose may be very low antibiotic resistance mechanisms 400 mg norfloxacin generic mastercard, and fructose is more readily excreted in urine than glucose virus plushies 400 mg norfloxacin buy. Despite these differences bacteria unicellular purchase 400 mg norfloxacin amex, the metabolic fates of glucose and fructose are intently related because most fructose is in the end transformed to glucose safe antibiotics for acne during pregnancy 400 mg norfloxacin buy amex. In some instances, the center is the principle organ concerned; in others, the nervous system is severely affected; autosomal recessive. Hypoglycemia; diminished hyperglycemic response to epinephrine or glucagon; normal hyperglycemic response to fructose or galactose; autosomal recessive. Six subtypes have been defined primarily based on relative effects on liver and muscle, and on properties of the enzyme. Rare, or troublesome to acknowledge; cirrhosis and storage of irregular glycogen; diminished hyperglycemic response to epinephrine; abnormal liver function; autosomal recessive. Hepatomegaly; elevated hepatic glycogen shops; most likely X-linked, but there could also be multiple type, with some autosomally inherited; have to be distinguished from glycogen phosphorylase deficiency. The situation is asymptomatic however, as with pentosuria, could also be misdiagnosed as diabetes mellitus. The next step in fructose metabolism is catalyzed by aldolase B (fructose-1-phosphate aldolase), which cleaves fructose-1-phosphate to the trioses dihydroxyacetone 3-phosphate and glyceraldehyde. Glyceraldehyde is phosphorylated by triosekinase, and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone 3-phosphate can either enter the glycolytic pathway or be combined to kind fructose-1,6bisphosphate by the motion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Thus, fructose metabolism bypasses phosphofructokinase, the most important regulatory site of glycolysis. Most dietary fructose is converted to glucose by method of gluconeogenesis, by way of condensation of the triose phosphates to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Aldolase B is also called fructose-1-phosphate aldolase, in distinction to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. This scenario could additionally be likened to hereditary fructose intolerance, which is attributable to insufficient amounts of aldolase B exercise. Although usually asymptomatic, individuals with this situation exhibit hypoglycemia, metabolic acidosis, vomiting, convulsions, coma, and signs of liver failure following ingestion of fructose or sucrose. Glycogenolysis is inhibited by fructose-1-phosphate at the degree of phosphorylase. If sucrose, fructose, and sorbitol are eliminated from the food plan, full recovery happens. Galactose Metabolism Most galactose ingested by humans is within the type of lactose, the principal sugar in human and bovine milk. Milk sugar aside from lactose is found within the sea lion and marsupials, whose first pouch milk accommodates a trisaccharide of galactose. Lactose is hydrolyzed to galactose and glucose by lactase, situated on the microvillar membrane of the small gut (Chapter 11). The enzymes required are discovered in many tissues, however the liver is quantitatively an important website for this epimerization. This enzyme may be regulated by substrate availability, because the normal hepatic concentration of galactose-1-phosphate is near the Km for this enzyme. However, infants with deficiency of epimerase in hepatic and extrahepatic tissues require small quantities of dietary galactose for normal improvement and progress. An isolated deficiency of epimerase in erythrocytes, which is clinically benign, has been described. Genetically determined deficiencies of galactokinase and galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase cause clinically vital galactosemia. Galactokinase deficiency is a uncommon, autosomal recessive trait during which high concentrations of galactose are discovered within the blood, notably after a meal that features lactose-rich foods, corresponding to milk and nonfermented milk merchandise. Patients regularly develop cataracts earlier than one yr of age due to the buildup of galactitol in the lens. Galactose in the urine is detected by nonspecific tests for lowering substances, as are fructose and glucose. Symptoms include cataracts, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, failure to thrive, and mental retardation. If