
Ventolin
| Contato
Página Inicial

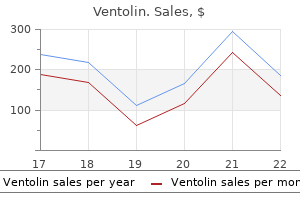
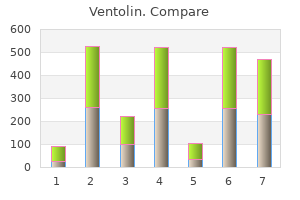
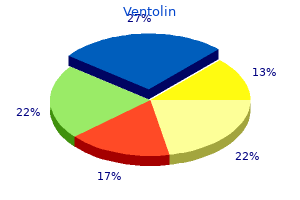
"Ventolin 100 mcg cheap mastercard, asthma symptoms in 9 year old".
X. Tragak, MD
Medical Instructor, Tulane University School of Medicine
This ends in rapid drug absorption directly into the blood capillaries under the tongue asthma definition volatile ventolin 100 mcg buy free shipping. Thus asthma definition purchase ventolin 100 mcg without prescription, whilst systemic results are generally obtained following oral and parenteral drug administration asthma symptoms 9dpo order 100 mcg ventolin fast delivery, other routes can be used as the drug and state of affairs demand asthma treatment during pregnancy proven 100 mcg ventolin. Local effects are usually restricted to dosage forms applied immediately, corresponding to those applied to the pores and skin, ear, eye, throat and lungs. Some drugs could additionally be nicely absorbed by one route but not by one other and must subsequently be thought-about individually. Infants generally choose liquid dosage varieties, normally options and mixtures, given orally. Children can have problem in swallowing solid dosage varieties, and for that reason many oral preparations are ready as pleasantly flavoured syrups or mixtures. Adults typically favor solid dosage varieties, primarily because of their comfort. However, alternative liquid preparations are normally available for these unable to take tablets and capsules. Alternative technologies for preparing particles with the required properties � crystal engineering � present new alternatives. Supercritical fluid processing using carbon dioxide as a solvent or antisolvent is one such method, allowing fine-tuning of crystal properties and particle design and fabrication. Undoubtedly, these new technologies and others, in addition to subtle formulations, will be required to deal with the arrival of gene therapy and the necessity to ship such labile macromolecules to particular targets and cells in the physique. Interest can be more likely to be directed to particular person patient necessities corresponding to age, weight and physiological and metabolic components, options which might affect drug absorption and bioavailability, and the increasing application of diagnostic brokers will play a key role on this space. This subject incorporates (1) using in silico procedures to predict drug substance properties and (2) decision making and optimization tools, such as experimental design, synthetic intelligence and neural computing. All these can facilitate quicker and rational design of formulations and manufacturing processes. Summary this text has demonstrated that the formulation of medicine into dosage types requires the interpretation and application of a broad range of information and data from several examine areas. Whilst the physical and chemical properties of medication and additives must be understood, the factors influencing drug absorption and the requirements of the disease to be treated also need to be taken into consideration when potential supply routes are being recognized. The formulation and related preparation of dosage types demand the best requirements, with careful examination, analysis and evaluation of wide-ranging info by pharmaceutical scientists to obtain the target of making high-quality, protected and efficacious dosage types. Crystal engineering of lively pharmaceutical components to improve solubility and dissolution price. Crystallisation processes in computing and formulation pharmaceutical expertise and drug optimization. This article discusses the principles underlying the formation of solutions from a solute and a solvent and the factors that affect the rate and extent of the dissolution process. This process will be discussed particularly in the context of a strong dissolving in a liquid as that is the scenario more than likely to be encountered in the formation of a drug resolution, both during manufacturing or throughout drug supply. Because of the variety of rules and properties that need to be thought-about, the contents of every of those chapters should only be thought to be introductions to the assorted topics. The pupil is encouraged, subsequently, to refer to the bibliography at the end of every chapter to augment the current contents. The authors use numerous pharmaceutical examples to assist the understanding of physicochemical rules. Definition of phrases this text will begin by clarifying and defining a variety of the key terms relevant to solutions. Since the above definitions are common ones, they may be applied to all kinds of solution involving any of the three states of matter (gas, liquid, solid) dissolved in any of the three states of matter, i. Solution, solubility and dissolution A solution could additionally be defined as a combination of two or extra parts that form a single section which is homogeneous down to the molecular