
Pariet
| Contato
Página Inicial

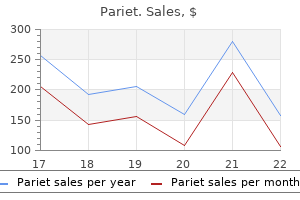
"Pariet 20 mg discount line, gastritis muscle pain".
M. Irmak, M.A.S., M.D.
Deputy Director, Emory University School of Medicine
Biomarkers and diagnostics for tuberculosis: Progress gastritis diet in hindi pariet 20 mg on line, wants gastritis diet ����� pariet 20 mg order with mastercard, and translation into follow chronic non erosive gastritis definition 20 mg pariet purchase otc. The molecular basis of resistance to isoniazid gastritis for dogs generic 20 mg pariet overnight delivery, rifampin, and pyrazinamide in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tumour necrosis factor- inhibitors and the reactivation of latent tuberculosis an infection. Guidelines for stopping the transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in health care settings. Comparable specificity of two business tuberculin reagents in persons at low danger for tuberculosis infection. Updated guidelines for interferon gamma release assay to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, United States. Interferon- release assays for diagnosis of tuberculosis an infection and disease in youngsters. Performance of business blood exams for the analysis of latent tuberculosis infection in children and adolescents. Performance of checks for latent tuberculosis in several teams of immunocompromised patients. American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control/Infectious Disease Society of America. Increasing adherence for latent tuberculosis infection remedy with well being departmentadministered remedy. Recommendations to be used of isoniazid�rifapentine regimen with direct remark to deal with Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Drug resistant tuberculosis � present dilemmas, unanswered questions, challenges, and priority wants. Therapeutic drug monitoring for sluggish response to tuberculosis in a state control program. The effect of hemodialysis on cycloserine, ethionamide, para-aminosalicylate, and clofazimine. Pharmacokinetics of isoniazid beneath fasting situations, with meals, and with antacids. Low isoniazid focus associated with end result of tuberculosis remedy with once-weekly isoniazid and rifapentine. Pharmacokinetics of rifampin underneath fasting situations, with food, and with antacids. Serum concentrations of rifampin, isoniazid, and intestinal absorption, permeability in sufferers with multidrug resistant tuberculosis. Pharmacokinetics of pyrazinamide underneath fasting conditions, with meals, and with antacids. Pharmacokinetics of ethambutol under fasting conditions, with food, and with antacids. Pharmacokinetics of p-aminosalicylate underneath fasting conditions, with orange juice, food, and antacids. Pharmacokinetics of cycloserine underneath fasting conditions, with orange juice, food, and antacids. Moxifloxacin versus ethambutol in the first 2 months of remedy for pulmonary tuberculosis. Substitution of moxifloxacin for isoniazid throughout intensive part remedy of pulmonary tuberculosis. Fluoroquinolone resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: the effect of length and timing of fluoroquinolone exposure. Modeling the epidemiology and economics of instantly observed therapy in Baltimore. Serum concentrations of antimycobacterial medicine in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis in Botswana. Resurgent tuberculosis in New York City: Human immunodeficiency virus, homelessness, and the decline of tuberculosis management applications. Its etiology consists of various bacteria, viruses, and protozoans, with viral causes being most predominant globally. Two kinds of infectious diarrhea embody watery or enterotoxigenic diarrhea and dysentery or bloody diarrhea. Common pathogens liable for watery diarrhea are viruses and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Fluid and electrolyte alternative is the cornerstone of therapy for diarrheal illnesses. Oral rehydration therapy is preferred generally of gentle and average diarrhea. Loperamide and diphenoxylate/atropine may supply symptomatic aid in sufferers with reasonable watery diarrhea; however, use of antimotility brokers must be avoided in patients with watery and dysentery diarrhea. Diarrheal illness may be largely prevented by procedures to forestall contaminated meals or water provides and with appropriate private hygiene. Metronidazole is the drug of selection for delicate to reasonable illness and fidaxomicin could provide a bonus in sufferers at excessive danger for disease recurrence. Inflammation-induced vomiting and diarrhea are responsible for a lot of the morbidity and mortality of these circumstances. Diarrhea is outlined as a lower in consistency of bowel actions (ie, unformed stool) and an increase in frequency of stools to three or more per day. A extensive number of viral, bacterial, and parasitic pathogens are answerable for these infections. This chapter will focus on pathogenesis and administration of