
Sildigra
| Contato
Página Inicial
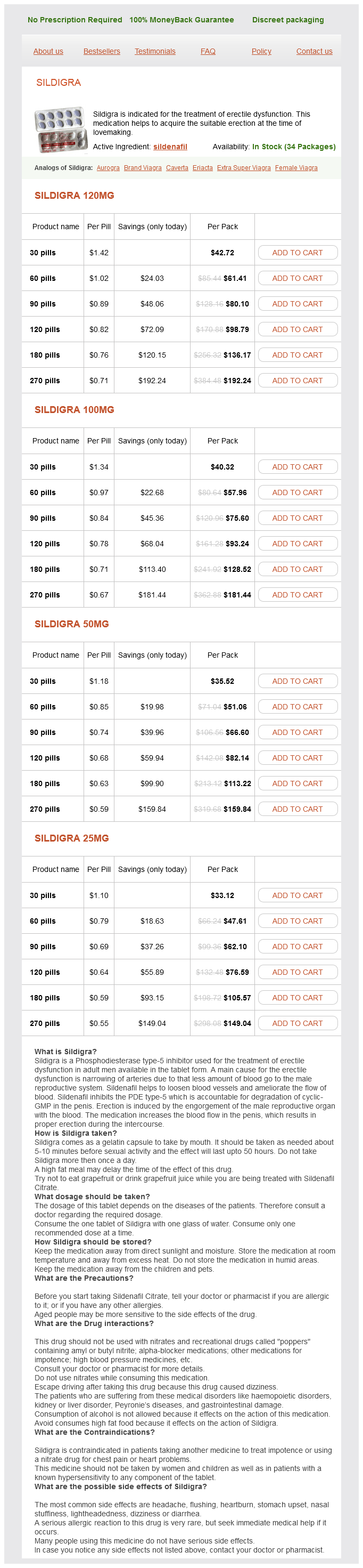
"Sildigra 25 mg for sale, impotence natural treatment clary sage".
A. Kaffu, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Medical Instructor, Louisiana State University
The Relevance of a Novel Quantitative Assay to Detect as a lot as impotence venous leakage ligation sildigra 50 mg buy overnight delivery 40 Major Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotypes Directly in Clinical Nasopharyngeal and Blood Specimens erectile dysfunction doctor sydney sildigra 25 mg overnight delivery. Comprehensive molecular testing for respiratory pathogens in community-acquired pneumonia erectile dysfunction first time discount sildigra 50 mg with visa. Streptococcus pneumoniae infections of the feminine genital tract and within the new child baby erectile dysfunction organic buy sildigra 25 mg on-line. Septic arthritis in the adult brought on by Streptococcus pneumoniae: a report of 4 instances and review of the literature. Streptococcus pneumoniae spinal infection in Nottingham, United Kingdom: not a uncommon occasion. Pyogenic mind abscess caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae: case report and evaluation. Pneumococcal soft-tissue infections: possible association with connective tissue diseases. Bacteremic pneumococcal cellulitis in contrast with bacteremic cellulitis brought on by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. Unusual manifestations of pneumococcal infection in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals: the previous revisited. Prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus infection, mortality price, and serogroup distribution among sufferers with pneumococcal bacteremia at Denver General Hospital, 1984-1994. The position of an infection in cardiovascular disease: more support however many questions stay. Streptococcus pneumoniae translocates into the myocardium and forms unique microlesions that disrupt cardiac operate. A fresh look at the definition of susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae to beta-lactam antibiotics. Rationale for revised penicillin susceptibility breakpoints versus Streptococcus pneumoniae: coping with antimicrobial susceptibility in an era of resistance. Alterations in penicillin-binding protein 2B from penicillin-resistant wild-type strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Genetic variety of penicillin-binding protein 2B and 2X genes from Streptococcus pneumoniae in South Africa. Identification of a quantity of clones of extended-spectrum cephalosporinresistant Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in the United States. Penicillinresistant Streptococcus pneumoniae strains recovered in Houston: identification and molecular characterization of multiple clones. Evidence for the introduction of a multiresistant clone of serotype 6B Streptococcus pneumoniae from Spain to Iceland within the late l980s. The molecular epidemiology of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae within the United States, 1994-2000. Evidence of a clonal growth of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A in adults as in kids assessed by the DiversiLab(R) system. Outpatient antibiotic use and prevalence of antibiotic-resistant pneumococci in France and Germany: a sociocultural perspective. Decreased susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae to fluoroquinolones in Canada. Invasive pneumococcal disease among the many aged residing in long-term care amenities and community-living elderly. Persistence and complex evolution of fluoroquinolone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae clone. Failure of macrolide antibiotic therapy in patients with bacteremia due to erythromycin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. A prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Beta-Lactam monotherapy vs beta-lactam-macrolide combination treatment in reasonably severe community-acquired pneumonia: a randomized noninferiority trial. Beta-Lactam/macrolide dual therapy versus beta-lactam monotherapy for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in adults: a systematic evaluate and meta-analysis. Beta-lactam plus macrolides or beta-lactam alone for community-acquired pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Immunomodulatory agents within the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia: