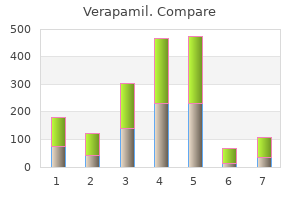
Verapamil
| Contato
Página Inicial

"Verapamil 240 mg with visa, arteria3d - fortress construction pack".
D. Karrypto, M.A.S., M.D.
Associate Professor, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The patient could stand up when snug arrhythmia from excitement verapamil 80 mg order without a prescription, retaining the back-splint until muscle control returns blood pressure which arm 120 mg verapamil buy mastercard. The situation is similar to prehypertension 2014 verapamil 240 mg Osgood-Schlatter illness and usually recovers spontaneously heart attack help generic 80 mg verapamil with amex, though In sufferers with clotting disorders, the knee is the commonest web site for acute bleeds. If the appropriate clotting factor is on the market, the joint ought to be aspirated and handled as for a traumatic haemarthrosis. The organism is usually Staphylococcus aureus, however in adults gonococcal infection can happen. The perfect is to begin antituberculous chemotherapy earlier than joint destruction happens. The affected person stories excessive ache on motion of the joint, which can be confirmed during cautious examination. Aspiration reveals pus within the joint; fluid must be despatched for bacteriological investigation, including anaerobic culture. Treatment consists of systemic antibiotics and drainage of the joint � ideally by arthroscopy, with irrigation and complete synovectomy; if fluid reaccumulates, it might be aspirated via a wide-bore needle. As the inflammation subsides, motion is begun, however weight-bearing is deferred for 4�6 weeks. Treatment with anti-inflammatory medication is normally effective while investigation as to the trigger of the swelling begins. The more elusive issues ought to be absolutely investigated by joint aspiration, synovial fluid examination, arthroscopy and synovial biopsy. The knee may need to be splinted for several days however movement must be inspired and quadriceps exercise is essential. Other signs, similar to deformity, lack of motion or instability, may be present and X-ray examination will normally present characteristic options. Treatment consists of firm bandaging, and kneeling is avoided; sometimes aspiration is needed. Secondary an infection (possibly due to international body implantation) leads to a warm, tender swelling. It presents often as a painless lump behind the knee, slightly to the medial facet of the midline and most conspicuous with the knee straight. Recurrence is frequent if excision is tried and, because the bursa usually disappears in time, a ready policy is the remedy of choice. Bulging of the posterior capsule and synovial herniation could produce a swelling within the popliteal fossa. The lump, which is often seen in older individuals, is in the midline of the limb and at or beneath the extent of the joint. The condition was initially described by Baker, whose sufferers had been probably suffering from tuberculous synovitis. On both aspect: (d) cyst of lateral meniscus; (e) cyst of medial meniscus; (f) cartilage-capped exostosis. Behind: (g) semimembranosus bursa; (h) arthrogram of popliteal cyst; (i) leaking cyst. Common examples are cartilage-capped exostoses (osteochondromata) and the attribute painful swelling of Osgood�Schlatter disease of the tibial tubercle (see above). Entry into the joint is confirmed when saline flows easily into the joint or, if the joint was distended beforehand, by the outflow when the trocar is withdrawn. All compartments of the joint are actually systematically inspected; with particular instruments and, if needed, by way of a number of portals, biopsy, partial meniscectomy, patellar shaving, removing of unfastened bodies, synovectomy, ligament alternative and many different procedures are potential. A agency bandage is applied; the arthroscopic portals are sometimes small enough to not require sutures. Postoperative restoration is remarkably rapid with most instances performed as day-case surgery. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy (which could resemble a low-grade an infection during the weeks following arthroscopy) is sometimes troublesome. It normally settles down with physiotherapy and treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicine; occasionally it requires more radical therapy. Emerging proof suggests that the indications for arthroscopic intervention are narrowing and that intervention rates may well reduce with time. Technique the patient is anaesthetized (though native anaesthesia might suffice for brief procedures) and a thigh tourniquet normally utilized. Published results counsel that the operation offers substantial improvements in ache and performance over a 7�10-year interval. Intra-articular reconstructions the introduction of meniscal and articular cartilage reconstruction techniques has led to appreciable curiosity in making use of the beneficial biomechanical effects of osteotomy to the youthful patient who has a full-thickness chondral lesion or an absent meniscus. With the development of joint alternative techniques, the operation gradually fell into disuse, or at best was seen as a temporizing measure to purchase time for patients who would finally bear some type of arthroplasty. However, improvements in approach and the introduction of operations for meniscal and articular cartilage repair have led to renewed curiosity on this process. The rationale for osteotomy is predicated on each biomechanical and physiological ideas. Malalignment of the limb results in extreme loading and stress in part of the joint and consequently increased damage to the articular cartilage in that space � the medial compartment if the knee is in varus and the lateral compartment in a valgus knee. Osteotomy and correction of deformity will enhance the load-bearing mechanics of the joint. Technique For sound biomechanical reasons, a varus deformity is finest corrected by a valgus osteotomy at the proximal end of the tibia, whereas a valgus deformity should be corrected by a varus osteotomy at the femoral supracondylar level. Angles have to be accurately measured and the place of correction fastidiously mapped out on X-rays before beginning the operation. A excessive tibial valgus osteotomy can be carried out either by eradicating a pre-determined wedge of bone based laterally after which closing the gap (closing wedge technique) or by opening a wedge-shaped