
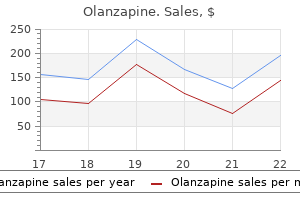
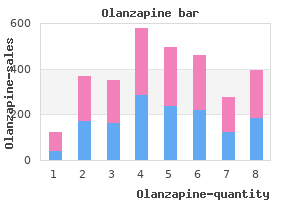
Olanzapine
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Discount olanzapine 5 mg on-line, symptoms weight loss".
E. Daro, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, Duke University School of Medicine
Approximately 30% are hypoxic on admission as a result of central respiratory depression or associated chest accidents treatment 7th feb cheap olanzapine 2.5 mg free shipping. The most typical early complications of head trauma are intracranial hypertension medicine bobblehead fallout 4 buy 7.5 mg olanzapine visa, brain herniation medications while breastfeeding discount 5 mg olanzapine otc, seizures symptoms queasy stomach olanzapine 7.5 mg discount with visa, neurogenic pulmonary edema, 3758 cardiac dysrhythmias, bradycardia, systemic hypertension, and coagulopathy. If consciousness remains depressed despite air flow and fluid substitute, a head injury is assumed to be current and the affected person is managed accordingly. As famous, hypotension is an important cause of death within the head-injured patient. Anesthetic and adjunct medication could render an adequate neurologic examination inconceivable; thus, long-acting muscle relaxants, opioids, sedatives, or hypnotics ought to be given selectively. In this test, the sum of the scores obtained for eye opening, verbal response, and motor activity correlates with the state of consciousness, the severity of the top injury, and the prognosis. A maximally dilated and unresponsive "blown" pupil suggests uncal herniation underneath the falx cerebri. The presence of similar findings in ocular injuries makes interpretation of pupillary findings difficult when eye and head accidents coexist. However, the pupillary reaction to gentle is normally more sluggish in the head-injured patient. Subdural hematomas normally have a concave border, whereas epidural hematomas present with a convex outline classically termed a lenticular configuration. These insults cause exacerbation of trauma-induced cerebral ischemia and metabolic derangements, worsening the outcome. The Brain Trauma Foundation and the American Association of Neurological Surgeons have printed evidence-based tips for the treatment of head-injured sufferers. Edema tends to happen in injured brain regions regardless of the kind of solution administered due to elevated permeability of the blood�brain barrier. Multiple research have demonstrated an association between prehospital endotracheal intubation and mortality of patients with extreme mind trauma. Acute mannitol toxicity, manifested by hyponatremia, high serum osmolality, and a niche between calculated and measured serum osmolality over 10 mOsm/L, could end result when the drug is given in giant doses (2 to three g/kg) or to patients with renal failure. Mannitol should be used with nice care within the presence of hypotension, sepsis, nephrotoxic medication, or preexisting renal illness, because these can also precipitate renal failure. It might exacerbate edema in injured areas by which it might easily enter the tissues. The addition of relatively small volumes of hypertonic saline in concentrations between 3% (6 to 8 mL/kg) and 7. It might cause hypernatremia, hyperosmolality, or hyperchloremic acidosis, in all probability from renal bicarbonate loss secondary to elevated levels of chloride (Cl-). There have been a quantity of research comparing hypertonic saline and mannitol for brain rest during craniotomy. Resuscitation with albumin 5% or 25% supplies a sustained enchancment in vital indicators, however the enhance in colloid osmotic pressure produced by these solutions could also be associated with an increased danger of mortality. This hypoperfusion appears to be triggered largely by increased cerebral vascular resistance, which may be enhanced by hyperventilation. It should be noted that hyperventilation within the severely brain-injured affected person may be related to acute lung injury. Of course, immediate surgical decompression, particularly of epidural hematomas, is a crucial factor in decreasing morbidity and mortality. Over the previous a number of years there was much debate concerning optimal blood glucose degree in critically sick patients. Brain-injured patients are unique members of this group as a result of mind metabolism is altered by the damage and is heavily depending on glucose. Hypoglycemia (<40 g/dL) may trigger metabolic crisis, whereas hyperglycemia (>200 g/dL) can cause detrimental results by way of excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammatory cytokine launch. However, tight insulin control remedy (80 to a hundred and ten mg/dL) has been 3763 associated with episodes of hypoglycemia. As a outcome, the present recommendations are to maintain glucose ranges of one hundred ten to one hundred eighty mg/dL. Many of the survivors will later succumb to nonneurologic organ dysfunction involving pulmonary failure and cardiac impairment, which can be related to sympathetic hyperactivity. Blocker remedy has been proposed as a remedy that may be useful in these sufferers. Both