level. The element that determines the part of the answer is termed the solvent; it usually (but not necessarily) constitutes the largest proportion of the system. The different components are termed solutes, and these are dispersed as molecules or ions throughout the solvent, i. The switch of molecules or ions from a solid state into solution is known as dissolution. Fundamentally, this course of is controlled by the relative affinity between the molecules of the strong substance and those of the solvent. The extent to which the dissolution proceeds beneath a given set of experimental conditions is referred to as the solubility of the solute within the solvent. The solubility of a substance is the quantity of it that has passed into solution when equilibrium is established between the solute in answer and the surplus (undissolved) substance. A answer with a focus lower than that at equilibrium is said to be subsaturated. Solutions with a concentration greater than that at equilibrium could be obtained in certain situations; these are known as supersaturated options (see Chapter eight for further information). Process of dissolution Dissolution mechanisms nearly all of medicine are crystalline solids. Liquid, semisolid and amorphous solid medication do exist however these are within the minority. In addition, to simplify the discussion, will in all probability be assumed that the drug is molecular in nature. Similarly, to avoid undue complication within the explanations that comply with, it could be assumed that most stable crystalline supplies, whether medication or excipients, will dissolve in an identical method. The dissolution of a strong in a liquid could also be regarded as being composed of two consecutive phases. First is an interfacial reaction that results in the liberation of solute molecules from the solid phase to the liquid part. This involves a part change in order that molecules of the stable turn out to be molecules of the solute in the solvent during which the crystal is dissolving. After this, the solute molecules must migrate via the boundary layer surrounding the crystal to the bulk of solution. Diffusion via the boundary layer this step entails transport of the drug molecules away from the solid�liquid interface into the bulk of the liquid part underneath the affect of diffusion or convection. Boundary layers are static or slowmoving layers of liquid that surround all stable surfaces that are surrounded by liquid (discussed additional later on this chapter and in Chapter 6). Mass switch occurs more slowly (usually by diffusion; see Chapter 3) via these static or slow-moving layers. These layers inhibit the movement of solute molecules from the surface of the stable to the majority of the solution. The means of the removing of drug molecules from a strong, and their replacement by solvent molecules, is decided by the relative affinity of the assorted molecules involved. The solvent/solute forces of attraction should overcome the cohesive forces of attraction between the molecules of the strong. Energy/work adjustments during dissolution For the process of dissolution to occur spontaneously at a continuing pressure, the accompanying change in free enthalpy. The free power (G) is a measure of the power obtainable to the system to perform work. Its worth decreases during a spontaneously occurring course of until an equilibrium place is reached when no extra power can be made out there, i. On leaving the strong surface, the drug molecule must become integrated in the liquid section, i. Dissolution charges of solids in liquids Like any reaction that includes consecutive stages, the general fee of dissolution might be dependent on which of the steps beforehand described is the slowest (the rate-determining or rate-limiting step). In dissolution, the interfacial step (as described earlier) is nearly always virtually instantaneous, and so the rate of dissolution will most frequently be decided by the rate of the slower step of diffusion of dissolved solute through the static boundary layer of liquid that exists at a solid�liquid interface. The vitality distinction between the two concentration states supplies the driving force for the diffusion. In the current context, C is the difference within the focus of the answer on the strong floor (C1) and the majority of the answer (C2). If C2 is lower than saturation, the molecules will move from the stable to the majority of solution (as during dissolution). If the concentration of the majority (C2) is greater than saturation, the answer is referred to as being supersaturated and motion of solid molecules will be within the course of bulk resolution to the floor (as occurs during crystallization). Noyes�Whitney equation An equation known as the Noyes�Whitney equation was developed to define the dissolution from a single spherical particle. This equation has found great usefulness in the estimation or prediction of the dissolution fee of pharmaceutical particles.