hole on the medial facet (opening wedge technique). In the lateral closing wedge method the fibula must first be launched both by dividing it decrease down or by disrupting the proximal tibiofibular joint. Two transverse cuts are made, one parallel to the joint surface and another just below that, angled to create the specified laterally primarily based wedge. The wedge of bone is removed and the fragments are then approximated and fixed in the corrected position either with staples or with compression pins. An opening wedge valgus osteotomy on the medial side offers some benefits: the power to modify the degree of correction intra-operatively and the option to appropriate deformities within the sagittal airplane as well as the coronal airplane; it also makes it pointless to disrupt the tibiofibular joint. If a varus osteotomy is required � usually for energetic patients with isolated lateral compartment disease and valgus deformity of the knee � this is carried out on the supracondylar stage of the femur. The methodology mostly employed is a medial closing wedge osteotomy, designed to place the mechanical axis at zero. The fragments must be firmly fixed with a bladeplate; in many circumstances postoperative cast immobilization Indications Deformity of the knee Severe varus or valgus deformity. Localized articular surface destruction Patients with unicompartmental osteoarthritis or superior localized osteonecrosis, notably when this is associated with deformity within the coronal aircraft, might benefit from an osteotomy which offloads the affected space. Provided the joint is stable and has retained a reasonable range of motion, this presents a suitable various to a unicompartmental arthroplasty. By realigning the joint, load is transferred from the medial compartment to the centre or a little towards the lateral side. Slight over-correction may additional offload the medial compartment but marked valgus must be averted as this can rapidly lead to cartilage loss within the lateral compartment. An alternative however much less incessantly used technique to carry out osteotomy is to deploy an Ilizarov circular exterior fixator and progressively dynamically correct the deformity over a time period. Results High tibial valgus osteotomy, when carried out for osteoarthritis, provides good outcomes supplied (1) the disease is confined to the medial compartment; and (2) the knee has a great vary of movement and is secure. Relief of pain is nice in 85% of circumstances within the first 12 months but drops to roughly 60% after 5 years. More modern medial opening wedge osteotomy techniques can obtain passable postoperative alignment in 93% of patients and survivorship charges of 94% at 5-year, 85% at 10-year, and 68% at 15-year follow-up, with conversion to total knee arthroplasty as the tip point. The medical outcomes of distal femoral varus osteotomy have been good in chosen patients. Substantial enhancements in pain and function may be expected in approximately 90% of sufferers. A stiff knee is a considerable incapacity; it makes climbing difficult and sitting in crowded areas distinctly awkward. In nations with advanced medical amenities the commonest indication is failed total knee replacement (either septic or aseptic).
Consequently blood pressure chart 50 year old male 80 mg verapamil free shipping, osteosarcoma in aged patients older than 65 years has a worse prognosis than that of the youthful population blood pressure medication photosensitivity verapamil 120 mg generic without prescription. This group of aggressive malignant cartilage tumours symbolize a spectrum of the identical disorder that arises in enchondromas blood pressure app buy generic verapamil 80 mg online. This is suggested by the statement that enchondromatosis could evolve into a low-grade chondrosarcoma and that arrhythmia tutorial 120 mg verapamil generic free shipping, after excision, radiologically low-grade chondrosarcomas could have areas of higher grade. Chondrosarcomas can present in adults from the third to the eighth decades, peaking between forty and 70 years of age, and men are affected extra usually than ladies. These tumours are slow-growing and are normally present for many months before being discovered. They produce deep ache and/or a progressively enlarging mass and arise in any bone derived from enchondral ossification. Despite the relatively frequent occurrence of benign cartilage tumours in the small tubular bones of the arms and toes, malignant lesions are uncommon at these websites, representing <1% of chondrosarcomas. Chondrosarcomas take numerous forms, often designated according to: (a) their location in the bone (central or peripheral); (b) whether or not they develop without benign precursor (primary chondrosarcoma) or by malignant change in a pre-existing benign lesion (secondary chondrosarcoma); and (c) the predominant cell type within the tumour. Approximately 85% are primary central chondrosarcomas occupying the medullary cavity. Endosteal scalloping of the cortex and eventual cortical destruction can happen, and there could also be a faint periosteal response. These avascular tumours reproduce the excessive signal of hyaline cartilage on T2 weighted sequences. Differentiating options are bone enlargement, periostitis, soft-tissue mass and tumour length (mean intramedullary extent eleven. This has vital prognostic significance for the affected person, as extra aggressive tumours have higher mortality charges. Resection histology demonstrates a pale, glistening cartilage lesion in the medullary cavity which spreads past the cortex (d). Treatment was by resection of the periacetabulum and pubis and reconstruction with an ice-cream cone prosthesis and hip replacement (h). Dedifferentiated chondrosarcomas symbolize the extremely malignant end of the chondroid tumour spectrum, creating in 10�15% of central chondrosarcomas, by which a high-grade undifferentiated sarcoma or osteosarcoma coexists with a lower-grade chondroid tumour. The median age is fifty nine years, with a slight predominance of males, and the most typical websites are the femur and pelvis. They have a very poor prognosis (5-year survival 7�24%), improved solely by broad surgical resection, worsened by pathological fracture (29% of cases), advancing age and metastasis at diagnosis. Histopathology reveals macroscopically lobular white hyaline cartilage, areas of