a scientific review. Optimizing therapy for communityacquired pneumonia with the goal of rapid resolution of sickness. Combined results of antenatal receipt of influenza vaccine by moms and pneumococcal conjugate vaccine receipt by infants: results from a randomized, blinded, managed trial. Prolonged and preferential production of polymeric immunoglobulin A in response to Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular polysaccharides. Revaccination with the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine in middle-aged and aged persons beforehand handled for pneumonia. Reduction in practical antibody activity towards Streptococcus pneumoniae in vaccinated aged individuals extremely correlates with decreased IgG antibody avidity. Immune response to pneumococcal polysaccharides 4 and 14 in elderly and younger adults: analysis of the variable heavy chain repertoire. Revaccination with a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine induces elevated and persistent functional antibody responses in adults aged 65 > or = years. Pneumococcal vaccine prevents demise from acute lower-respiratory-tract infections in Papua New Guinean youngsters. Efficacy of nine-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in opposition to pneumonia and invasive pneumococcal illness within the Gambia: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Efficacy and safety of seven-valent conjugate pneumococcal vaccine in American Indian kids: group randomised trial. Safety and efficacy of the seven-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: evidence from Northern California. Long-term immunogenicity and efficacy of a 9-valent conjugate pneumococcal vaccine in human immunodeficient virus infected and non-infected children in the absence of a booster dose of vaccine. The impact of 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on invasive pneumococcal illness: a literature review. Effectiveness of heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children younger than 5 years of age for prevention of pneumonia. Pneumococcal vaccination among Medicare beneficiaries occurring after the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices advice for routine use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for adults aged >/=65 years. Effectiveness of pneumococcal vaccination for aged people in Catalonia, Spain: a case-control examine. Surveillance of Pneumococcal Infection for Field Trials of Polyvalent Pneumococcal Vaccines. Clinical efficacy of pneumococcal vaccine within the aged: a randomized, single-blind population-based trial. Randomised trial of 23-valent pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide vaccine in prevention of pneumonia in middle-aged and elderly people. Incremental effectiveness of pneumococcal vaccine on simultaneously administered influenza vaccine in stopping pneumonia and pneumococcal pneumonia amongst persons aged sixty five years or older. Clinical trial of an antipneumococcal vaccine in elderly subjects dwelling in establishments. Changing epidemiology of invasive pneumococcal disease amongst older adults within the era of pediatric pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Licensure of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine for adults aged 50 years and older. Effect of use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in youngsters on invasive pneumococcal illness in youngsters 347. Bacterial pneumonia vaccines and childhood pneumonia: are we profitable, refining, or redefining Effect of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection on the antibody response to a glycoprotein conjugate pneumococcal vaccine: results from a randomized trial. Reimmunization with 23-valent pneumococcal vaccine for patients contaminated with human immunodeficiency virus type 1: scientific, immunologic, and virologic responses. Association of invasive pneumococcal illness with season, atmospheric circumstances, air pollution and the isolation of respiratory viruses. Specifications Manual for National Hospital Quality Measures � Pneumococcal Immunization 2015. Clinical Presentations Colonization, Virulence, and Genomics Therapy and Antimicrobial Resistance � Although most E. The first scientific and pathologic description of an enterococcal an infection was published the identical year (1899)2 and concerned a affected person admitted to "Dr.