common viral and bacterial etiologies. Because the scientific consequences of dysenteric diarrhea can be more severe compared with cases of watery diarrhea, the chapter is organized accordingly. In the United States, 179 million episodes of acute gastroenteritis occur annually, leading to more than 600,000 hospitalizations and more than 5,000 deaths. Etiologic agents are hardly ever recognized because of the rare collection of stool samples, or incapability of many laboratories to detect the full vary of pathogenic organisms. Common pathogens related to dysenteric diarrhea mentioned will be Shigella spp. Characteristics of watery and dysenteric diarrhea and customary pathogens liable for them are outlined in Table 113-1. Noroviruses, beforehand generally identified as Norwalk-like viruses, account for higher than 90% of viral gastroenteritis among all age groups, and 50% of outbreaks worldwide. In the United States, noroviruses have been estimated to trigger 21 million cases of acute gastroenteritis yearly together with greater than 70,000 hospitalizations and nearly 800 deaths. After the preliminary infection, 40% of youngsters are protected towards subsequent rotavirus an infection, 75% are protected against subsequent gastroenteritis, and as much as 88% are protected in opposition to extreme gastroenteritis. Other viral etiologies embody astrovirus, enteric adenovirus, pestivirus, coronavirus, and enterovirus. Characteristics of viral pathogens inflicting gastroenteritis are outlined in Table 113-2. Characteristics of acute bacterial pathogens causing gastroenteritis are summarized in Table 113-3. Vibrio cholerae is a gram-negative bacillus sharing related traits with the household Enterobacteriaceae. Although there are 14 completely different species, Campylobacter jejuni is the species responsible for more than 99% of Campylobacterassociated gastroenteritis. The most prevalent S enterica serotypes are Typhi and Paratyphi, which trigger enteric fever. In the United States, the biggest burden of Salmonella infection is because of nontyphoidal serotypes, causing roughly 1. Four species most frequently related to illness are Shigella dysenteriae kind 1, Shigella flexneri, Shigella boydii, and Shigella sonnei. Poor sanitation or personal hygiene, insufficient water supply, malnutrition, and increased population density are related to an increased risk of Shigella gastroenteritis epidemics.
One early study with pertuzumab was stopped early because of cardiotoxicity that surpassed 50% at the time of study discontinuation gastritis diet ������� buy pariet 20 mg cheap. Drug interactions that improve systemic exposure to lapatinib might predispose patients to this rare complication gastritis diet fish generic 20 mg pariet with visa. These occur in about 40% of sufferers receiving trastuzumab through the preliminary infusion and customarily go unrecognized by patients symptoms of gastritis ulcer 20 mg pariet buy. Other infusion-related reactions with trastuzumab embrace mild nausea gastritis keeping me up at night discount 20 mg pariet with amex, pain at tumor sites, rigors, complications, dizziness, hypotension, rash, and asthenia, which are a lot less widespread. It is necessary to educate patients regarding the pulmonary reactions as a outcome of these might occur as a lot as 24 hours after the infusion and could be fatal if not promptly handled. Other antagonistic events associated with lapatinib include primarily rash and diarrhea. These adverse effects appear to be extra significant when mixed with chemotherapy (eg, capecitabine, paclitaxel) but are generally manageable with aggressive antidiarrheal remedy or dose reductions. Further analyses investigating what different predictive markers may be clinically useful are currently ongoing. Cell cycle regulators play an necessary role in drug resistance and a nice deal of investigation has occurred to elucidate specific pathways at work in breast cancers. Preclinical data with different palbociclib combos is promising, however remains investigational until further info on optimal timing and sequencing with specific agents is elucidated. Targeting tumor blood vessels is one other strategy to struggle breast cancer and probably reverse drug resistance. Endocrine Therapy the pharmacologic aim of endocrine therapy for breast most cancers is to either (a) decrease circulating ranges of estrogen or (b) prevent the results of estrogen on the breast cancer cell by blocking the hormone receptors or downregulating the presence of those receptors. Achievement of the first goal is decided by the menopausal status of the affected person, but achievement of the second goal is impartial of menopausal standing. Many endocrine therapies can be found to goal either pathway, and combinations of medication with differing mechanisms of action have also been investigated. These combos address de novo or acquired resistance with endocrine therapy and have demonstrated efficacy over single brokers in specific