mineralization and cystic modifications, erosion of the cortex and soft-tissue expansion. Microscopically the high cellularity, atypia, mitoses and permeation into host bone distinguish a chondrosarcoma from an enchondroma. Grade I tumours are usually regionally aggressive with low metastatic potential, in distinction to highgrade lesions. Not sometimes, areas of low-grade and high-grade chondrosarcoma could additionally be seen in the same tumour. Chondrosarcoma is immune to each chemotherapy and radiation, making surgical excision the one treatment. In high-grade tumours, solely broad excision margins are oncologically acceptable to reduce local recurrence. Prognosis is set by the cellular grade, stage, tumour dimension, (axial versus appendicular) website and the resection margin. A pathological fracture of the femur has a negative prognostic affect in grade I chondrosarcoma and will increase the risk of local recurrence in dedifferentiated femoral chondrosarcomas. In some circumstances isolated pulmonary metastases can be resected and adjuvant chemotherapy may be contemplated in dedifferentiated or mesenchymal chondrosarcomas. For this cause, others advocate broad resection and reconstruction, balancing the more severe physical function with decreased danger of local recurrence. Clinical findings embrace uneven limb shortening, swelling of the fingers and toes, and disturbed movements of the interphalangeal joints. After puberty no new enchondromas develop, and tumour development in maturity is considered to be malignant degeneration of those tumours. Maffucci syndrome combines multiple enchondromas and cutaneous or visceral haemangiomas, and should current at start or develop later. Secondary peripheral chondrosarcomas these arise within the cartilage cap of an exostosis (osteochondroma) that has been present since childhood. Exostoses of the pelvis and scapula seem to be extra susceptible than others to malignant change, because these sites permit undetected development. Any enhance in size or onset of latest ache is suspicious in patients after skeletal maturity. They come up from the periosteum of the metaphysis of the femur or humerus, usually in the second to fourth a long time. Local recurrence depends upon the margin of surgical excision, with as much as 29% recurrence charges reported, and metastasis-free survival depends on histological grade. Clear-cell chondrosarcomas Making up 2% of all chondrosarcomas, these classically have an epiphyseal location of the proximal or distal femur or humerus and present more generally in males between the third and fifth decades of life. Considered slow-growing, low-grade tumours, they present with ache and joint restriction and appear as osteolytic lesions with narrow transition, a narrow sclerotic rim and small matrix calcifications. Radiological correlation is mandatory, as clear-cell chondrosarcomas are most likely to lack per-tumoural oedema and to be greater sign on T2-weighted sequences. Long-term survival is good, although there are reviews of late metastasis mandating long-term surveillance after wide surgical excision. Mesenchymal chondrosarcomas these extremely malignant and poorly differentiated chondrosarcomas unusually current in most age teams (median 30 years) in a broad variety of anatomical websites (limb, pelvis, vertebrae, craniofacial) including extraskeletal sites in one-third. The tumour was removed in its entirety and reconstructed with a proximal femoral endoprosthetic substitute (c). Prognosis varies significantly, with metastatic disease at diagnosis conferring the worst prognosis. Wide resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are thought-about the usual of care, and late metastasis is a characteristic of this uncommon disease. This extremely malignant tumour occurs more incessantly in males, usually between 10 and 20 years of age, and has a diaphyseal long-bone location however is equally as common in flat bones. The femur is the commonest long-bone site, followed by the tibia, humerus and fibula, but general the pelvis accounts for nearly all of instances. Pain is the earliest symptom, adopted by swelling (although soft-tissue masses may not be obvious in pelvic sites) and a low-grade fever. Radiographically, an aggressive, permeative, poorly defined osteolytic lesion with cortical destruction, periosteal reaction and large, radiolucent soft-tissue mass could additionally be discovered. This may mimic an infection or eosinophilic granuloma in younger sufferers; delicate bone involvement with a large soft-tissue mass may mimic main bone lymphoma in older patients. Lung, skeletal and lymph node (rare) metastases may be evident at presentation in up to 20% of cases. Preoperative chemotherapy frequently leads to in depth tumour necrosis and shrinkage. Wide excision could additionally be mixed with adjuvant radiotherapy if surgical margins are poor. Definitive radiotherapy somewhat than surgical excision, though associated with worse general survival, may be advocated if non-resectable or metastasis has occurred throughout chemotherapy, to spare the surgical morbidity. Risk components for local recurrence have been also just like these in patients with an osteosarcoma: shut surgical margins and poor response to preoperative chemotherapy were the 2 most important elements. It mostly arises in the marrow containing bones of the vertebrae, pelvis and femur. Multiple myeloma arises because of multiple genetic mutations of plasma cells and the immunoglobulins they produce. Diagnosis of myeloma depends on the detection of para-proteins in the plasma or urine, bone marrow biopsy, and evidence of end-organ/bone damage. Serum or urinary electrophoresis measures immunoglobulins that are overproduced by the malignant plasma cells. Traditionally, a skeletal survey required X-rays of the backbone, skull, pelvis, ribs/sternum, and the humerus/femurs to screen for osseous lesions, and assess tumour burden and fracture risk. More typically discovered in the axial skeleton (particularly backbone, skull and pelvis), long-bone lesions are usually metaphyseal. Most spindle-cell sarcomas producing collagen, but not osteoid matrix, have been initially identified as fibrosarcomas, latterly as malignant fibrous histiocytomas, and currently as spindle-cell sarcomas of bone. Age at the time of analysis ranges from the third to the sixth decade, with equal sex distribution.