These are hooked up to perineal body anteriorly and to coccyx by way of anococcygeal ligament posteriorly asthma treatments generic ventolin 100 mcg with visa. Lower fibres lie under the level of inner anal sphincter and are separated from anal epithelium by submucosa asthma definition wikipedia ventolin 100 mcg generic online. In addition asthma treatment steps cheap ventolin 100 mcg with amex, in females asthma treatment asthma medications ventolin 100 mcg discount with amex, transverse perinei and bulbospongiosus fuse with exterior anal sphincter in lower a half of perineum. Conjoint Longitudinal Coat It is about eight mm long and is lined by true skin containing sebaceous glands. The epithelium of the lowest part resembles that of pigmented pores and skin during which sebaceous glands, sweat glands and hair are present. Musculature of the Anal Canal Anal Sphincters It is shaped by fusion of the puborectalis with the longitudinal muscle coat of the rectum on the anorectal junction. When traced downwards, it turns into fibroelastic and at the degree of the white line, it breaks up into a number of fibroelastic septa which spread out fan-wise, pierce the subcutaneous a half of the exterior sphincter, and are attached to the pores and skin across the anus known as as corrugator cutis ani. The most medial septum types, the anal intermuscular septum, which is hooked up to the white line. It is formed by the fusion of the puborectalis, uppermost fibres of exterior sphincter and the interior sphincter. It incorporates the decrease fibres of external sphincter, the exterior rectal venous plexus, and the terminal branches of the inferior rectal vessels and nerves. It drains mainly into the superior rectal vein, but communicates freely with the external plexus and thus with the middle and inferior rectal veins. The inner plexus is, due to this fact, an important web site of communication between the portal and systemic veins. The lower part of the exterior plexus is drained by the inferior rectal vein into inner pudendal vein; the center part by middle rectal vein into inside iliac vein; and the higher half by superior rectal vein which continues because the inferior mesenteric vein. They communicate with the interior rectal plexus and with the inferior rectal veins. Excessive straining through the defaecation may rupture considered one of these veins, forming a subcutaneous perianal haematoma often identified as external piles. Nerve Supply 1 Above the pectinate line, the anal canal is equipped by autonomic nerves-both sympathetic (inferior hypogastric plexus-L1, 2) and parasympathetic (pelvic splanchnic-S2, 3, 4). The exterior sphincter is provided by the inferior rectal nerve and by the perineal branch of the fourth sacral nerve. Identify the thickened a half of the round muscle layer forming the inner sphincter of the anus. Locate the exterior anal sphincter with its elements, partly overlapping the interior sphincter. Poor support to veins from the surrounding loose connective tissue, so that the veins are less able to resisting increased blood pressure. Compression of the veins on the sites where they pierce the muscular coat of the rectum. Direct transmission of the increased portal stress on the portosystemic communications. For these reasons, the event of piles is favoured by constipation, extended standing, excessive straining at stool, and portal hypertension. External piles or false piles occur beneath the pectinate line and are, therefore, very painful. Fissure in ano: Anal fissure is caused by the rupture of one of the anal valves, usually by the passage of dry exhausting stool in a constipated particular person. Because of the involvement of skin, the situation is extremely painful and is associated with marked spasm of the anal sphincters. Fistula in ano is caused by spontaneous rupture of an abscess around the anus or may follow surgical drainage of the abscess. Most of these abscesses are formed by the small vestigial glands opening into the anal sinuses. Such an anorectal abscess tends to track in numerous directions and should open medially into the anal sinus, laterally into the ischioanal fossa, inferiorly at the surface, and superiorly into the rectum. The fistula is alleged to be complete when it opens both internally into the lumen of the gut and externally at the surface. Nerve supply Hindgut (endoderm) Simple columnar epithelium squamous Mainly superior rectal Chiefly into portal vein Internal iliac lymph nodes Autonomic nerves: Sympathetic (L1, 2) Parasympathetic (S2, 3, 4) Ischaemia, distension and spasm Internal painless piles Lower part (15 + eight mm) Proctodaeum (ectoderm) Stratified columnar and stratified Mainly inferior rectal Chiefly into systemic veins Superficial inguinal lymph nodes Inferior rectal (somatic) nerves (S2, three, 4) 7. Most of the anorectal malformations are caused by irregular partitioning of the cloaca by the urorectal septum. Primitive anorectal canal varieties the decrease a part of rectum and proximal a half of anal canal. Lower part, beneath the third transverse fold, is shaped from the dorsal part of the cloaca. Lower half under the pectinate line (lower 15 + 8 mm) is formed from ectodermal invagination, i. The epithelium lining of higher 15 mm is straightforward