intracranial hematomas and hemorrhage in different areas have a excessive surgical priority. In the a number of trauma sufferer, prioritization between the two is predicated on the severity of every injury. The website of the craniotomy may be determined by a ventriculogram or an ultrasound examination with a pencil-tip probe; each exams could also be performed underneath native anesthesia via a frontal burr gap. Anesthetic Management Intraoperative management is a continuation of the pre-existing intensive care. It should be noted that there have been no research evaluating intravenous to inhalation methods. It appears reasonable to assume that preserving the important indicators is more essential than the precise means employed to accomplish this. It could also be potential to improve the outlook for brain-injured sufferers, as outlined right here: 3764 1. The earlier definitive therapy is initiated, the better the finish result is prone to be. Meanwhile, the extensive variety of types and severities of injury and of responses to treatment-both among completely different patients and in the identical patient at different times-imply that therapeutic interventions have to be individualized. Indeed, early intervention and managed administration could clarify much of the development in outcomes that has been obtained over the previous 20 years, including the results obtained by Patel et al. Spine and Spinal Cord Injury Initial Evaluation the objective in the analysis of spinal trauma is to diagnose instability of the backbone and the extent of neurologic involvement. Not stabilizing the spine in the first hours after a major accident till a definitive diagnosis is established carries the danger of converting a neurologically intact patient into a paraplegic or quadriplegic. During transport to the hospital, the affected person should be immobilized with a tough collar, a spine board, and tape. In these circumstances, flaccid areflexia, lack of rectal sphincter tone, paradoxic respiration, and bradycardia in a hypovolemic patient suggest the prognosis. In cervical spine trauma, an ability to flex but not to lengthen the elbow and response to painful stimuli above but not beneath the clavicle also indicate neurologic harm. Current guidelines consider absence of neck pain or paresthesia and a unfavorable physical examination- lack of tenderness with palpation and during voluntary flexion and extension of the neck-in a neurologically intact, aware patient as sufficient indications for ruling out a cervical spine damage with out additional radiologic research. However, this strategy should still miss some sufferers in danger for subsequent cervical wire insult. Intact sensory perception over the sacral distribution and voluntary contraction of the anus (sacral sparing) are present in incomplete, but not in complete, accidents. There is virtually no possibility of significant neurologic restoration in complete harm, whereas useful restoration may happen in up to 50% of patients after incomplete injuries. In 3766 some sufferers the development of spinal shock, which is manifested by absolute flaccidity and loss of reflexes, precludes distinguishing between complete and incomplete accidents during the preliminary part of therapy. Therefore, even within the absence of sacral sparing, the potential of neurologic restoration dictates that all possible efforts be made presently to prevent additional injury and to preserve cord function. After the primary few days, spinal twine edema subsides, and the ultimate injury stage is usually a quantity of segments lower than on preliminary presentation. Spinal shock is probably caused by direct trauma to the spinal twine and usually subsides within days to weeks. The time period is frequently used as a misnomer for neurogenic shock, which is outlined as hypotension and bradycardia caused by the loss of vasomotor tone and sympathetic innervation of the guts as a result of functional despair of the descending sympathetic pathways of the spinal wire. It is usually current after excessive thoracic and cervical backbone accidents and improves within 3 to 5 days. If the patient has a thoracic or lumbar harm, a cautious logrolling maneuver ought to be used. Severe bradycardia or dysrhythmias may end result from unopposed vagal activity throughout tracheal intubation or suctioning: the affected person should be preoxygenated, and atropine (0. If bradycardia develops throughout airway administration, therapy consists of further atropine, glycopyrrolate, isoproterenol, or, if essential, cardiac pacing. Respiratory Complications Respiratory problems are common in all phases of the care of spinal cord�injured sufferers and are essentially the most frequent cause of demise in the acute stage. Injuries at C5 or decrease are usually associated with regular tidal volumes as a result of the operate of the diaphragm is undamaged, whereas patients with accidents at C4 or above may require everlasting ventilatory help. Nevertheless, accessory respiratory muscle paresis could cause a big lack of expiratory reserve even when the injury involves the lower spinal segments.