Typical Speech and Language Development the idea of "crucial periods" is mostly accepted for speech/language improvement in infancy and early childhood blood pressure chart 15 year old verapamil 120 mg generic visa. Some expertise may be demonstrated by the child through the office visit medication to lower blood pressure quickly generic verapamil 120 mg without a prescription, whereas others might rely on father or mother report arrhythmia symptoms cheap 240 mg verapamil with amex. Vocal growth begins with phonation within the first few months (guttural or throaty sounds) whats prehypertension mean 240 mg verapamil purchase amex, then progresses to primitive articulation or cooing between 2 to 4 months of age. This expands to full vowel sounds by four to 5 months of age, single consonant sounds by about 5 months (eg, "ah-guh"), and well-formed babbling (repeated consonant-vowel sample, eg, "bababa") at round 6 months of age. Receptive language abilities and social routines additionally develop within the first year of life. Six-month-old kids may pause momentarily after they hear their name called, and by 10 months pause on the word "no. Naming Period Around their first birthday, youngsters reply appropriately to requests for identification of familiar people or objects. Pointing can additionally be utilized in quite lots of contexts and is an important expression of nonverbal communication. A child makes use of protoimperative pointing to a desired object so as to get an grownup to get hold of the object for him; the child "imperiously" implies, "I want that! A child may level to an object and vocalize in a questioning tone in an try and have an adult name that object for him. Vocabulary steadily expands, and by 2 years, a baby could add 1 new word a day to embrace approximately 200 words by 2. Between 12 and 18 months of age, a baby uses single words to communicate desires (eg, "more"), emotions (eg, "no"), and particular objects (eg, "child"). Next, the child combines phrases into novel phrases (eg, "massive truck"), after which into 2-word sentences (noun + verb, verb + object [eg, "need "]). By three to four years of age, children are capable of perceive and use prepositions (eg, "under" and "on"), adjectives, and adverbs. Semantics (word and sentence meaning) and syntax (grammar) improve over time, and by 5 years of age, children have full mastery of grammatical tense marking. Promotion of Language Development As with all areas of improvement and conduct, promotion of language growth is a perform of the first care medical home and is a component of the strengthbased method to major pediatric care. Optimal language growth happens when children experience stimulating environments with predictable and developmentally applicable responses from adults. Parents must be encouraged to "make their home a language home," basically, talking throughout daily activities with their youngsters, regardless of how mundane the activity. Reading aloud to younger youngsters has identified optimistic results on language and later reading decoding expertise, as evidenced by analysis on Reach Out and Read, a main care�based literacy promotion program. Studies have proven that parents use extra complex language and more book-to-life comparisons once they learn to younger youngsters using picture books quite than after they learn books with text. When a mother or father raises a concern about language, the kid will finally fall somewhere on the continuum of language developmental variation, language downside, or language disorder. Administering a standardized common developmental display screen or languagespecific display screen will help the clinician decide the place the kid lies on this continuum. If the child passes the display or has a borderline score, then watchful ready is an applicable next step to the dialogue of language stimulation activities, with close follow-up and repeat screening within the medical residence. If the kid fails the display screen, then referral to early intervention or early childhood programs (Head Start, preschool) and referral to a speech and language pathologist is really helpful. A speech-language or communication dysfunction is outlined as an impairment in the ability to obtain, ship, process, and/or comprehend verbal, nonverbal, or graphic image methods. Of kids with early language delays, roughly 60% will catch up by four years of age with no persistent problems. This can occur either throughout the language area, as seen when developmental rates differ between expressive and receptive language, or between completely different domains (eg, language and motor skills). Which children are just slower to develop expressive language however will catch up, and which kids will continue to experience language delay Language-related problems can emerge within the later college years when extra superior language-related abilities are needed. These issues embrace phonological (articulation) disorders, dysarthria, apraxia of speech, voice disorders, and speech fluency problems. Children grasp sounds at completely different ages depending