or stratified columnar, whereas that of center 15 mm is stratified squamous without any sweat gland or sebaceous gland or hair follicle. The epithelium of lowest eight mm resembles that of true skin with sweat and sebaceous glands and hair follicles. The thick internal circular layer covers the higher threefourths of anal canal to form the inner anal sphincter. These are as a result of prolapse of the mucous membrane containing the tributaries of internal rectal venous plexus draining blood from the anal canal. Since these comprise varicose venous radicles, these rupture because of strain, leading to painless bleeding throughout defaecation. These kinds of piles might outcome from irregular bowel habits, chronic constipation, an extreme amount of straining throughout defaecation and in addition in case of portal hypertension ensuing due to liver cirrhosis. Topography of the inferior rectal artery: A potential reason for continual major anal fissure. A detailed postmortem angiographic examine demonstrating the association of anal arterial provide. An anatomical and medical examine directed at understanding the character of haemorrhoids. Which artery provides the posterior a part of anorectal junction and posterior part of anal canal These organs are supplied due safety and diet by the bones, muscular tissues, fascia, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves of the pelvis. The posterior superior iliac spine, seen as a dimple (mostly covered), lies reverse the middle of the sacroiliac joint. Contents: In this article the vessels, nerves, muscular tissues, fascia, and joints of the pelvis shall be thought of. The internal iliac artery begins in front of the sacroiliac joint, at the stage of the intervertebral disc between the fifth lumbar vertebra and the sacrum. The inside iliac artery is the smaller terminal branch of the widespread iliac artery. It provides: 1 Pelvic organs except those supplied by the superior rectal, ovarian and median sacral arteries. In the foetus, inner iliac artery is double the dimensions of the exterior iliac artery because it transmits blood to the placenta through the umbilical artery. The umbilical artery with the internal iliac then types the direct continuation of the widespread iliac artery. After birth, the proximal part of the umbilical artery persists to form superior vesical artery, and the rest of it degenerates right into a fibrous twine, the medial umbilical ligament. Parietal Branches of Anterior Division 1 Inferior gluteal artery: It is the largest department of the anterior division of the interior iliac artery. Vesical branches to the base of the bladder, the seminal vesicles and the prostate. Very little of its blood goes to the rectum, and that too goes solely to its muscle coats. Its branches are inferior rectal, perineal, artery to bulb, urethral, deep and dorsal arteries. The lumbar branch represents the fifth lumbar artery, and supplies the psoas, the quadratus lumborum and the erector spinae. Their branches enter the 4 anterior sacral foramina to supply the contents of the sacral canal. Also takes half in anastomoses round anterior superior iliac backbone and in trochanteric anastomoses to supply close by muscles and overlying pores and skin.
It lies in the anal triangle of perineum in between the proper and left ischioanal fossae asthma symptoms 9 dpo generic ventolin 100 mcg amex, which allows its expansion throughout passage of the faeces asthma symptoms worse in fall discount 100 mcg ventolin visa. The anal canal is surrounded by inner involuntary and outer voluntary sphincters which hold the lumen closed in the type of an anteroposterior slit asthma 3 year old 100 mcg ventolin amex. The anus is the surface opening of the anal canal asthma definition quorum effective ventolin 100 mcg, situated about four cm beneath and in entrance of the tip of the coccyx in the cleft between the 2 buttocks. The surrounding pores and skin is pigmented and thrown into radiating folds and contains a hoop of huge apocrine glands. The lower ends of the anal columns are united to one another by quick transverse folds of mucous membrane; these folds are known as the anal valves. The anal valves, collectively form a transverse line that runs all-round the anal canal. It is situated reverse the middle of inner anal sphincter, the junction of ectodermal and endodermal parts. The secretion of those glands produces peculiar smell which is essential in decrease animals to attract. The mucosa has a bluish appearance because of a dense venous plexus that lies between it and the muscle coat. It is made up of a striated muscle and is provided by the inferior rectal nerve and the perineal department of the fourth sacral nerve. It surrounds the entire length of the anal canal and has three parts-subcutaneous, superficial and deep. Contrary to earlier view, the exterior anal sphincter types a single useful and anatomic entity. Its tributaries correspond with the branches of the artery, except for the iliolumbar vein which joins the common iliac vein. Veins arising in and outdoors the pelvic wall 1 Superior gluteal is the biggest tributary. Relations the pelvic lymphatics drain into the following lymph nodes, which lie along the vessels of the identical name. The inferior epigastric and