patient populations. Sequential use of single endocrine agents is frequent in the metastatic setting when a patient is progressing on one agent after experiencing an initial response. Responsive sufferers are often handled with a series of endocrine brokers, often over several years, earlier than chemotherapy is taken into account. In conjunction with biologic therapies, such sequential approaches are at present untested, but are being investigated and make logical sense given the indolent nature of those hormone-sensitive metastases. Data with lapatinib, everolimus, and palbociclib put these regimens squarely in the forefront in the battle against this disease. Myelosuppression, primarily neutropenia, is the dose-limiting toxicity seen with palbociclib and happens in 50% to 80% of sufferers. Interestingly, the implications of this appear to be minimal at least in the short-term knowledge currently obtainable. Rates of neutropenic fever are very low (less than 1%) and different infections have included only mild higher respiratory infections. Pulmonary embolism was seen in 1% to 4% of patients and other widespread unwanted side effects include mild fatigue and nausea. Other, confirmatory trials with palbociclib plus letrozole or exemestane are presently underway. Adverse occasions related to this mixture are extra outstanding than that seen with palbociclib and include metabolic syndrome, mucositis, fatigue and pneumonitis to name a few. The use of this mix after palbociclib/letrozole has not but been reported, however concerns concerning adjustments in resistance patterns exist and future trials addressing sequencing these regimens are needed to determine the optimum order of administration. Consequently, the choice of a specific endocrine remedy relies primarily on the mechanism of action, toxicity, and patient preference (Tables 128-9 and 128-10). In postmenopausal and castrated ladies, the principle source of estrogen is derived from the peripheral conversion of androstenedione, produced by the adrenal gland, into estrone and estradiol. Aromatase additionally catalyzes the conversion of androgens to estrogens in the ovary in premenopausal ladies and in extraglandular tissue, together with the breast and breast most cancers cells, in postmenopausal women. A major benefit of these specific compounds is their preferable toxicity profile, which consists mainly of bone loss and/or osteoporosis, delicate nausea, scorching flashes, arthralgias and/or myalgias, and delicate fatigue. Anastrozole and letrozole are nonsteroidal compounds that exhibit reversible, aggressive inhibition of aromatase. Exemestane is a steroidal compound that binds irreversibly to aromatase, forming a covalent bond. Exemestane does possess some androgenic properties at doses which are a lot larger than these used clinically and will have distinctive toxicities in some sufferers. Based on the obtainable proof, pre- or premenopausal women, whose ovaries are functioning, are inappropriate candidates for these therapies. Fulvestrant is currently the only pure antiestrogen commercially out there in the United States. The toxicities of tamoxifen are described in the Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy part earlier. This reaction is seen much less incessantly with the concurrent use of bisphosphonates on account of their inhibition of osteoclasts, subsequently stopping the release of calcium from the bone. It displays related efficacy and tolerability compared with tamoxifen within the metastatic setting. Cross-resistance to toremifene has been demonstrated in sufferers with tamoxifen-refractory illness. Details regarding its metabolism have gotten out there, however an absence of robust clinical knowledge to suggest it as a substitute for tamoxifen in settings the place there are concerns concerning drug interactions leaves its role in therapy unclear presently. Available information with raloxifene as a therapy for breast cancer present very low response rates and no significant clinical benefit. Consequently, use of this agent for breast cancer remedy ought to be discouraged. The use of raloxifene for breast cancer danger discount in high-risk postmenopausal women has been reported (see Prevention and Early Detection). Biologically, fulvestrant should produce similar outcomes in premenopausal women, but no data exist to affirm the protection or efficacy in premenopausal women in the presence of active ovarian function. In conjunction with ovarian suppression or ablation, fulvestrant is an applicable remedy in young ladies. This loading approach to dosing facilitates reaching steady-state plasma ranges more rapidly, allowing for a response to be seen inside a clinically relevant timeframe. To accomplish this dosing, two intramuscular injections of 5 mL every are administered simultaneously. Although cumbersome and slightly extra uncomfortable, sufferers seem to tolerate this higher dose relatively nicely, exhibiting similar toxicity profiles