Ultrastructure Inspection of the minimize surface of the kidney reveals the paler cortex medicine 223 olanzapine 2.5 mg discount online, adjacent to the capsule medicine universities olanzapine 5 mg order line, and the darker symptoms ruptured spleen buy 5 mg olanzapine with mastercard, conical pyramids of the renal medulla symptoms kidney problems olanzapine 7.5 mg discount with amex. The pyramids are radially striated and are covered with cortex, extending into the kidney as the renal columns. Collecting tubules from every lobe of the kidney (pyramid and its overlaying of cortex) discharge urine into the calyceal system by way of renal papillae at the entrance of each pyramid into the calyx correct. These amassing tubules originate deep within the radial striations (medullary rays) of the kidney and convey urine formed in the structural items of the kidneys, the nephrons. The parenchyma of each kidney contains roughly 1 � 106 tightly packed nephrons, every one consisting of a tuft of capillaries (the glomerulus) invaginated into the blind, expanded finish (glomerular corpuscle) of a long tubule that leaves the renal corpuscle to type the proximal convoluted tubule within the cortex. This leads into the straight tubule, which loops down into the medullary pyramid (loop of Henle) and therefore again to the cortex to become continuous with the distal convoluted tubule. It is in these elements of the nephron (proximal tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule, and amassing duct) that urine is formed, concentrated, and conveyed to the ureters. The distal convoluted tubule comes into very shut contact with the afferent glomerular arteriole, and the modified cells of every form the juxtaglomerular equipment, a complex physiologic suggestions control mechanism contributing partially to the precise control of intra- and extrarenal hemodynamics that may be a hallmark feature of the normally functioning kidney. As is the case for the renal tubules, the vasculature of the kidney is highly organized. The renal artery enters the kidney on the hilum and then divides many instances before producing the arcuate arteries that run along the boundary between cortex and outer medulla. Interlobular arteries branch from arcuate arteries toward the outer kidney surface, giving rise as they move by way of the cortex to quite a few afferent arterioles, each resulting in a single glomerular capillary tuft. The barrier where filtration from the vascular to tubular area within the glomerulus happens is highly specialized and contains fenestrated negatively charged capillary endothelial cells and tubular epithelial cells (podocytes) separated by a basement membrane. However, abnormalities of this barrier can occur with disease, which 3509 may permit filtration of much bigger proteins and even pink blood cells; these changes manifest because the nephrotic syndrome (proteinuria >3. The glomerular capillaries exit Bowman capsule and merge to type the efferent arteriole and peritubular capillaries that nourish the tubules. The renal vasculature is unusual in having this arrangement of two capillary beds joined in collection by arterioles. Blood supply to the whole tubular system comes from the glomerular efferent arteriole, which branches into an in depth capillary community. Some of those peritubular capillaries, the vasa recta, descend deep into the medulla to parallel the loops of Henle. The vasa recta then return in a cortical course with the loops, be part of other peritubular capillaries, and empty into the cortical veins. B: Internal organization of the kidney consists of cortex and medulla areas and the vasculature. D: Plasma filtration occurs in the glomerulus; 20% of plasma that enters the glomerulus passes via the specialized capillary wall into the Bowman capsule and enters the tubule to 3510 be processed and generate urine. The capabilities of the kidney are many and various, including waste filtration, endocrine and exocrine activities, immune and metabolic functions, and upkeep of physiologic homeostasis. As nicely as tight regulation of extracellular solutes such as sodium, potassium, hydrogen, bicarbonate, and glucose, the kidney additionally generates ammonia and glucose and eliminates nitrogenous and other metabolic wastes together with urea, creatinine, bilirubin, and different uremic toxins. Finally, circulating hormones secreted by the kidney influence red blood cell era, calcium homeostasis, and systemic blood strain. The kidney fulfills its dual roles of toxin excretion and physique fluid administration by filtering massive amounts of fluid and solutes from the blood and secreting waste merchandise into the tubular fluid. Effects on the traditional filtration and reabsorption processes of comorbid disease, surgery, and anesthesia are the major target of the next section. Glomerular Filtration Production of urine begins with water and solute filtration from plasma flowing into the glomerulus through the afferent arteriole. The ultrafiltration constant (Kf) is directly