circumflex iliac nodes are outlying members of this group. Follow the branches of each of its divisions to the place of the viscera and the parieties. Both lie in entrance of the sacroiliac joint before passing onto the surface of the piriformis. The lumbosacral trunk is fashioned by the descending branch of the ventral ramus of nerve L4 and the whole of ventral ramus L5. It provides the hamstring muscular tissues, all muscle tissue of calf and intrinsic muscular tissues of the sole. In common, the dorsal divisions supply the extensors and the abductors, and the ventral divisions supply the flexors and the adductors, of the limb. Muscular Branches Nerves to the levator ani or iliococcygeus part and the coccygeus or ischiococcygeus come up from nerve S4 and enter their pelvic surfaces. The nerve to the middle a part of the sphincter ani externus is called the perineal department of the fourth sacral nerve. It runs forwards on the coccygeus and reaches the ischioanal fossa by passing between the coccygeus and the levator ani. In addition to the decrease finish of exterior sphincter, it supplies the skin between the anus and the coccyx. The inferior hypogastric plexus (see Chapter 27), one on both sides of the rectum and different pelvic viscera, is formed by the corresponding hypogastric nerve from the superior hypogastric plexus; branches from the higher ganglia of the sacral sympathetic chain; and the pelvic splanchnic nerves. Branches of the plexus accompany the visceral branches of the interior iliac artery; and are named: a. Abdomen and Pelvis the nervi erigentes represent the sacral outflow of the parasympathetic nervous system. Some parasympathetic fibres ascend with the hypogastric nerve to the superior hypogastric plexus and thence to the inferior mesenteric plexus. Others ascend independently and directly to the part of the colon derived from the hindgut. Lift the sacral plexus forwards and expose its terminal branches, the sciatic and pudendal nerves. Trace the sympathetic trunks within the pelvis until these terminate within the single ganglion impar on the coccyx. Trace the large grey rami communicantes from the ganglia to the ventral rami of the sacral nerves. The chain bears four sacral ganglia on both sides and the one ganglion impar within the central part. It covers the lateral pelvic wall and the pelvic floor known as parietal pelvic fascia; and likewise surrounds the pelvic viscera called visceral pelvic fascia. Principles of Distribution 1 the fascia is dense and membranous over nonexpansile constructions. In this respect, the fascia of Waldeyer is an exception, which extends from the sacrum to the ampulla of rectum. It is hooked up along a line from iliopectineal line to the inferior border of pubic bone. Because of the free nature of the fascia, infections can spread rapidly within it. The varied ligaments are dealt with particular person viscera including the prostate, bladder, uterus and the rectum. Visceral Pelvic Fascia this fascia surrounds the extraperitoneal components of the pelvic viscera. It is free and mobile around distensible organs like bladder, rectum and vagina, but is dense round non-distensible organs, just like the prostate. The visceral layer is connected alongside a line extending from the middle of again of pubis to the ischial spine. The levator ani and coccygeus may be regarded as one morphological entity, divisible from before backwards into the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus and the ischiococcygeus or coccygeus. They have a continuous linear origin from the pelvic floor of the physique of the pubis, the obturator fascia or white line or tendinous arch and the ischial spine. The muscle fibres slope downwards and backwards to the midline, making a gutter-shaped pelvic flooring. Pubococcygeus Part these fibres surround the vagina and kind the sphincter urethrovaginalis. Iliococcygeus Part Abdomen and Pelvis 1 the anterior fibres of this part arise from the medial a part of the pelvic floor of the physique of the pubis. In the male, these fibres intently encompass the prostate and represent the levator prostatae. In the female, the fibres of this half come up from: 1 the posterior half of the white line on the obturator fascia. Both these are inserted into the anococcygeal ligament and into the facet of the final two items of coccyx. Ischiococcygeus Part Section Ischiococcygeus represents the posterior a part of the pelvic diaphragm. Fibres from a and b get inserted into the facet of the coccyx, and into the fifth sacral vertebra. Actions of Levator Ani and Coccygeus 1 the levators ani and coccygeus close the posterior part of the pelvic outlet. In micturition, defaecation and parturition, a particular pelvic outlet is open, however contraction of fibres around other openings resists elevated intraabdominal pressure and prevents any prolapse via the pelvic ground. The improve in the intraabdominal stress is momentary in coughing and sneezing and is more extended in yawning, micturition, defaecation and lifting heavy weights. Relations of the Levator Ani 2 In decrease mammals, the levator ani arises from the pelvic brim. In man, the origin has shifted down to the side wall of the pelvis as a result of attainment of erect posture of human and gravity.