whatever the dose administered. Although the mix does appear to be nicely tolerated, the overall advantages (if any) seem to be modest, and sequential single agents are mostly administered within the palliative setting of metastatic disease. Adverse occasions associated to fulvestrant embody injection-site reactions, sizzling flashes, asthenia, and complications. Ovarian ablation (surgically or chemically) continues to be commonly utilized in some components of the United States and is considered by many specialists to be the endocrine therapy of alternative in premenopausal girls. The mortality rate with surgical oophorectomy is low, usually lower than 3% in appropriately chosen sufferers. While radiotherapeutic ablation of the ovaries is efficient, this strategy is typically not used in the United States. If the affected person tolerates this therapy, then an oophorectomy may be proposed as a everlasting therapeutic intervention. This flare response is similar to that seen with tamoxifen, and sufferers with high-volume, bulky illness must be monitored for increasing pain and hypercalcemia during the initiation period. Typically, these brokers are less properly tolerated than extra modern agents mentioned previously. The most typical facet impact of megestrol acetate is weight acquire, occurring in 20% to 50% of sufferers. Less widespread unwanted effects include areolar hyperpigmentation, breast tenderness and engorgement, vaginal discharge, incontinence, hot flashes, and phlebitis. All of the efficient androgens trigger masculinizing results, including hirsutism and zits, in additional than 50% of patients. The mechanism by which these agents exert a therapeutic impact in breast most cancers is unknown. However, these brokers might inhibit aromatase, amongst different pharmacologic effects that antagonize estrogen.
Proposed modifications to the Duke standards for the analysis of infective endocarditis gastritis otc pariet 20 mg order line. Temporal tendencies in infective endocarditis within the context of prophylaxis guideline modifications chronic gastritis grading buy discount pariet 20 mg on-line. Emergency surgical procedure for native mitral valve endocarditis: the influence of septic and cardiogenic shock gastritis diet food recipes buy discount pariet 20 mg line. Outcomes after surgical therapy of native and prosthetic valve infective endocarditis gastritis kaffee buy cheap pariet 20 mg line. Association between valvular surgical procedure and mortality among patients with infective endocarditis sophisticated by coronary heart failure. The want for a particular threat prediction system in native valve infective endocarditis surgical procedure. Surgical administration of endocarditis: the Society of Thoracic Surgeons medical apply guideline. Guidelines for the antibiotic remedy of endocarditis in adults: Report of the Working Party of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Clinical follow guidelines for the administration of candidiasis: 2009 replace by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. The role of aminoglycosides in combination with a beta-lactam for the remedy of bacterial endocarditis: A meta-analysis of comparative trials. Ceftriaxone once every day for four weeks compared with ceftriaxone plus gentamicin as soon as day by day for 2 weeks for treatment of endocarditis as a outcome of penicillinsusceptible streptococci. Combination antimicrobial remedy versus monotherapy: the contribution of meta-analyses. Treatment of streptococcal endocarditis with a single every day dose of ceftriaxone and netilmicin for 14 days: A potential multicenter examine. Effect of gentamicin dosing interval on therapy of viridans streptococcal experimental endocarditis with gentamicin plus penicillin. Endocarditis attributable to Staphylococcus aureus: A reappraisal of the epidemiologic, medical, and pathologic manifestations with analysis of things figuring out outcome. Prevalence of infective endocarditis in sufferers with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: the worth of screening with echocardiography. Clinical follow tips for the analysis and administration of intravascular catheter-related infection: 2009 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Initial low-dose gentamicin for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and endocarditis is nephrotoxic. Combination antimicrobial therapy for Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in sufferers hooked on parenteral medicine and in nonaddicts: A potential study. Combination therapy with an aminoglycoside for Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis and/or persistent bacteremia is associated with a decreased fee of recurrent bacteremia: A cohort research. Questionable history of immediate-type hypersensitivity to penicillin in staphylococcal endocarditis: Treatment based on skin-test results versus empirical different treatment-A determination analysis. Linezolid for the therapy of patients with