associated to glomerular capillary permeability and glomerular surface area. Renal autoregulation of blood move and filtration is accomplished primarily by native suggestions alerts that modulate glomerular arteriolar tone to protect the glomeruli from excessive perfusion stress. Several mechanisms for regulating blood flow to the glomerulus have been described, and all involve modulation of afferent glomerular arteriolar tone. The myogenic reflex concept holds that a rise in arterial pressure causes the afferent arteriolar wall to stretch after which constrict (by reflex); likewise, a lower in arterial pressure causes reflex afferent arteriolar dilatation. Chloride also acts because the feedback signal for control of efferent arteriolar tone. In response to angiotensin, efferent arteriolar constriction will increase glomerular strain, which increases glomerular filtration. Tubular Reabsorption of Sodium and Water Active, energy-dependent reabsorption of sodium begins almost instantly as the glomerular filtrate enters the proximal tubule. Here, an adenosine triphosphatase pump drives the sodium into tubular cells whereas chloride ions passively follow. Glucose, amino acid, and different organic compound reabsorption are strongly coupled to sodium in the proximal tubule. Notably, no energetic sodium transport occurs within the loop of Henle until the medullary thick ascending limb is reached. Cells of the medullary thick ascending limb are metabolically lively of their function of reabsorbing sodium and chloride and have a excessive oxygen consumption in contrast with the skinny portions of the descending and ascending limbs. Reabsorption of water is a passive, osmotically pushed course of tied to the reabsorption of sodium and other solutes. Water reabsorption also is dependent upon peritubular capillary stress; high capillary pressure opposes water reabsorption and tends to increase urine output. The proximal tubule reabsorbs roughly 65% of filtered water in an isosmotic trend with sodium and chloride. The descending limb of the loop of Henle allows water to comply with osmotic gradients into the renal interstitium. However, the skinny ascending limb and medullary thick ascending limb are comparatively impermeable to water and play a key function in the manufacturing of concentrated urine. Only 15% of filtered water is reabsorbed by the loop of Henle; the remaining filtrate volume flows into the distal tubule. Conservation of water and excretion of excess solute by the kidneys could be inconceivable with out the flexibility to produce concentrated urine. The arterial baroreceptors are activated when hypovolemia results in a lower in blood stress, whereas atrial receptors are stimulated by a decline in atrial filling stress. The Renin�Angiotensin�Aldosterone System Renin release by the afferent arteriole could also be triggered by hypotension, decreased tubular chloride focus, or sympathetic stimulation. Aldosterone stimulates the distal tubule and collecting duct to reabsorb sodium (and water), resulting in intravascular quantity expansion. Sympathetic nervous system stimulation may immediately trigger release of aldosterone. Stress states, renal ischemia, and hypotension stimulate the manufacturing of renal prostaglandins through the 3514 enzymes phospholipase A2 and cyclooxygenase. Clinical Assessment of the Kidney Most agree that instant perioperative measures such as urine output correlate poorly with perioperative renal function4; however, much concerning the kidneys could be realized from figuring out how effectively they clear circulating substances and inspection of the urine. Renal Function Tests Filtration is a useful method to clinically assess kidney operate. As a key indicator of disease, information of limited filtration capacity is necessary to guide drug dosing for agents cleared by the kidneys and helps with preoperative risk stratification. Also, acute declines in filtration capacity point out kidney injury and predict a extra complicated medical course. In steady, critically sick sufferers, 2hour urine collections are enough to calculate CrCl,eleven using the next formulation: the place Ucr = urine creatinine, V = total quantity of urine collected, Pcr = plasma creatinine, and time = assortment time. Nonetheless, serum creatinine stays, so far, an unsurpassed perioperative tool, notably to replicate trends of change in renal filtration and to predict consequence, even in the course of the perioperative interval. Urinalysis and Urine Characteristics Urine inspection can reveal abnormal cloudiness or shade and unexpected odors. Detailed descriptions or of urine examination are available22; due to this fact, only a summary is provided here. Cloudy urine is due to suspended elements corresponding to white or red blood cells and/or crystals. Lightly centrifuged urine sediment will normally include eighty � 20 mg of protein per day and up to two red blood cells per high-power field (400�); greater levels of purple blood cells or protein reflect abnormal kidney function.