Between the inner jugular vein and the internal carotid artery asthmatic bronchitis 4 weeks buy discount ventolin 100 mcg online, deep to the styloid process and the muscle tissue connected to it asthma quiz generic ventolin 100 mcg on-line. The three nuclei within the upper a part of medulla are: 1 Nucleus ambiguus (branchiomotor) 2 Inferior salivatory nucleus (parasympathetic) 3 Nucleus of tractus solitarius (gustatory) asthma definition vintage ventolin 100 mcg discount overnight delivery. It enters the submandibular region by passing deep to the hyoglossus asthma treatment experimental purchase ventolin 100 mcg with visa, the place it breaks up into tonsillar and lingual branches. Superior ganglion is a detached part of the inferior ganglion, and provides no branches. The inferior ganglion is bigger, occupies notch on the lower border of petrous temporal, and provides out communicating and tympanic branches. It enters the middle ear by way of the tympanic canaliculus, takes part in the formation of the tympanic plexus in the middle ear and distributes its fibres to the center ear, the auditory tube, the mastoid antrum and air cells. It incorporates preganglionic secretomotor fibres for the parotid gland and relays in the otic ganglion. The pharyngeal branches take part in the formation of the pharyngeal plexus, together with vagal and sympathetic fibres. The glossopharyngeal fibres are distributed to the mucous membrane of the pharynx and palate. The tonsillar branches supply the tonsil and be a part of the lesser palatine nerves to form a plexus from which fibres are distributed to the soft palate and to the palatoglossal arches. The lingual branches carry taste and common sensations from the posterior one-third of the tongue together with the circumvallate papillae. Absence of style from posterior one-third of tongue and the circumvallate papillae. They deliver sensations from the pharynx, larynx, trachea, oesophagus and from the abdominal and thoracic viscera. These are conveyed by the central processes of the ganglion cells to the decrease part of nucleus of tractus solitarius. They carry sensations of taste from the posteriormost part of the tongue and from the epiglottis. The central processes of the cells involved terminate in the higher part of the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. The upper a part of the nucleus of tractus solitarius includes superior, center and inferior elements. The postganglionic neurons are situated in ganglia mendacity near (within) the viscera to be provided. The fibres of the cranial root of the accessory nerve are additionally distributed via it. The left vagus enters the thorax by passing between the left common carotid and left subclavian arteries, behind the internal jugular and brachiocephalic veins. It gives meningeal and auricular branches of vagus, and is connected to glossopharyngeal and accessory nerves and to superior cervical ganglion of sympathetic chain. It gives pharyngeal, carotid, superior laryngeal branches and is related to hypoglossal nerve, superior cervical ganglion and the loop between first and second cervical nerves. Branches in Head and Neck In the jugular foramen, the superior ganglion gives off: � Meningeal, and � Auricular branches. The ganglion additionally provides off speaking branches to the glossopharyngeal and cranial root of accent nerves and to the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. It passes behind the inner jugular vein, and enters the mastoid canaliculus (within the petrous temporal bone). It crosses the facial canal 4 mm above the stylomastoid foramen, emerges through the tympanomastoid fissure, and ends by supplying the concha and root of the auricle, the posterior half of the exterior auditory meatus, and the tympanic membrane (outer surface). The pharyngeal branch arises from the lower part of the inferior ganglion of the vagus, and incorporates chiefly the fibres of the cranial root of accessory nerve. It passes between the exterior and inside carotid arteries, and reaches the higher border of the middle constrictor of the pharynx where it takes part in forming the pharyngeal plexus. Its fibres are finally distributed to the muscles of the pharynx and soft palate (except the tensor veli palatini which is equipped by the mandibular nerve). The superior laryngeal nerve arises from the inferior ganglion of the vagus, runs downwards and forwards on the superior constrictor deep to the inner carotid artery, and reaches the middle constrictor the place it divides into the exterior and internal laryngeal nerves. It accompanies the superior thyroid artery, pierces the inferior constrictor and ends by supplying the cricothyroid muscle. The left recurrent laryngeal nerve arises from the vagus in the thorax, because the latter crosses the left aspect of the arch of the aorta. It loops across the ligamentum arteriosum and reaches the tracheo-oesophageal groove. Out of the four cardiac branches of the vagi (two on every side), the left inferior branch goes to the superficial cardiac plexus. It passes downwards and forwards, pierces the thyrohyoid membrane with the superior laryngeal vessels and enters the larynx. Sometimes a sensory ganglion could have a viral an infection (called herpes zoster) and vesicles appear on the area of pores and skin equipped by the ganglion. In herpes zoster of the geniculate ganglion, vesicles appear on the pores and skin of auricle. Paralysis of muscles of soft palate ends in nasal regurgitation of fluids and nasal tone of voice. Lesions of superior laryngeal nerve