endocarditis: A systematic evaluation of the published evidence. Daptomycin versus standard therapy for bacteremia and endocarditis brought on by Staphylococcus aureus. Daptomycin versus vancomycin for bloodstream infections as a result of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with a high vancomycin minimal inhibitory focus: A case management examine. Daptomycin within the treatment of patients with infective endocarditis: Experience from a registry. Daptomycin versus vancomycin plus gentamicin for therapy of bacteraemia and endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus: Subset evaluation of sufferers contaminated with methicillin-resistant isolates. Daptomycin for the remedy of gram-positive bacteremia and infective endocarditis: A retrospective case sequence of 31 sufferers. High-dose daptomycin for cardiac electronic device-related infective endocarditis. High-dose daptomycin for treatment of sophisticated gram-positive infections: A large, multicenter, retrospective examine. High-dose daptomycin remedy for left-sided infective endocarditis: A potential examine from the International Collaboration on Endocarditis. Right-sided Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in intravenous drug abusers: Two-week combination therapy. Short-course antibiotic remedy for right-sided endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus in injection drug customers. Antimicrobials for right-sided endocarditis in intravenous drug users: A systematic evaluation. Effectiveness of cloxacillin with and without gentamicin in short-term therapy for right-sided Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Intravenous followed by oral antimicrobial remedy for staphylococcal endocarditis. Treatment of right-sided Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in intravenous drug customers with ciprofloxacin and rifampicin. Oral antibiotic treatment of right-sided staphylococcal endocarditis in injection drug users: Prospective randomized comparability with parenteral therapy. Definition, medical profile, microbiological spectrum, and prognostic components of early-onset prosthetic valve endocarditis. Enterococcal endocarditis to begin with of the 21st century: Analysis from the International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study. Vancomycin-resistant enterococcal infections: Epidemiology, scientific manifestations, and optimal management. Treatment of experimental endocarditis because of Enterococcus faecalis using once-daily dosing routine of gentamicin plus simulated profiles of ampicillin in human serum. Pharmacodynamics of vancomycin and ampicillin alone and in combination with gentamicin once every day or thrice daily in opposition to Enterococcus faecalis in an in vitro an infection model. Once-versus thrice-daily netilmicin mixed with amoxicillin, penicillin, or vancomycin in opposition to Enterococcus faecalis in a pharmacodynamic in vitro mannequin. Importance of the aminoglycoside dosing regimen within the penicillin�netilmicin combination for therapy of Enterococcus faecalis-induced experimental endocarditis. Influence of gentamicin dosing interval on the efficacy of penicillin-containing regimens in experimental Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis. Enterococcal endocarditis in Sweden, 1995�1999: Can shorter therapy with aminoglycosides be used A new period for treating Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis: Ampicillin plus short-course gentamicin or ampicillin plus ceftriaxone: That is the question! Enterococcal endocarditis on native and prosthetic valves: A review of scientific and prognostic elements with emphasis on hospital-acquired infections as a serious determinant of consequence. Single center experience of a vancomycin resistant enterococcal endocarditis cohort. Combination remedy with ampicillin and daptomycin for therapy of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis. High-dose daptomycin for treatment of difficult gram-positive infections: A massive, multi-center, retrospective examine. Ampicillin enhances daptomycin- and cationic host protection peptide-mediated killing of ampicillin- and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium. Relapse of enterococcal prosthetic valve endocarditis with aortic root abscess following treatment with daptomycin in a patient not match for surgery. Current points within the diagnosis and administration of blood culture-negative infective and non-infective endocarditis. Outpatient parenteral antimicrobial remedy is protected and effective therapy of infective endocarditis: A retrospective cohort examine. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin in adult patients: A consensus review of the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Role of inflammatory markers within the prognosis and management of infective endocarditis. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in infective endocarditis: correlation with etiology and prognosis.