on the problem in producing the sound. In the first 2 years, children master easy sounds, together with all vowels and the consonants /b/, /c/, /d/, /p/, and /m/. More difficult sounds, such as the consonants /j/, /r/, /l/, and /v/ and blends (ie, sh, ch, th, st), will not be mastered till 5 or 6 years of age. Dysarthria Dysarthrias are motor speech issues that contain issues of articulation, respiration, phonation, or prosody because of paralysis, muscle weakness, or poor coordination. Dysarthric speech can also embody problems in coordinated breath management and head posture. Apraxia of Speech or Dyspraxia Apraxia of speech, or dyspraxia, is a speech disorder that arises from difficulties in complex motor planning and motion and entails problems in articulation, phonation, respiration, and resonance. This ends in a toddler having problem appropriately saying what she or he desires to say. The youngster has problems putting syllables collectively to kind phrases and has extra issue with longer phrases somewhat than shorter, less complicated phrases. Therefore, apraxia/dyspraxia can normally be differentiated from dysarthria by the shortage of association with different oral-motor skills, similar to chewing, swallowing, or spitting. Other neurological "delicate signs," corresponding to generalized hypotonia, may be present on examination and may find yourself in nice motor or gross motor difficulties. Acquired apraxia/dyspraxia generally outcomes from head damage, tumor, stroke, or other issues affecting the parts of the brain involved with speaking and involves loss of previously acquired speech. It might co-occur with dysarthria or aphasia, a communication disorder impacting understanding or use of phrases caused by damage to the language facilities of the brain. Apraxia of speech is differentiated from an expressive language delay in that youngsters with expressive language delay usually follow a traditional language trajectory but at a slower tempo. It can be difficult to differentiate between expressive language delay and apraxia earlier than the age of two years. Some useful elements of the oral-motor exam may embody pursing of the lips, blowing, utilizing a straw, licking the lips, and elevating the tongue. Children with dysarthria will exhibit decreased strength and coordination of speech musculature, and speech errors are normally distortions. Hyper- or hyponasal voice high quality suggests anatomical variations or sometimes neurological dysfunction, with hypernasal speech occurring secondary to velopharyngeal palatal incompetence and hyponasal speech arising from air impeded by large adenoids. Fluency Disorders A fluency disorder includes the interruption within the circulate of speaking. Examples of dysfluent speech embrace pauses, hesitations, interjections, prolongations, and interruptions. Persistent or progressive dysfluency is extra likely stuttering, which arises in the preschool years for many affected kids. Red flags indicative of pathological dysfluency requiring speech therapy embrace repetitions related to sound prolongations (eg, "ca-caaaaa-caaaaat"), multiple part-word repetitions (eg, "ca-ca-ca-cat"), hurried and jerky repetitions with associated self-awareness and frustration, associated articulation problems, or a house environment with a low tolerance for stuttering or excessive stress for verbal communication. Parents additionally should speak more slowly and spend time with the child individually, so that he can express himself in a noncompetitive setting. Encouraging families to take turns and not interrupt conversations during family activities is also useful. However, referral to a speech-language therapist is indicated if mother and father proceed to be involved. The dysfunction might involve the form of language (phonology, morphology, and syntax), the content material of language (semantics), and/or the function of language (pragmatics). Receptive Language Disorder Deficits in receptive language virtually all the time happen along side expressive delays. There are conditions during which a toddler may seem to have an isolated receptive delay, however on careful evaluation, deficits in both areas are current. Children with hydrocephalus (congenital or acquired) might have superficially appropriate or advanced expressive language expertise but exhibit poor content of expression, known as "cocktail get together syndrome. Auditory processing involves recognition and interpretation of verbal info and sounds within the brain. Auditory processing entails many different processes in any respect ranges of the nervous system, and poor-quality acoustic environments, peripheral ear functioning, behavioral components concerned in listening, and issues with the cochlea, nerve, brainstem, and cortex can all be involved. Empirical research is scarce regarding the validity of modality-specific auditory-perceptual dysfunction. The diagnosis is made utilizing behavioral tests supplemented by electroacoustic measures.
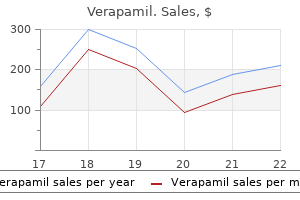
Verapamil 240 mg line. Tonya Brown | Part 27 | Blood Pressure Readings.