produces anaesthesia within the higher part of larynx and paralysis of cricothyroid muscle. The cranial root is assisting the vagus, and is distributed by way of its branches as vagoaccesory complex. Functional Components 1 the cranial root is special visceral (branchial) efferent. It arises from a protracted spinal nucleus situated in the lateral part of the anterior grey column of the spinal cord extending between segments C1 to C5. The spinal root arises from a protracted spinal nucleus situated on the lateral part of anterior gray column of spinal cord, extending from C1 to C5 segments. Course and Distribution of the Cranial Root 1 the cranial root emerges within the form of four to 5 rootlets that are hooked up to the posterolateral sulcus of the medulla. Then it runs downwards and backwards superficial to the inner jugular vein and is surrounded by lymph nodes. The nerve pierces the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid at the junction of its higher onefourth with the lower three-fourths, and communicates with second and third cervical nerves throughout the muscle. The nerve enters the posterior triangle of the neck by emerging through the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid a little above its middle. In the triangle, it runs downwards and backwards embedded within the fascial roof of the triangle. The nerve leaves the posterior triangle by passing deep to the anterior border of the trapezius 5 cm above the clavicle. On the deep floor of the trapezius, the nerve communicates with spinal nerves C3 and C4, and ends by supplying the trapezius. By asking the affected person to shrug his shoulders (trapezius) in opposition to resistance and comparing the power on the 2 sides. By asking the patient to turn the chin to the other side (sternocleidomastoid) in opposition to resistance and once more comparing the power on the 2 sides. Nucleus the hypoglossal nucleus, 2 cm long, lies in the flooring of fourth ventricle beneath the hypoglossal triangle. Nucleus for genioglossus muscle receives only contralateral corticonuclear fibres. The rootlets run laterally behind the vertebral artery, and be part of to form two bundles which pierce the dura mater separately close to the hypoglossal canal. Branches and Distribution Branches containing fibres of the hypoglossal nerve correct. Extrinsic muscle tissue are styloglossus, genioglossus, hyoglossus and intrinsic muscular tissues are superior longitudinal, inferior longitudinal, transverse and vertical muscular tissues. Only extrinsic muscle, the palatoglossus, is provided by fibres of the cranial accessory nerve through the vagus and the pharyngeal plexus. It enters the skull by way of the hypoglossal canal, and provides bone and meninges in the anterior a part of the posterior cranial fossa. The descending department continues as the descendens hypoglossi or the upper root of the ansa cervicalis. On protrusion of tongue, its tip deviates to paralysed side as regular genioglossus muscle pulls the base in course of normal side. Nasociliary-anterior ethmoidal branch anterior ethmoidal canal External nasal nerve notch in nasal nerve Posterior ethmoidal branch-posterior ethmoidal canal b.
Testis begins to descend throughout 2nd month of intrauterine life reaches iliac fossa (3rd month) reaches inguinal canal in 7th month asthma treatment cks ventolin 100 mcg line, comes all the means down to asthma treatment 2 year old buy ventolin 100 mcg free shipping superficial inguinal ring throughout 8th month and reaches scrotum during 9th month asthma triggers 100 mcg ventolin cheap otc. Origin asthma homeopathy purchase 100 mcg ventolin otc, growth and destiny of the gubernaculum Hunteri, processus vaginalis peritonel and gonadal ligaments. This paper presents wonderful pictures of early human testis and its descent into the scroturm. Ultrastructure of the seminiferous epithelium and intertubular tissue of the human testis. Cavernous tissue is lesser in amount in corpus spongiosum as compared to the corpus cavernosum d. Fascia transversalis of abdominal wall forms one of the following coverings of testis. What are the constructions associated to the lower border of L1 vertebra/transpyloric airplane Parietal layer clings to the wall of parieties while visceral layer is intimately adherent to viscera concerned. So their vascular supply and nerve provide are same as the parieties and viscera, respectively. These had to be disciplined with restricted actions for proper functioning of the gut in particular and the physique in general. Referred pain from the viscera to a distant area is due to somatic and sympathetic nerves reaching the same spinal section. Anteriorly, it passes via the tips of the ninth costal cartilage; and posteriorly via the physique of vertebra L1 near its lower border. Organs present on this airplane are pylorus of abdomen beginning of duodenum, neck of pancreas and hila of the kidneys. The transtubercular plane passes through the tubercles of the iliac crest and the body of vertebra L5 close to its upper border. The proper and left lateral planes correspond to the midclavicular or mammary traces. Each of these vertical planes passes through the midinguinal level and crosses the tip of the ninth costal cartilage. The 9 areas marked out on this means are organized in three vertical zones-median, proper and left. From above downwards, the median regions are epigastric, umbilical and hypogastric. The right and left areas, in the same order, are hypochondriac, lumbar and iliac. The peritoneum is in the type of a closed sac which is