Diseases
- Rickets
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Pure red cell aplasia
- Entomophthoramycosis
- Lysosomal alpha-D-mannosidase deficiency
- Tricyclic antidepressant overdose
- Ceramidase deficiency
- Lichen spinulosus
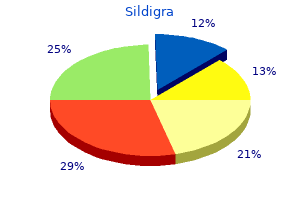
Development and analysis of an IgM seize enzyme immunoassay for prognosis of current Norwalk virus infection impotence and age cheap sildigra 25 mg mastercard. Homotypic and heterotypic IgG and IgM antibody responses in adults infected with small round structured viruses causes of erectile dysfunction in youth sildigra 100 mg discount free shipping. Correlation of patient immune responses with genetically characterized small round-structured viruses involved in outbreaks of nonbacterial acute gastroenteritis in the United States erectile dysfunction pump amazon generic sildigra 25 mg otc, 1990 to 1995 erectile dysfunction hernia sildigra 100 mg buy line. Increased jejunal IgA synthesis in vitro throughout acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. Heterotypic humoral and cellular immune responses following Norwalk virus an infection. Acquisition of serum antibody to Norwalk virus and rotavirus and relation to diarrhea in a longitudinal examine of younger kids in rural Bangladesh. Evidence of immunity induced by naturally acquired rotavirus and Norwalk virus an infection on two remote Panamanian islands. High serum levels of norovirus genotype-specific blocking antibodies correlate with safety from an infection in youngsters. Management of hospital outbreaks of gastro-enteritis as a end result of small round-structured viruses. Surveillance for outbreaks of gastroenteritis in long-term care amenities, Australia, 2002-2008. Visualization of 27 nm particle related infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. Detection of Norwalk virus in stool specimens by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain response and nonradioactive oligoprobes. Sensitive detection and differentiation of Sapporo virus, a member of the household Caliciviridae, by commonplace and booster nested polymerase chain reaction. Identification of Norwalk virus in artificially seeded shellfish and selected meals. Outbreak of viral gastroenteritis because of a contaminated well: worldwide penalties. Detection and evaluation of a small round-structured virus pressure in oysters implicated in an outbreak of acute gastroenteritis. European multicenter evaluation of business enzyme immunoassays for detecting norovirus antigen in fecal samples. Detection of Norwalk virus and other genogroup 1 human caliciviruses by a monoclonal antibody, recombinantantigen-based immunoglobulin M capture enzyme immunoassay. Inhibition of human norovirus by a viral polymerase inhibitor within the B cell tradition system and within the mouse mannequin. Recombinant Norwalk virus-like particles given orally to volunteers: phase I examine. A novel intramuscular bivalent norovirus-like particle vaccine candidate-reactogenicity, safety, and immunogenicity in a phase 1 trial in healthy adults. Human immune responses to a novel Norwalk virus vaccine delivered in transgenic potatoes. Chapter 176 Noroviruses and Sapoviruses (Caliciviruses) 177 Definition Astroviruses and Picobirnaviruses Raphael Dolin and John J. Therapy Epidemiology Clinical Manifestations � Astroviruses are worldwide in distribution; they cause illness most regularly in young youngsters, however can also cause gastroenteritis in adults and in immunosuppressed patients. Illness may be somewhat much less extreme than that seen with noroviruses and rotaviruses. Astroviruses are also established as important causes of gastroenteritis, albeit substantially less frequently than the aforementioned viruses. Picobirnaviruses are extra lately described viruses that have a potential, although not but established, position as agents of gastroenteritis. Analysis of virus grown in cell tradition has shown the virus particles to exhibit a layer of 41-nm spikelike projections on the floor. They have been estimated to cause 2% to 9% of circumstances of nonbacterial gastroenteritis. The virions are nonenveloped, display icosahedral symmetry, and are about 28 to 30 nm in diameter. Transmission is presumably by the fecal-oral route, and astrovirus an infection has been induced by oral administration of stool filtrates to regular volunteers. Astrovirus infections in animals have been related to small intestinal villus shortening and with mild inflammatory infiltrates in the lamina propria. As famous previously, stool filtrates that contain astroviruses can infect volunteers after oral administration, however compared to noroviruses, astroviruses containing filtrates appear to induce sickness less incessantly when administered to wholesome adults. The incubation period of sickness has been estimated to be three to 4 days, and within the absence of coexisting pathogens, illness manifestations normally last 5 days or much less, with often longer period. Epidemiologic observations recommend that an