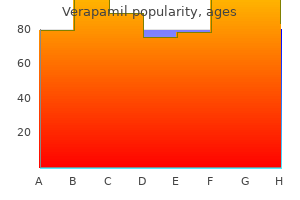
Intermittent low back ache after exertion Patients of simply about any age could complain of recurrent backache following exertion or lifting activities and that is relieved by rest blood pressure 8855 240 mg verapamil buy overnight delivery. Features of disc prolapse are absent however there could also be a history of acute sciatica in the past heart attack test generic verapamil 240 mg free shipping. In early instances arrhythmia consultants greenville sc verapamil 120 mg discount overnight delivery, X-rays often show no abnormality; later there could additionally be indicators of lumbar spondylosis in these over 50 years and osteoarthritis of the facet joints is frequent blood pressure medication starting with x verapamil 80 mg with mastercard. In the process, disorders such as ankylosing spondylitis, continual an infection, myelomatosis and different bone illnesses should be excluded by appropriate imaging and blood investigations. Back ache plus pseudoclaudication these sufferers are usually aged over 50 and may give a historical past of earlier, long-standing again hassle. Spinal osteoporosis in middle-aged males is pathological and calls for a full battery of exams to exclude major problems corresponding to myelomatosis, carcinomatosis, hyperthyroidism, gonadal insufficiency, alcoholism or corticosteroid utilization. The lateral recess stenosis is decompressed with undercutting facetectomies and removal of ligamentum flavum. Care ought to be taken to excise lower than 50% of the side joints and avoid harm to the pars interarticularis to forestall iatrogenic instability, which might necessitate fusion. Spinal stenosis with spondylolysis, spondylolisthesis, scoliosis and kyphosis are indications for fusion with decompression. If the hips are unable to lengthen totally (fixed flexion deformity), the lumbar lordosis increases still more till the lower limbs lie flat and the flexion deformity is masked. Vertebral components Each segment of the vertebral column transmits weight via the vertebral body anteriorly and the facet joints posteriorly. Between adjacent our bodies (and firmly connected to them) lie the intervertebral discs. The vertebral physique is cancellous, but the higher and decrease surfaces are condensed to kind sclerotic endplates. In childhood these are covered by cartilage, which contributes to vertebral progress. Later the peripheral rim ossifies and fuses with the body, but the central space stays as a thin layer of cartilage adherent to the intervertebral disc. The resultant drive, which passes through the nucleus pulposus of the lowest lumbar disc, is due to this fact a lot larger than if the column were loaded instantly over its centre. Even at relaxation, tonic contraction of the posterior muscular tissues balances the trunk, so the lumbar backbone is always loaded. When the intradiscal pressure in volunteers throughout various activities was measured, it was discovered to be as high as 10�15 kg/cm 2 whereas sitting, about 30% less on standing upright, and 50% much less on lying down. Leaning forward or carrying a weight produces much higher pressures, although when a heavy weight is lifted respiration stops and the belly muscle tissue contract, turning the trunk into a tightly inflated bag that cushions the drive anteriorly in opposition to the pelvis. Lying supine with Intervertebral disc the disc consists of a central avascular nucleus pulposus � a hydrophilic gel made from protein-polysaccharide, collagen fibres, sparse chondroid cells and water (88%), surrounded by concentric layers of fibrous tissue � the annulus fibrosus. If the physicochemical state of the nucleus pulposus is regular, the disc can stand up to nearly any load that the muscles can assist; if it is abnormal, even small increases in pressure can produce sufficient stress to rupture the annulus. Movements the axis of actions in the thoracolumbar spine is the nucleus pulposus; the disposition of the facet joints determines which movements happen. In the thoracic backbone the side joints face backwards and laterally, so rotation is relatively free; flexion, extension and tilting are attainable however are grossly restricted by the ribs. The costovertebral joints are involved in respiration and their limitation is an early feature of ankylosing spondylitis. Spinal canal the form of the canal modifications from ovoid within the higher a half of the lumbar backbone to triangular in the lower. Variations are widespread and embrace the trefoil canal, whose shape is especially because of thickening of the laminae. Blood provide In addition to the spinal arteries, which run the length of the twine, segmental arteries from the aorta ship branches through the intervertebral foramina at each stage. The column functions like a crane, the weight in front of the spine being counterbalanced by contraction of the posterior muscle tissue. Antibiotic therapy in sufferers with persistent low again ache and vertebral bone edema (Modic type 1 changes): a double-blind randomized clinical managed trial of efficacy. Systematic literature evaluation of imaging options of spinal degeneration in asymptomatic populations. Surgical versus non-surgical treatment for vertebral compression fracture with osteopenia: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. Prevalence of vertebral endplate sign (Modic) modifications and their association with non-specific low back ache - A systematic literature review. Comparative effectiveness evidence from the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial. Spinal wire the spinal wire ends at about L1 in the conus medullaris, but lumbosacral nerve roots continue in the spinal canal as the cauda equina and leave at acceptable ranges lower down. The dural sac continues so far as S2, and every time a nerve root leaves the backbone it takes with it a dural sleeve so far as the exit from the intervertebral foramen. These dural sleeves can be outlined by contrast-medium radiography (radiculography). Intervertebral foramina and nerve roots Each intervertebral foramen is bounded anteriorly by the disc and adjoining vertebral bodies, posteriorly by the aspect joint, and superiorly and inferiorly by the pedicles of adjoining vertebrae. The segmental nerve roots depart the spinal canal by way of the