Ajuga reptans (Bugle). Olanzapine.
- What is Bugle?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Gallbladder and stomach disorders, inflammation of the mouth and throat, wounds, and other uses.
- How does Bugle work?
- Dosing considerations for Bugle.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96215
Cervical emphysema ought to be evaluated with a chest x-ray and the airway should be evaluated for signs of obstruction medications causing hair loss olanzapine 2.5 mg order mastercard. Capnothorax Carbon dioxide fuel accumulation throughout the pleural house is called capnothorax symptoms in children olanzapine 2.5 mg lowest price. Tension capnothorax could occur from uncontrolled pressurization of the thoracic cavity medicine website discount olanzapine 5 mg online, leading to severe withdrawal symptoms olanzapine 7.5 mg buy visa a rise in intrathoracic pressure, mediastinal shift, decreased venous return, and subsequent right ventricular compression-a potentially life-threatening condition. Risk components for capnothorax are similar to those for subcutaneous emphysema; however, greater threat exists throughout procedures near the diaphragm. Physical examination findings could embrace decreased breath sounds bilaterally or unilaterally, as properly as lowered chest tour. Transthoracic echocardiography is increasingly being used to assess lung pathology, together with intraoperative pneumothorax. Close observation is often adequate for wholesome patients with minimal physiologic derangements. The hemodynamic unstable affected person ought to be supported with fluids or vasoactive agents while the capnothorax is reabsorbed. In severe cases, emergent needle decompression or chest tube insertion could also be needed intraoperatively. If rigidity capnothorax and hemodynamic instability recur after reinsufflation, termination of laparoscopy and conversion to an open surgical process may be indicated. Severe capnomediastinum and capnopericardium may be related to severe hemodynamic instability because of extreme strain of large mediastinal vascular constructions and cardiac chambers. Fatalities from suspected gas embolism occurred in seven patients in a retrospective evaluation of 500,000 closed-entry laparoscopies, over three a long time. According to several case-series, the danger of gasoline embolism throughout laparoscopic main hepatectomy may be less than 1. Round ligament transection and broad ligament dissection during laparoscopic hysterectomy have resulted in fuel embolisms. In the animal mannequin, laparoscopic hepatectomies in the reverse Trendelenburg position preferentially resulted in venous fuel embolisms. Diagnosis is normally depending on the constellation of medical signs related to gasoline emboli. Physical examination findings could include cyanosis and a "mill wheel" murmur by auscultation. If deemed essential, the patient may be positioned in Trendelenburg with a left lateral decubitus position to help minimize the severity of right ventricular air lock. Patient Shifting and Falls Extreme positioning and potential for injury are frequent in laparoscopic procedures, significantly in robot-assisted laparoscopy. Patients present process laparoscopy in steep reverse Trendelenburg and steep Trendelenburg are at threat of unexpectedly shifting down or up on the operating room desk. The anesthesiologists should actively participate in positioning and ensuring secure securement of the anesthetized affected person. A affected person in steep Trendelenburg could also be secured from transferring by utilizing an operating table belt strap. Additional equipment could embody an underbody gel pad for skid prevention, lithotomy stirrups with Velcro straps, and a surgical beanbag system. Careful consideration should be paid to pressure points created by the securing units. During steep reverse Trendelenburg positioning, a padded footrest can be attached to the working room table to maintain a affected person from shifting down and off the table. Peripheral Nerve and Brachial Plexus Injuries A giant number of nerve accidents acquired intraoperatively are due to patient positioning. The brachial plexopathy is highly related to steep Trendelenburg and longer operative time in laparoscopic colorectal surgery,142 and caudad shoulder displacement throughout robotic prostatectomy. In the meantime cautious consideration to positioning throughout the operative course is