Tables 111-8 and 111-9 record drug dosing and monitoring recommendations for adult and pediatric patients gastritis diet �������� 20 mg pariet discount with mastercard. Because these pointers focus on common causes of endocarditis gastritis diet ������������� generic 20 mg pariet fast delivery, readers are referred to different references for extra in-depth discussion of unusually encountered organisms chronic atrophic gastritis definition pariet 20 mg purchase with amex. Haemophilus parainfluenzae gastritis remedies 20 mg pariet safe, Haemophilus aphrophilus, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Cardiobacterium hominis, Eikenella corrodens, and Kingella kingae. For some pathogens, similar to enterococci, the usage of synergistic antimicrobial mixtures (including an aminoglycoside) is crucial to get hold of a bactericidal impact. Streptococcal Endocarditis Streptococci are a standard reason for infective endocarditis, with most isolates being viridans group streptococci. Viridans group streptococci refers to a lot of different species, similar to Streptococcus sanguinis, Streptococcus oralis, Streptococcus salivarius, Streptococcus mutans, and Gemella morbillorum. Streptococcal endocarditis is often subacute, and the response to medical treatment is very good. A tolerant organism is inhibited but not killed by an antibiotic normally thought of bactericidal. Two single-drug regimens encompass high-dose parenteral penicillin G or ceftriaxone for four weeks. If quick term, 2 week remedy is desired, the rules counsel both high-dose parenteral penicillin G or ceftriaxone together with an aminoglycoside. Although streptomycin was listed in previous guidelines, gentamicin is the popular aminoglycoside as a result of serum drug concentrations are obtained simply, clinicians are extra conversant in its use, and the few strains of streptococci resistant to the results of streptomycin-penicillin remain vulnerable to gentamicin�penicillin. The choice of which routine to use depends on the perceived threat versus profit. For instance, a 2-week course of gentamicin in an aged affected person with renal impairment may be associated with ototoxicity, worsening renal function, or each. On the opposite hand, a 4-week course of penicillin alone generally entails larger expense, particularly if the patient stays in the hospital. Monotherapy with once-daily ceftriaxone provides ease of administration, facilitates house healthcare remedy, and may be cost-effective. No cardiovascular threat factors such as heart failure, aortic insufficiency, or conduction abnormalities three. Abiotrophia defectiva and Granulicatella species have nutritional deficiencies that hinder growth in routine tradition media. Some authors question the need for mixture remedy in comparatively resistant streptococci, emphasizing that few human knowledge suggest that sufferers with endocarditis caused by these organisms reply much less well to penicillin alone. Whether extended-interval aminoglycoside dosing has a task in infective endocarditis continues to be debated. At this time, knowledge support extended-interval dosing for the therapy of streptococcal infective endocarditis, and as in contrast with three-times-daily dosing this strategy may have greater efficacy. Both regimens had been secure and effective with similar clinical remedy rates at 3 months following treatment. Another consideration in staphylococcal endocarditis is that some organisms might exhibit tolerance to antibiotics. Many investigators have attempted to develop standards that identify the bacteremic patient likely to have infective endocarditis. In animal fashions of endocarditis, combos of penicillin with an aminoglycoside eradicate organisms from vegetations more rapidly than penicillins alone. During the previous decade, staphylococci extra commonly have turn into resistant to penicillinaseAlthough vancomycin remains to be the resistant penicillins (ie, methicillin-resistant S. Furthermore, though the data to be used of high-dose daptomycin (8-10 mg/kg/day) is restricted, the favorable drug tolerability and the potential for decreased treatment-emergent resistance may compel some prescribers to go for high-dose therapy in complicated cases. Yet the chance of staphylococcal endocarditis stays elevated for as a lot as 12 months after valve alternative. Valve dehiscence and incompetence may find yourself in acute coronary heart failure, and surgical procedure is usually a part of treatment. In common, those that require anticoagulation for a prosthetic valve should proceed the anticoagulant cautiously during endocarditis therapy, unless a contraindication to remedy exists. It is beneficial to maintain all anticoagulation for at least 2 weeks for sufferers with S. These organisms are often of low virulence but can become