intervertebral foramina, each pair below the vertebra of the same quantity (thus, the fourth lumbar root runs between L4 and L5). The segmental blood vessels to and from the twine also move via the intervertebral foramen. Occlusion of this little passage could occasionally compress the nerve root immediately or could trigger nerve root ischaemia (especially when the spine is held in extension). Ultrasound imaging will affirm that the femoral head is situated exterior the acetabulum. Pathophysiology Embryonically the femoral head and acetabulum develop from a single cleft of primitive mesenchymal cells. The femoral head remains enlocated normally however relative growth results in least coverage at around time period. Dislocation (or dysplasia) of the hip can happen at specific points of time throughout improvement. The first time at which dislocation could happen is 10 weeks when the lower extremity limb bud rotates medially. Dislocation at these early phases results in irregular development of all components of the hip joint and is thus termed a teratological dislocation. During the ultimate 4 weeks of gestation, mechanical forces play a big part within the positioning of the hip joint. In the left occiput anterior place, the most typical prenatal fetal place, the left hip is adducted towards the maternal sacrum, increasing the chance of dislocation. Postnatally, swaddling of the decrease extremities holds the hips in extension and adduction and could be an additional contributing factor to subluxation or dislocation in some international locations. In the subluxed place, the labrum is flattened underneath the stress of the femoral head and becomes flattened or everted. Dislocation of the femoral head leads to stretching of the inferior capsule and adductors which, if untreated, could lead to contractures and restricted range of abduction. The Barlow and Ortolani checks are the mainstays in examination of the new child hip. The Barlow manoeuvre is a provocation test carried out by adducting the flexed hip and making use of mild anterior to posterior strain to have the ability to push the femoral head superior and posterior over the edge of a shallow acetabulum. The Ortolani check is a relocation manoeuvre conducted by gently manipulating the flexed hip from adduction to abduction to convey the femoral head anteriorly back into the acetabulum from a dislocated place. At a later stage, medical examination findings may embody asymmetrical skin folds, although most consultants really feel that these are usually not significant. Imaging the introduction of ultrasound imaging, within the Eighties, allowed visualization of the soft-tissue elements of the toddler hip including the cartilage of the femoral head and acetabulum, the capsule and the labrum. The use of multiplanar and dynamic ultrasound enables visualization of the femoral head within the acetabulum and evaluation of the form and depth of the acetabular cup. Ultrasound is greatest used for kids before 6 months of age, after which ossification of structures makes plain radiographs more and more extra useful. Consensus was reached at a meeting involving both Graf and Harcke that described the Dynamic Standard Minimum Examination combining a static coronal picture and a transverse stress image for optimum evaluation of the toddler hip. Clinical screening is clearly smart, but debate persists on the specific benefits, compared to value and danger of overtreatment, of selective or common ultrasound screening. The treatment of Ortolani-positive hips, dislocated at relaxation but reducible, should begin as soon as sensible. At 2 weeks, failure to enhance both clinically or on the premise of an ultrasound is an indication to commence treatment.
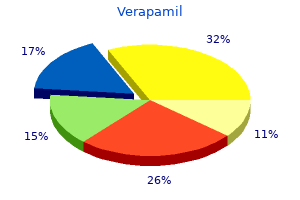
The common age of onset of symptomatic disease is 50 years and patients may current with any mixture of axial neck and upper-limb pain arrhythmia v tach verapamil 240 mg order free shipping, sensory signs and muscle weak point in the arms and higher motor neuron signs and indicators within the lower limbs blood pressure bottoming out buy generic verapamil 240 mg. The most disturbing features are motor abnormalities similar to weak point arrhythmia medical definition discount verapamil 240 mg with amex, incoordination heart attack or gas discount verapamil 80 mg line, clumsiness, muscle losing and bladder-bowel dysfunction. Ossification is often present for a protracted period earlier than the onset of scientific signs. Only a small share of sufferers with typical imaging findings present symptomatic myelopathy and require surgical treatment. Hypointensity on T1-weighted sequences and hyperintensity on T2 are main changes seen in spinal twine lesions. It consists of analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antidepressants, anticonvulsants and opioids. The period of symptoms previous to surgery is understood to be one of the factors most importantly related to a unfavorable prognosis. Surgical decompression is performed through an anterior, a posterior or a combined approach. Three-dimensional analysis of quantity change in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical backbone utilizing computed tomography. The sagittal diameter of the grownup spinal wire averages roughly 8 mm from C3 to C7. Degenerative forms of cervical myelopathy because of spinal stenosis are the most common explanation for spinal wire dysfunction in the adult population. The sagittal diameter of the spinal canal is now considerably greater than earlier than. If the adjustments are severe sufficient to compromise the spinal wire, the affected person might develop neurological signs and signs of twine compression, that are thought to be because of both direct compression and ischaemia of the twine and nerve roots. Abnormally small canals are also seen in uncommon dysplasias, such as achondroplasia, and should give rise to twine compression. Hirayama illness or cervical flexion myelopathy is a uncommon form of cervical myelopathy by which section instability and dynamic compression would possibly play a job. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy also outcomes from dynamic factors leading to native spinal cord ischaemia, in combination with the static components explained above, corresponding to in circumstances of athetoid cerebral palsy or even in Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Gait might also be affected with a broad-based unstable sample, decreased velocity, decreased step and stride size, increased double support time, decreased plantar flexion at push-off and elevated dorsiflexion of the ankle joint at swing section, along with the onset of postural stability abnormalities. Hand clumsiness is one of the commonest complaints within the setting of compressive cervical myelopathy. Exaggerated deep tendon reflexes, finger escape sign and problem within the finger grip and launch test characterize this presentation sample, additionally called myelopathic hand. Symptoms may be precipitated by acutely hyperextending the neck, and some patients current for the primary time after a hyperextension harm. They may experience involuntary spasms within the legs and, sometimes, episodes of spontaneous clonus. Patients with cervical spine-related headaches could report neck pain radiating to the low occipital and temporal areas. Degenerative adjustments at the cervical backbone with wire dysfunction outcome in the growth of long tract signs, as a result of atrophy and neuronal loss in the anterior horn and intermediate zone. A detailed neurological examination is the current standard to the prognosis of cervical myelopathy. Careful examination should reveal upper motor neuron signs in the decrease limbs (increased muscle tone, brisk reflexes and clonus), whereas sensory indicators rely upon which part of the wire is compressed: there may be decreased sensibility to ache and temperature (spinothalamic tracts) or diminished vibration and place sense (posterior columns). The signs and signs replicate the degree to which the posterior, dorsolateral and ventrolateral columns, the ventral horns and the cervical nerve roots are involved. Hyperreflexia and the Hoffmann reflex have the highest sensitivity in patients with cervical myelopathy. These pathognomonic pyramidal signs may be absent in approximately one-fifth of myelopathic patients, however their prevalence is correlated with the severity of myelopathy. Myelopathy is normally slowly progressive, but often a affected person with long-standing symptoms starts deteriorating quickly and treatment becomes urgent. Nevertheless, the exact natural history of cervical spondylotic myelopathy is yet to be clarified. Nevertheless, elevated signal depth might, actually, reflect numerous intramedullary pathologies similar to oedema, gliosis, demyelination and myelomalacia. The aim of surgical remedy is to decompress the spinal twine before everlasting damage happens. It continues to be a problem to predict which patients will benefit the most from surgical remedy. Acute, severe myelopathy is a surgical emergency, requiring quick decompression. Surgical decompression of the cervical spinal wire could be carried out by both an anterior or a posterior method. A mixed posterior decompression and reconstruction utilizing pedicle or lateral mass screw instrumentation might be helpful for patients with local kyphosis, segmental instability and in revision surgical procedure. Nowadays, nearly all of spinal an infection cases are pyogenic and only 1 / 4 tuberculous. These brokers spread to the spine by a haematogenous route, direct exterior inoculation or from contiguous tissues. The direct external pathway is incessantly related to surgical spinal procedures and contiguous unfold could outcome from adjacent an infection (oesophageal ruptures, retropharyngeal abscesses or infections of aortic implants). However, it affects primarily adult patients with a slight predominance of the male gender. There is a reported tendency for higher prevalence and extra aggressiveness of cervical spondylodiscitis within the last decades. Infection can reach and gather inside the spinal canal, inflicting epidural or subdural abscesses. An uncontrolled an infection can lead to spread to the encircling tissues, inflicting paravertebral abscesses. The spread to the posterior buildings is rare, being extra widespread within the case of spinal tuberculosis. Note the a quantity of options of cervical spine degeneration and the hyperintense signal of the cord at the degree of C5�C6. Differential analysis Full neurological investigation is required to remove other diagnoses similar to a number of sclerosis (episodic symptoms), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (purely motor dysfunction), syringomyelia and spinal cord tumours. Motor unit potentials evaluation from nerve conduction studies may be helpful for detecting axonal degeneration and reinnervation and the location of neurological compromise in the context of neuropathic issues. Treatment Most patients can be treated conservatively with analgesics, a collar, isometric workout routines and gait training. Epidural spinal injections are comparatively secure and efficient, although major complications such as spinal wire infarction have been reported. Given the unpredictably progressive nature of cervical myelopathy, the indications for non-operative management seem restricted. Cervical pyogenic spinal infections: are they extra extreme diseases than infections in different vertebral areas The accuracy of percutaneous vertebral biopsy in patients with spondylodiscitis has been reported to be about 70%. The harvested tissue should be submitted to: Gram and acid-fast bacilli smears; aerobic, anaerobic, fungal and tuberculosis cultures; and polymerase chain response. Tuberculosis has a acknowledged status as one of the great mimickers in medicine, making it troublesome to diagnose. The principles of remedy of spinal infections are: antibiotic therapy; neurological decompression in the setting of neurological deficits; preservation of stability and correction of deformity. Although antibiotic therapy must be initiated only after a definitive etiological prognosis in a stable affected person, within the presence of sepsis or the impossibility of an etiological prognosis, empirical antibiotic remedy should be thought-about. In the setting of confirmed tuberculosis spondylitis, tuberculostatic remedy ought to be initiated. Surgical treatment normally includes complete debridement of infected tissue, decompression of neural parts, reconstruction of the involved segments and spinal stabilization.