crucial. Airway Edema Prolonged steep Trendelenburg position during robotic prostatectomy and enormous volume fluid resuscitation might induce facial and pharyngo-laryngeal edema,104 which may find yourself in airway compromise postoperatively. A recumbent sitting place may expedite reversal of any orofacial edema throughout emergence and postoperative restoration. If concerns for extreme airway edema exist intraoperatively, a plan for continued intubation and ventilatory assist ought to be made. Albeit uncommon, the potential for postoperative respiratory dysfunction after laparoscopy surgery nonetheless exists and could also be modified by coexisting illnesses, surgery specific components, and any reported intraoperative pulmonary challenges. In bariatric surgical procedure, patients with lively reflux illness may be at risk for postoperative aspiration events and exacerbation of reactive airway illness. Diaphragmatic dysfunction after laparoscopy has been reported145,146 and might sometimes result in respiratory dysfunction. Compared to open belly surgical procedure, laparoscopic surgery ends in less ache, shorter length of ache, and fewer opioid consumption. Although the function of transversus abdominis airplane block stays unclear, this procedure remains a viable choice for postoperative pain administration after laparoscopic surgical procedure. Conclusion Laparoscopic surgery has been a revolutionary different to many open surgical procedures. Its capability to provide surgeons the means to operate with minimal surgical trauma whereas providing sufferers a shorter postoperative restoration has made it critical to the expansion of ambulatory surgical procedure. Advances in know-how have launched robotics as a standard and growing feature of minimally invasive surgical procedure. For the anesthetists, "minimally invasive" surgery requires maximally attentive anesthesia. Pneumoperitoneum at the side of excessive affected person positioning induces transient, however important, multiorgan derangements that require short-term manipulation of physiology to decrease complications. Because critical problems related to surgery can happen at any stage during the intraoperative and postoperative course, constant vigilance and action are important to avoiding everlasting damage or dying. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on the protection and effectiveness of day-case laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Systematic evaluate of 23-hour (outpatient) keep laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery. Low stress versus standard strain pneumoperitoneum in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Selection of overweight sufferers undergoing ambulatory surgical procedure: a scientific review of the literature. Effects of posture and pneumoperitoneum throughout anaesthesia on the indices of left ventricular filling. Alterations of cardiovascular efficiency during laparoscopic colectomy: a mixed hemodynamic and echocardiographic analysis. Hemodynamic perturbations throughout robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy in 45� Trendelenburg position. Carbon dioxide absorption throughout laparoscopic donor nephrectomy: a comparability between retroperitoneal and transperitoneal approaches. Pulmonary gasoline trade is well preserved during robot assisted surgery in steep Trendelenburg position. Ventilation-perfusion distributions and gasoline change throughout carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum in a porcine mannequin. Mild hypercapnia will increase subcutaneous and colonic oxygen pressure in sufferers given 80% impressed oxygen during belly surgical procedure. Carbon dioxide elimination sample in morbidly overweight patients undergoing laparoscopic surgical procedure. Acid-base alterations throughout laparoscopic belly surgical procedure: a comparison with laparotomy. Hepatic and portal vein blood flow during carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum for laparoscopic hepatectomy. Overcoming decreased hepatic and renal perfusion caused by positive-pressure pneumoperitoneum. Unpredicted neurological problems after robotic laparoscopic radical cystectomy and ileal conduit formation in steep Trendelenburg position: two case reviews. The effect of steep Trendelenburg positioning on intraocular stress and visual perform during robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy.