galactosuria is extreme, nephrotoxicity with albuminuria and aminoaciduria might occur. The more extreme medical course may be because of accumulation of galactose-1-phosphate in cells. Measurement of transferase activity in purple blood cells is the definitive test for this disorder. Both types of galactosemia are treated by rigorous exclusion of galactose from the food regimen. In pregnancies the place the household history suggests that the infant could additionally be affected, the most effective outcomes have been reported when the mom was maintained on a galactose-free food regimen throughout gestation. This enzyme is a complex of galactosyltransferase, a membranebound enzyme that participates in glycoprotein synthesis (Chapter 10), and -lactalbumin, a soluble protein secreted by the lactating mammary gland. Binding of -lactalbumin to galactosyltransferase modifications the Km of the transferase for glucose from 1 mol/L to 1023 mol/L. Synthesis of -lactalbumin by the mammary gland is initiated late in being pregnant or at parturition by the sudden decrease in progesterone ranges that occurs at the moment. Prolactin promotes the speed of synthesis of galactosyltransferase and -lactalbumin. This diagram is intended to show the two major parts of the pathway: oxidation and decarboxylation of glucose-6-phosphate to ribulose-5-phosphate; and resynthesis of the previous from the latter. Thus, the pathway offers a means for producing glucose from ribose and other pentoses that may be transformed to ribose 5-phosphate. Nucleotide synthesis is best in quickly dividing tissues, such as bone marrow, pores and skin, and gastric mucosa. Metabolism of Amino Sugars In amino sugars, one hydroxyl group, often at C2, is changed by an amino group. Amino sugars are necessary constituents of many complex polysaccharides, together with glycoproteins and glycolipids, and of glycosaminoglycans (Chapter 10). De novo synthesis of amino sugars begins from glucose-6-phosphate, but salvage pathways can even function. Stoichiometrically, this process requires the rearrangement of six molecules of ketopentose phosphate to five molecules of aldohexose phosphate. One of the steps is catalyzed by transketolase, which requires thiamine pyrophosphate and Mg21 as cofactors. The versatility of this phase of the pathway allows for interconversion of a selection of sugars and glycolytic intermediates, partly due to the ready reversibility of the reactions and regulation of the enzymes by substrate availability. Genetically decided deficiencies of -glutamylcysteine synthase and glutathione synthase could cause hemolytic anemia. Abnormalities of glutathione metabolism can even end result from dietary deficiencies of riboflavin or selenium. Selenium deficiency diminishes activity of glutathione peroxidase and may result in peroxidative injury. This could be partially ameliorated by vitamin E, an antioxidant (Chapters 35 and 36). The erythrocytes are most severely affected due to their lengthy half-lives and incapability to carry out protein synthesis. The severity of the reaction depends, in part, on the actual inherited mutation. The urine may flip dark, even black, from the excessive concentration of hemoglobin, and a excessive urine flow have to be maintained to prevent injury to the renal tubules by the high protein load. If the affected person survives the initial crisis, with or with out transfusions, recovery usually happens because the reticulocyte rely will increase. The traits of the dysfunction had been elucidated throughout investigations into the hemolytic crises noticed in some sufferers following administration of 8-aminoquinoline derivatives, similar to primaquine and pamaquine, used for prophylaxis and remedy of malaria. Following administration of a drug known to promote hemolysis, Heinz our bodies are seen in erythrocytes in the peripheral blood. These also occur in some thalassemias and consist of oxidized and denatured forms of hemoglobin known as hemichromes (Chapter 27). The disorder is incessantly fatal unless a appreciable amount of blood is transfused quickly. Sons of affected males are usually normal (because they obtain their X-chromosome from their mothers), and daughters of affected males are normally heterozygotes (because they obtain one X-chromosome from their father). The rarest genotype is that of the homozygous feminine, because it requires that each mother and father have at least one irregular X-chromosome.