infection leads to no much less than short-term safety against reinfection with the identical serotype. In distinction to caliciviruses, astroviruses are sometimes shed in massive amounts in stool and can be readily detected with electron microscopy even without immune aggregation. Detection and transmission of 30 nm virus particles [astroviruses] within the faeces of lambs with diarrhoea. Measures to avoid person-to-person transmission from lively instances also seem prudent. Virus-like particles of astroviruses have been generated,73 elevating the chance of vaccine approaches at some point in the future. The genomes have been characterised into two varieties or profiles76,77-a massive profile (2. Prevalence of human astrovirus genotypes associated with acute gastroenteritis among children in B�lem, Brazil. Diversity of human astrovirus genotypes circulating in youngsters with acute gastroenteritis in Thailand during 2000-2011. Prevalence of antibodies to astrovirus sorts 1 and three in kids and adolescents in Norfolk, Virginia. Etiology and consequence of diarrhea after marrow transplantation: a potential research. Enteric virus infections and diarrhea in healthy and human immunodeficiency virus-infected youngsters. Persistent gastroenteritis in children infected with astrovirus: affiliation with serotype-3 strains. Prevalence of enteric viruses in human immunodeficiency virus seropositive sufferers in Venezuela. Astrovirus an infection in hospitalized infants with severe mixed immunodeficiency after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Two instances of huge genome profile picobirnavirus prevalence in Argentinian infants with diarrhea over a 26-year interval (1977-2002). Astrovirus infections in people and animals-molecular biology, genetic range, and interspecies transmissions. Antigen characterization of cell-cultivated astrovirus serotypes and growth of astrovirus-specific monoclonal antibodies. Prevalence of human astrovirus serotypes within the Oxford region 1976-1992, with evidence for 2 new serotypes. Typing of human astroviruses from scientific isolates by enzyme immunoassay and nucleotide sequencing. Characterisation of a South African human astrovirus as sort eight by antigenic and genetic analyses. Structural requirements of astrovirus virus-like particles assembled in insect cells. Characterization and seroepidemiology of a kind 5 astrovirus associated with an outbreak of gastroenteritis in Marin County, California. Electron microscopic reporting of gastrointestinal viruses in the United Kingdom, 1985-1987. Capsid protein composition of reference strains and wild isolates of human astroviruses.
Ajagandha (Ashwagandha). Sildigra.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Tumors, tuberculosis, liver problems, swelling (inflammation), ulcerations, stress, inducing vomiting, altering immune function, improving aging effects, fibromyalgia, and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Ashwagandha?
- Dosing considerations for Ashwagandha.
- How does Ashwagandha work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96916
Hepatitis A outbreak amongst adults with developmental disabilities in group homes�Michigan erectile dysfunction guide sildigra 25 mg cheap on-line, 2013 boyfriend erectile dysfunction young 120 mg sildigra purchase with amex. Evidence for 2 distinctive scientific can erectile dysfunction cause low sperm count purchase 50 mg sildigra mastercard, epidemiological impotence at 19 25 mg sildigra cheap amex, and immunological forms of infection. Hepatitis A virus replication in tamarins and host immune response in relation to pathogenesis of liver cell injury. Localization of hepatitis A antigen in marmoset organs during acute infection with hepatitis A virus. Pathogenetic features of hepatitis A virus an infection in enterally inoculated marmosets. Coproantibodies in hepatitis A: detection by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immune electron microscopy. Human lymphocyte responses to hepatitis A virus-infected cells: interferon manufacturing and lysis of infected cells. Identification of virus components in circulating immune complexes isolated throughout hepatitis A virus infection. Frequency of sickness related to epidemic hepatitis A virus infections in adults. Hepatitis A in Greenland: significance of specific antibody testing in epidemiologic surveillance. Clinical manifestations of hepatitis A: current experience in a neighborhood educating hospital. Declining hepatitis A mortality in the United States through the era of hepatitis A vaccination. Serious hepatitis A: an analysis of patients hospitalized throughout an urban epidemic within the United States. Etiology, incidence and outcomes of acute hepatic failure in 0-18 12 months old Filipino children. Photo-accentuated eruption and vascular deposits of immunoglobulin a related to hepatitis A virus infection. Vasculitis and cryoglobulinemia related to persisting cholestatic hepatitis A virus an infection. Trends in disease and problems of hepatitis A virus an