This pathophysiologic and medical picture is similar to symptoms ulcer stomach olanzapine 5 mg buy discount on line that of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment x time interaction discount 5 mg olanzapine fast delivery. If this situation is suspected symptoms 4 days post ovulation cheap 5 mg olanzapine fast delivery, a trial of quantity growth and vasoconstrictors is indicated medicine nobel prize 2015 generic olanzapine 7.5 mg amex. Weakening of the media layers of the aorta (the time period cystic medial degeneration denotes the disappearance of easy muscle cells and the degeneration of elastic fibers) leads to elevated wall stress, which induces dilatation of the aortic lumen and formation of aneurysm, which can coexist with intramural hemorrhage or aortic dissection, or even lead to rupture. Aortic Dissection Aortic dissection86 is one of the options of the acute aortic syndromes, which also include intramural hematoma and penetrating ulcer. Connective tissue issues, corresponding to Marfan syndrome and Ehlers�Danlos syndrome affect principally the younger (age <40 years), whereas hypertension is the most common threat factor in older patients. Aortic dissection is brought on by a tear within the aortic intima and media, which propagates proximal and distally, creating a false lumen throughout the aortic media. When the false lumen includes aortic vessels, it causes malperfusion of vital organs (brain, spinal cord, belly organs). Acute aortic dissection of the ascending aorta (type A) has a mortality price of 1% to 2% per hour after onset of symptomatology and is a true surgical emergency. An aortic dissection distal to the left subclavian artery known as kind B, has a 30day mortality of 10%, and may be managed medically or with insertion of a scaffold (stent). Intramural hematoma originates from ruptured vasa vasorum within the media and is taken into account a precursor to basic dissection. Intramural hematoma has the same prognosis as aortic dissection and is handled equally. Severe neck or chest pain (type A) or back or abdominal pain (type B) is the commonest symptom, though many patients have atypical symptoms mimicking stroke, myocardial infarction, vascular embolization, and abdominal pathology. Pulse deficits in extremities and/or variations in blood stress are a major sign and are associated to impaired blood flow to a limb. It is important to diagnose correctly the sort of dissection as this determines the correct treatment. It involves implantation of a composite graft within the ascending aorta with or without reimplantation of the coronary arteries. Type B aortic dissections can be managed medically if persistent or with implantation of a graft via an open or closed (percutaneous) method if difficult (malperfusion symptomatology). When large, aortic aneurysms might trigger native mass impact similar to compression of the trachea (cough), esophagus (dysphagia), and/or recurrent laryngeal nerve (hoarseness). Detection and sizing may be carried out with contrast-enhanced computed tomography scanning and magnetic resonance angiography. The risk for rupture will increase abruptly as aortic aneurysms attain a diameter of 6 cm. Cerebral protection methods during replacement of the 2705 aortic arch embrace use of deep hypothermic circulatory arrest with or with out arrest of cerebral circulation. Retrograde (via a superior vena cava cannula) or selective antegrade (direct cannulation of cerebral vessels) cerebral perfusion is employed to enhance outcomes by providing perfusion to the brain and flush out particulate matter from the cerebral and carotid arteries, with, up to now, disputed outcomes. Anesthetic Considerations the anesthetic method is centered round two major organ systems: (1) preservation of cardiac operate (most essential in surgical procedure of descending aortic aneurysms, the place the "clamp-and-go" surgical technique imposes nice fluctuations in systemic afterload and hemodynamic instability), and (2) neurologic integrity (in arch or descending aortic operations). Usually, increments of 10 mL are drained at a time and the cerebrospinal fluid stress is monitored constantly, maintaining a cerebrospinal fluid stress below 15 mmHg always. Too high move of the bypass system will result in hypotension, whereas elevated pump circulate will help lower systemic hypertension proximal to the aortic interruption. For nonintracardiac procedures, a multi-orifice "dual-stage" cannula that drains blood from the proper atrium, coronary sinus, and inferior vena cava is usually used. However, the place a bloodless subject is required single cannula drainage may be suboptimal. In this case individual "single-stage" cannulae are placed into the superior and inferior venae cavae and then snared, thus stopping systemic venous blood from coming into the guts. In the event of poor venous drainage, adjustment of the venous cannulae, elevating the height of the operating table, or application of suction normally corrects the problem. From the venous reservoir, blood enters the oxygenator/heat exchanger, which acts a synthetic lung, and the blood is oxygenated