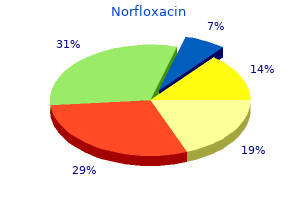
In all glycoproteins antibiotic coverage order norfloxacin 400 mg visa, the polypeptide part is synthesized first on the membrane-bound ribosomes of the tough endoplasmic reticulum; carbohydrate side chains are added during passage via the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus antibiotics starting with z buy norfloxacin 400 mg with visa. The carbohydrate additions contain particular glycosyltransferases and their substrates (uridine diphosphate sugars) and pcr antibiotic resistance norfloxacin 400 mg mastercard, in some glycoproteins antimicrobial agents antibiotics 400 mg norfloxacin buy visa, an oligosaccharide provider known as dolichol (a lipid). Glycoproteins can be fashioned by addition of carbohydrate residues with none of the advanced enzymatic pathways of carbohydrate addition. This course of, which is known as nonenzymatic glycation, proceeds by the condensation of a monosaccharide, normally glucose, with sure reactive amino groups on the protein. The initial, labile Schiff base adduct slowly rearranges to the steady ketoamine or fructosamine kind. In HbA1C, glucose is integrated through an N-glycosidic linkage into the N-terminal amino group of valine of each -chain. Enhanced levels of HbA1C occur in people with diabetes mellitus, and measurement of glycated hemoglobin has been helpful in monitoring the effects of remedy. Human serum albumin, which has a half-life of 19 days, can be subjected to nonenzymatic glycation producing a stable condensation product known as fructosamine. Fructosamine is a generic time period applied to the stable condensation product of glucose with serum proteins, of which albumin is quantitatively the most important fraction. Measurement of fructosamine concentration provides a way by which short-term (1 weeks) plasma glucose ranges may be estimated, whereas measurement of HbA1C focus reflects integrated plasma glucose ranges over a longer period (2 months). Human lens proteins, -, -, and -crystallins, which have for much longer lifespans than other proteins within the physique, also endure age-dependent, nonenzymatic glycation on the -amino groups of their lysine residues. In diabetics, this course of happens twice as often as in regular people of comparable age. However, the extent of nonenzymatic glycation of crystallins is much lower than that of hemoglobin. Crystallins represent 90% of the soluble proteins of the lens cells (also referred to as fiber cells). The human lens-a transparent, biconvex, elliptical, semisolid, avascular structure-is liable for focusing the visible image onto the retina. The lens grows all through life at a slowly decreasing rate, building layer upon layer of fiber cells round a central core and by no means shedding the cells. In addition to nonenzymatic glycation, crystallins undergo other age-dependent, post-translational modifications 112 Essentials of Medical Biochemistry in vivo: formation of disulfide bonds and other covalent cross-links; accumulation of high molecular weight aggregates; deamidation of asparagine and glutamine residues; partial proteolysis at attribute websites; racemization of aspartic acid residues; and photo-oxidation of tryptophan. Some of those processes contribute to the increasing amount of insoluble crystallins during getting older. Nonenzymatic incorporation of carbohydrates into proteins in vivo could be extensive and will contribute to the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus and galactosemia. In the body, membranes perform at the degree of tissues, cells, and intracellular domains. This characteristic selectivity of membranes to work together with specific molecules imparts distinctive properties to a given cell kind. Within the cell, the membranes of organelles are highly differentiated and have properties according to metabolic perform. Examples include electron transport and vitality conservation systems within the mitochondrial membrane, protein biosynthesis in the rough endoplasmic reticulum, modification and packaging of proteins for export in the membranes of the Golgi complex, drug detoxing within the easy endoplasmic reticulum, and light reception and transduction in the disk membranes of retinal cells. The ratio of protein:lipid:carbohydrate on a weight basis varies considerably from membrane to membrane. For instance, the human erythrocyte membrane has a ratio of about 49:43:8, whereas myelin has a ratio of 18:79:3. For example, in the erythrocyte membrane, phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine are situated primarily within the internal monolayer, whereas phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin are positioned within the external monolayer. Lipids are organized into bilayers that account for most of the membrane barrier properties. Peripheral proteins are positioned on both side of the bilayer and are easily eliminated by ionic options, whereas integral proteins are embedded within the bilayer to varying degrees. Some integral proteins penetrate the bilayer and are uncovered to each external and inner environments. By spanning each exterior and internal environments of the cell, these proteins might present a means of communication across the bilayer that could be helpful