invaginated by numerous viscera. Parietal Peritoneum 1 It traces the internal surface of the belly and pelvic walls and the decrease floor of the diaphragm. It is loosely attached to the walls by extraperitoneal connective tissue and can, therefore, be simply stripped. Because of the autonomic innervation, visceral peritoneum evokes pain when viscera is stretched, ischaemic or distended. Folds of Peritoneum 1 Many organs within the stomach are suspended by folds of peritoneum. The diploma and course of mobility are governed by the dimensions and course of the peritoneal fold. They rest directly on the posterior belly wall, and could also be lined by peritoneum on one side. Large peritoneal folds connected to the stomach are called omenta; singular of which is omentum which means cover. In many conditions, double-layered folds of peritoneum join organs to the abdominal wall or to one another. Some of the larger peritoneal folds are thought-about in this chapter, while others are considered along with the organs concerned. Intraperitoneal Organs Stomach, jejunum, ileum, caecum, appendix, transverse colon, and sigmoid colon Ascending colon, descending colon, and rectum Duodenum, pancreas, kidney, ureter, and suprarenal Urinary bladder, prostate, seminal vesicle, cervix uteri, and vagina the viscera which invaginate the peritoneal cavity completely fill it so that the cavity is reduced to a possible area separating adjoining layers of peritoneum. This fluid performs a lubricating perform and permits free movement of one peritoneal floor over another. Under irregular circumstances, there could also be assortment of fluid referred to as ascites, or of blood known as haemoperitoneum, or of air known as pneumoperitoneum throughout the peritoneal cavity. The primary, bigger half is identified as the larger sac, and the smaller part, situated behind the stomach, the lesser omentum and the liver, is named the omental bursa or lesser sac. The two sacs communicate with one another by way of the epiploic foramen or foramen of Winslow or opening into the lesser sac. Small pockets or recesses of the peritoneal cavity could also be separated from the primary cavity by small folds of peritoneum. Subperitoneal In the male, the peritoneum is a closed sac lined by mesothelium or flattened epithelium. Common causes of ascites are cirrhosis of the liver, tubercular peritonitis, congestive coronary heart failure, and malignant infiltration of the peritoneum. Section 2 Abdomen and Pelvis periodic adjustments within the capability of hole viscera related to their filling and evacuation. Protection of viscera: the peritoneum incorporates various phagocytic cells which guard towards an infection. Lymphocytes present in normal peritoneal fluid present both mobile and humoral immunological defence mechanisms. The higher omentum has the facility to move in direction of websites of infection and to seal them thus preventing spread of an infection. Absorption and dialysis: the mesothelium acts as a semipermeable membrane across which fluids and small molecules of varied solutes can move. Water and crystalloids are absorbed directly into the blood capillaries, whereas colloids move into lymphatics with the help of phagocytes. The larger absorptive energy of the upper stomach or subphrenic area is as a end result of of its larger surface area and since respiratory movements help absorption. Therapeutically, considerable volumes of fluid can be administered via the peritoneal route. Conversely, metabolites, like urea can be removed from the blood by artificially circulating fluid via the peritoneal cavity. Healing power and adhesions: the mesothelial cells of the peritoneum can rework into fibroblasts which promote healing of wounds. Storage of fat: Peritoneal folds are capable of storing giant amounts of fats, particularly in obese individuals. Provides passage for nerves, vessels and lymphatics to and from the suspended viscera. Laparoscopy is the examination of the peritoneal cavity under direct imaginative and prescient using an instrument called laparoscope. Greater omentum limits the unfold of infection by sealing off the positioning of ruptured vermiform appendix or gastric ulcer and tries to delay the onset of peritonitis. Inflammation of parietal peritoneum causes localized extreme pain and rebound tenderness on eradicating the fingers. The midgut types the remainder of the duodenum, the jejunum, the ileum, the appendix, the caecum, the ascending colon, and the right two-thirds of the transverse colon. The hindgut varieties the left one-third of the transverse colon, the descending colon, the sigmoid colon, proximal part of the rectum. The anorectal canal forms distal a half of rectum and the upper a half of the anal canal as a lot as the pectinate line. The stomach part of the foregut is suspended by mesenteries each ventrally and dorsally. The ventral mesogastrium becomes divided by the developing liver right into a ventral part and a dorsal half. The greater or caudal part of the dorsal mesogastrium turns into tremendously elongated and varieties the greater omentum. The spleen develops in relation to the cranial a half of the dorsal mesogastrium, and divides it into dorsal and ventral elements. The cranial most a part of the dorsal mesogastrium varieties the gastrophrenic ligament. The midgut and hindgut have only a dorsal mesentery, which types the mesentery of jejunum and ileum, the mesoappendix, the transverse mesocolon and the sigmoid mesocolon.
100 mcg ventolin purchase mastercard. Dr. H Paramesh on Asthma in Children: Kannada.