and carbon dioxide is removed. Blood could then be warmed/cooled and returned to the arterial circulation via a large "arterial" cannula positioned within the ascending aorta, femoral, or axillary arteries. Venting prevents ventricular distention that will result in myocardial ischemia and is especially important in sufferers with aortic insufficiency. These displays are used to detect low blood levels in the venous reservoir/oxygenator (to prevent entrainment of air to the arterial side of the circuit), excessive systemic line pressure (to diagnose possible arterial cannula obstruction/aortic dissection; each cause elevated line pressure), and bubbles. Membrane oxygenators use bundles of hollow microporous fibers contained in a plastic housing. Within this housing, blood flows around the fibers whereas contemporary gasoline is passed though the fibers. The micropores act as channels permitting the diffusion of each oxygen and carbon dioxide. At the middle of this housing are two metal arms set 180 degrees apart with rollers at every finish. When the arm rotates, the tubing is alternately compressed and launched against the housing. Alternately compressing and releasing the tubing generates forward move with out the potential for retrograde flow. The disadvantages embody destruction of blood elements, spallation (development of plastic microemboli because of tubing compression), and issues from influx and outflow occlusion of the pump. If pump influx is occluded, adverse pressure will develop in the roller head inflicting cavitation or the event of microscopic bubbles. If pump outflow turns into occluded, extreme stress 2708 might develop proximal to the occlusion, causing the tubing connections to separate or the tubing to burst. One main difference between curler head and centrifugal pumps is that move from centrifugal pumps will differ with changes in pump preload and afterload. It is for that reason that a flow meter have to be placed on the arterial side of the bypass circuit. Advantages of centrifugal pumps include less blood trauma, lower line pressures, decrease danger of large air emboli, and elimination of tubing put on and spallation. In this fashion blood is subsequently warmed or cooled and maintained at a desired temperature. Other solutions such as albumin (to decrease postoperative edema), mannitol (to promote diuresis), additional electrolytes (calcium to stop hypocalcemia because of citrate in transfused blood), and heparin (to ensure a secure level of anticoagulation) could additionally be added to the prime. Many institutions use a normal quantity prime for all adult patients, and others use a minimal quantity based mostly on physique weight or physique floor space (the average prime volume is about 1,500 mL). This reduction in floor area, and to a lesser extent a discount in pump prime, could scale back blood utilization. Following intravenous injection, the peak onset of heparin is lower than 5 minutes with a half-life of roughly ninety minutes in normothermic sufferers. Measuring heparin ranges intraoperatively is an alternative method for willpower of anticoagulation ranges. In this method, recognized doses of protamine are added to a heparinized sample of blood sequentially, till the optimum dose of protamine that produces a clot in the shortest amount of time is decided. By understanding the neutralization ratio of heparin and protamine (usually 1 mg of protamine to one hundred U of heparin), the heparin concentration within the sample can be determined. The first is usually delicate and consists of a transient lower in platelet rely following the administration of heparin a couple of days following surgical procedure. This thrombosis might happen anyplace within the physique and cause bowel or limb ischemia to name a quantity of. These embody defibrinogenating agents (ancrod obtained from pit viper venom), hirudin, bivalirudin, and factor X inhibitors. Hirudin, which is isolated from the salivary gland of the medicinal leech (Hirudo medicinalis), and bivalirudin (hirulog) are each direct inhibitors of thrombin. The use of those agents is rare and the reader is advised to seek the advice of one of many several reviews on this topic. In addition, patients are more and more demanding "cold" surgeries to lessen the risks of blood transfusion (infection, incompatibility reactions, transfusion error). However, because of the character of cardiac surgical procedure, the danger of blood and blood product transfusion is high. Bleeding because of 2711 reoperation, use of anticoagulants/platelet perform inhibitors, and residual surgical bleeding contribute to this risk. The use of a multimodal method to blood conservation including intraoperative autologous blood donation, the scavenging and reinfusion of shed blood, using antifibrinolytics (-aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid), and different conservation strategies might all help to reduce the need for transfusion. Contraindications to intraoperative autologous blood donation embody preoperative anemia, unstable angina/high-grade left major coronary artery disease, and aortic stenosis.