in the transport of metabolites, ions, and water, or in the transmission of signals in response to exterior stimuli offered by hormones, antibodies, or other cells. Because of hydrophobic interactions, isolation of integral proteins requires harsh methods, similar to physical disruption of the bilayer and chemical extraction procedures using synthetic detergents or bile salts to disrupt the lipidrotein interactions. Fluidity of the membrane structure is decided by the degree of unsaturation of the hydrocarbon chains of the phospholipids and by the quantity of ldl cholesterol in the membrane. Hydrocarbon chains with cis-double bonds produce kinks and permit a higher diploma of freedom of movement for the neighboring alkyl facet chains; hence, these unsaturated chains give rise to extra fluidity than do saturated alkyl chains, which associate in ordered arrays. Cholesterol, an rigid polycyclic molecule, is packed between fatty alkyl chains, the ring bearing the polar hydroxyl group interacting with the polar groups of phospho- and glycolipids. The presence of ldl cholesterol disrupts the orderly stacking of alkyl facet chains, restricts their mobility, and causes elevated membrane viscosity. Thus, the lipid composition of the membrane at physiological temperatures can have significant effects on fluidity and permeability. Some correlation appears to exist between the concentrations of sphingomyelin and ldl cholesterol in different membranes. Membrane proteins show considerable mobility in the airplane of the bilayer (lateral motion). The frequency of reorientation of lipid components (flip-flop migration) is extremely slow or nonexistent. These carbohydrate-containing molecules are exclusively present on the exterior floor of the plasma membrane. The function of glycoproteins in cellell interplay is coordination and regulation of adhesion, growth, differentiation of cells, and cell size. Disruption of those processes could lead to lack of management of cell division and growth, a property attribute of most cancers cells. When cells are allowed to grow in a tissue tradition medium under optimal circumstances on a floor, such as that of a Petri dish, they grow and divide until the surface is covered with a monolayer and further development is inhibited. The varied functional domains by which fibronectin can interact with different protein and membrane components are indicated. Cancer cells (malignant neoplastic cells), like remodeled cells, show continued progress and invasiveness (spreading) in tissue tradition. Reduced adhesion of most cancers cells to a matrix has been associated to a lowered synthesis of fibronectin and collagen. Fibronectin, a glycoprotein ample on the cell surface of regular cells, promotes that attachment and subsequent spreading of many cell types. Known additionally as a cell surface protein, fibronectin is a large, exterior, transformationsensitive protein that binds to numerous substances. Fibronectin is a multifunctional molecule containing regions that acknowledge glycoconjugates. Plasma fibronectin performs a number of roles in wound restore: in the formation of a fibrin clot as cross-linked fibronectin, in some reactions of platelets, in the enhancement of the opsonic exercise of macrophages (important for removing of international material and necrotic tissue), and in attracting fibroblasts (which take part within the production of repair elements similar to collagen and proteoglycans in the extracellular matrix). A distinctive type of fibronectin, often recognized as fetal fibronectin, is found within the extracellular matrix surrounding the extravillous trophoblast on the uteroplacental junction. The presence of fetal fibronectin in cervicovaginal secretions may be used as a marker in assessing the chance for preterm supply. In girls throughout 245 weeks of gestation with signs of preterm labor consisting of contractions and advanced cervical dilation, elevated fetal fibronectin levels ($50 mg/L) in the cervicovaginal fluid are indicative of an elevated threat of preterm delivery. The fetal fibronectin ranges have a high unfavorable predictive worth in the assessment of preterm delivery. Inhibition of uterine myometrial contractions, which is recognized as tocolysis, by acceptable therapeutic agents is used in stopping prematurity. Laminin mediates in adhesion of epithelial cells, whereas chondronectin mediates the attachment of chondrocytes to collagen. Mutations in a laminin molecule, particularly laminin 5, manifest in abnormalities of pores and skin fragility, causing one kind of dysfunction often identified as epidermolysis bullosa. A family of cell floor adhesion receptor proteins known as integrins binds with fibronectin. Integrins are a family of proteins containing heterodimers that possess receptors not only for fibronectin but additionally for collagens, laminin, fibrinogen, vitronectin, and integral membrane proteins of the immunoglobulin superfamily (Chapter 33). The emigration of leukocytes by way of the endothelial wall of a blood vessel requires coordinated activities of a group of glycoproteins, selectins, integrins, and intercellular adhesion molecules.
400 mg norfloxacin order with mastercard. MonoFoil Antimicrobial Spray Notre Dame Mats and Gloves.