pathogens following healthcare intervention or in predisposed sufferers (most commonly elderly with comorbid situations similar to diabetes or need for hemodialysis). When used alone, penicillins are only bacteriostatic in opposition to enterococci, and thus combination therapy is at all times recommended for prone strains. However, in the presence of an agent that disrupts the cell wall such as penicillin, the aminoglycoside can achieve entry, connect to bacterial ribosomes, and trigger rapid cell dying. An aminoglycoside�vancomycin combination can also be synergistic towards enterococci and is appropriate therapy for the penicillin-allergic patient. Recent literature means that ampicillin plus ceftriaxone is as efficient as ampicillin plus gentamicin and should be thought-about as a remedy choice. Streptomycin and gentamicin have similar efficacy, but gentamicin is most popular because of the shortcoming to get hold of streptomycin serum levels in most labs. In the remedy of enterococcal endocarditis, comparatively low serum concentrations of aminoglycosides seem enough for successful therapy, corresponding to a gentamicin peak focus of roughly three to 4 mcg/mL (mg/L; 6. Although some knowledge support the usage of extended-interval aminoglycoside dosing for other types of endocarditis (ie, streptococci), the info are more vague regarding this technique in enterococcal infective endocarditis. Although most gentamicin-resistant enterococci are resistant to all aminoglycosides (including amikacin), 30% to 50% stay prone to streptomycin. The incidence of high-level aminoglycoside resistance is increasing; nevertheless, data on acceptable remedy are sparse, and therapeutic choices are few. If these organisms are found, use of vancomycin or ampicillin�sulbactam in combination with gentamicin ought to be considered. Guidelines suggest either linezolid or daptomycin, although the latter agent has produced conflicting outcomes. Ceftriaxone, or an alternate third- or fourth-generation cephalosporin, is the popular treatment generally. Ciprofloxacin could also be thought-about as an possibility if an allergy to cephalosporins is current (see Table 111-7). Less Common Types of Infective Endocarditis Atypical Microorganisms Endocarditis brought on by organisms, similar to Bartonella; Coxiella burnetii; Brucella, Candida, and Aspergillus spp. Medical remedy for infective endocarditis brought on by these organisms is usually unsuccessful. Because these infections occur infrequently, scant scientific information are available to make strong treatment suggestions. It is a common explanation for infective endocarditis in certain areas of the world the place goat, cattle, and sheep farming are widespread. The most favorable remedy for Q fever is unknown however might embody doxycycline with hydroxychloroquine, trimethoprim�sulfamethoxazole, rifampin, or fluoroquinolones for a minimum of 18 months. Humans are infected by this organism after ingesting infected unpasteurized milk or undercooked meat, inhaling infectious aerosols, or contacting infected tissues. This type of infective endocarditis is extra widespread in veterinarians and livestock handlers. Cure requires valve alternative and antimicrobial brokers including doxycycline with streptomycin or gentamicin or doxycycline with trimethoprim�sulfamethoxazole or rifampin for an extended period (6 weeks to months). When blood cultures from sufferers suspected of infective endocarditis present no growth after 48 to seventy two hours, cultures must be held for as much as a month and particular testing strategies (eg, serological evaluation, polymerase chain reaction) pursued to detect fastidious or nonbacterial organisms. Selection of remedy can be tough, balancing the need to cover all probably organisms against potential toxic drug effects (eg, aminoglycosides). Antimicrobial choice should involve session with an infectious disease specialist. The empirical approaches for culture-negative infective endocarditis highlight the necessity for proper collection and monitoring of blood cultures and an in depth treatment history. In select cases, abbreviated and/or outpatient, oral antimicrobial therapy might appreciably reduce the value of care. The initiation of outpatient parenteral antibiotics must be thought of early within the therapy of infective endocarditis, after the patient is secure clinically and responds favorably to initial antibiotics. Advances in technology allow for the outpatient administration of complex antibiotic regimens that considerably scale back the worth of therapy. Simple regimens, such as single every day doses of ceftriaxone for streptococcal infective endocarditis, are significantly enticing.
Discount 20 mg pariet free shipping. This Doctor Shares The Fastest Way To Lose Weight | TRY IT FOR 3 DAYS!.