infection in the United States, 1999-2011: a new concern for adults. Clinical recurrence of hepatitis A following liver transplantation for acute liver failure. Persistence of hepatitis A virus in fulminant hepatitis and after liver transplantation. Serum immunoglobulin levels in hepatitis non-A, non-B: a comparison with hepatitis A and B. Window period of anti-hepatitis A virus immunoglobulin M antibodies in diagnosing acute hepatitis A. Optimal time for repeating the IgM anti-hepatitis A virus antibody check in acute hepatitis A sufferers with a negative preliminary test. Detection of immunoglobulin M antibody to hepatitis A virus in Alaska residents with out different evidence of hepatitis. Antibody response to nonstructural proteins of hepatitis A virus following an infection. Host antibody response to viral structural and nonstructural proteins after hepatitis A virus an infection. Simple technique of concentrating enteroviruses and hepatitis A virus from sewage and ocean water for speedy detection by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain response. Light microscopic findings of liver biopsy specimens from patients with hepatitis type a and comparison with type B. Liver biopsy features of acute hepatitis C in contrast with hepatitis A, B, and non-A, non-B, non-C. Localization of hepatitis A antigen in liver tissue by peroxidaseconjugated antibody methodology: light and electron microscopic studies. The position of natural killer cells and lymphokine activated killer cells within the pathogenesis of hepatic injury in hepatitis A [corrected]. An outbreak of hepatitis A amongst health care staff: threat components for transmission. A nosocomial and occupational cluster of hepatitis A virus an infection in a pediatric ward. Chemical, medical, and immunological research on the merchandise of human plasma fractionation. Efficacy of different doses of immune serum globulin in the prevention of hepatitis A: a three-year prospective study. Subclinical an infection with hepatitis A in peace corps volunteers following immune globulin prophylaxis. Comparison of two a lot of immune serum globulin for prophylaxis of infectious hepatitis. Immunopotentiating reconstituted influenza virus virosome vaccine supply system for immunization towards hepatitis A. Clinical and laboratory observations following oral or intramuscular administration of a live attenuated hepatitis A vaccine candidate. A controlled trial of a formalin-inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in healthy youngsters. Anatomy of a trial: a historic view of the monroe inactivated hepatitis A protective efficacy trial. Immunization against hepatitis A within the first 12 months of life: priming despite the presence of maternal antibody. Single and booster dose responses to an inactivated hepatitis A virus vaccine: comparability with immune serum globulin prophylaxis. Single dose inactivated hepatitis A vaccine: rationale and scientific evaluation of the protection and immunogenicity. Time course of hepatitis A virus antibody titer after active and passive immunization. Current seroepidemiological status of hepatitis A with a comparability of antibody titers after an infection and vaccination. Immunoprecipitation and virus neutralization assays demonstrate qualitative differences between protecting antibody responses to inactivated hepatitis A vaccine and passive immunization with immune globulin. Inactivated hepatitis A vaccine: lively and passive immunoprophylaxis in chimpanzees. Long-term immunogenicity of hepatitis A virus vaccine in Alaska 17 years after initial childhood sequence. Safety and immunogenicity of a live attenuated hepatitis A virus vaccine in seronegative volunteers. Rapid completion of the replication cycle of hepatitis A virus subsequent to reversal of guanidine inhibition. Testing for antibody to hepatitis A to decrease the worth of hepatitis A prophylaxis with immune globulin or hepatitis A vaccines. Long-term trends in hepatitis A incidence following the inclusion of hepatitis A vaccine in the routine nationwide immunization program. Impact of a statewide childhood vaccine program in controlling hepatitis A virus infections in Alaska. Era of vaccination heralds a decline in incidence of hepatitis A in high-risk teams in China. The impression of a national routine immunisation programme initiated in 1999 on hepatitis A incidence in Israel, 1993 to 2012. Meeting of the strategic advisory group of specialists on immunization, November 2011- conclusions and recommendations. Seroprevalence and susceptibility to hepatitis A within the European union and European economic area: a systematic evaluation. Considerations on the current universal vaccination coverage in opposition to hepatitis A in Greece after latest outbreaks. Economic evaluation of the single-dose immunization strategy towards hepatitis A in Argentina. A cost-effectiveness analysis of universal childhood hepatitis A vaccination in China. Universal vaccination of children against hepatitis A in Chile: a cost-effectiveness examine.